RelativeLayout 是一种视图组,它以相对位置显示子视图。每个视图的位置可以指定为相对于同级元素(例如在另一个视图的左侧或下方)或相对于父级 RelativeLayout 区域(例如与底部、左侧或中心对齐)。
注意:为了获得更好的性能和工具支持,建议您 使用 ConstraintLayout 构建布局。

一个 RelativeLayout 是一个非常强大的用户界面设计工具,因为它可以消除嵌套的视图组,保持布局层次结构扁平,从而提高性能。如果您发现自己使用了多个嵌套的 LinearLayout 组,则可以考虑使用单个 RelativeLayout 来替代它们。
视图定位
RelativeLayout 允许子视图指定其相对于父视图或彼此(通过 ID 指定)的位置。因此,您可以根据右边框对齐两个元素,或者将一个元素放在另一个元素下方、屏幕中心、左侧中心等位置。默认情况下,所有子视图都绘制在布局的左上角,因此您必须使用 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams 中提供的各种布局属性来定义每个视图的位置。
RelativeLayout 中的视图可用的许多布局属性包括
android:layout_alignParentTop- 如果
"true",则使此视图的顶部边缘与父视图的顶部边缘对齐。 android:layout_centerVertical- 如果
"true",则在此父级中垂直居中此子级。 android:layout_below- 将此视图的顶部边缘定位在由资源 ID 指定的视图下方。
android:layout_toRightOf- 将此视图的左边缘定位在由资源 ID 指定的视图的右侧。
这些只是一部分示例。所有布局属性都记录在 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams 中。
每个布局属性的值可以是布尔值,用于启用相对于父级 RelativeLayout 的布局位置,也可以是引用布局中另一个视图的 ID,视图将相对于该视图定位。
在您的 XML 布局中,针对布局中其他视图的依赖项可以按任意顺序声明。例如,您可以声明“view1”位于“view2”下方,即使“view2”是层次结构中声明的最后一个视图。下面的示例演示了这种情况。
示例
强调了控制每个视图相对位置的每个属性。
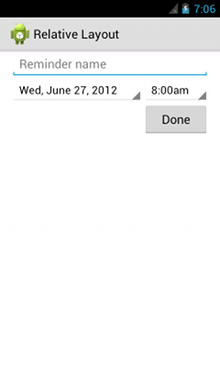
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
有关 RelativeLayout 的每个子视图可用的所有布局属性的详细信息,请参阅 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams。

