快捷方式可帮助用户快速访问应用的某些部分,从而向他们提供特定类型的内容。
您通过快捷方式提供内容的方式取决于您的用例以及快捷方式的上下文是由应用驱动还是由用户驱动。虽然静态快捷方式的上下文不变,而动态快捷方式的上下文会不断变化,但这两种情况下上下文都由您的应用驱动。在用户选择您的应用向他们提供内容的方式(例如通过固定快捷方式)的情况下,上下文由用户定义。以下场景介绍了各种快捷方式类型的一些用例
- 静态快捷方式 最适合在其整个生命周期内使用一致的结构链接到内容的应用。由于大多数启动器一次只显示四个快捷方式,因此静态快捷方式非常适合以一致的方式执行例行任务,例如,如果用户希望以特定方式查看其日历或电子邮件。
- 动态快捷方式用于应用中对上下文敏感的操作。 对上下文敏感的快捷方式是针对用户在应用中执行的操作量身定制的。例如,如果您构建的游戏允许用户从其当前关卡开始启动,则需要频繁更新快捷方式。使用动态快捷方式可让您在用户每完成一个关卡后更新快捷方式。
- 固定快捷方式用于特定的用户驱动操作。 例如,用户可能希望将特定网站固定到启动器。这很有益,因为它允许用户一步执行自定义操作(例如导航到网站),比使用默认浏览器实例更快。
创建静态快捷方式
静态快捷方式提供指向应用内通用操作的链接,这些操作在应用当前版本的整个生命周期内必须保持一致。静态快捷方式的不错选项包括查看已发送消息、设置闹钟以及显示用户当天的运动活动。
如需创建静态快捷方式,请执行以下操作
- 在应用的
AndroidManifest.xml文件中,找到 intent 过滤器设置为android.intent.action.MAIN操作和android.intent.category.LAUNCHER类别的 Activity。 -
向此 Activity 中添加
<meta-data>元素,此元素引用定义应用快捷方式的资源文件<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.myapplication"> <application ... > <activity android:name="Main"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> <meta-data android:name="android.app.shortcuts" android:resource="@xml/shortcuts" /> </activity> </application> </manifest>
-
创建一个名为
res/xml/shortcuts.xml的新资源文件。 -
在新资源文件中,添加一个
<shortcuts>根元素,其中包含一个<shortcut>元素列表。在每个<shortcut>元素中,包含有关静态快捷方式的信息,包括其图标、描述性标签及其在应用中启动的 intent<shortcuts xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <shortcut android:shortcutId="compose" android:enabled="true" android:icon="@drawable/compose_icon" android:shortcutShortLabel="@string/compose_shortcut_short_label1" android:shortcutLongLabel="@string/compose_shortcut_long_label1" android:shortcutDisabledMessage="@string/compose_disabled_message1"> <intent android:action="android.intent.action.VIEW" android:targetPackage="com.example.myapplication" android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.ComposeActivity" /> <!-- If your shortcut is associated with multiple intents, include them here. The last intent in the list determines what the user sees when they launch this shortcut. --> <categories android:name="android.shortcut.conversation" /> <capability-binding android:key="actions.intent.CREATE_MESSAGE" /> </shortcut> <!-- Specify more shortcuts here. --> </shortcuts>
自定义属性值
以下列表包含静态快捷方式内不同属性的说明。为 android:shortcutId 和 android:shortcutShortLabel 提供值。所有其他值均为可选。
-
android:shortcutId -
当
ShortcutManager对象对其执行操作时,表示快捷方式的字符串字面量。 -
android:shortcutShortLabel -
一个简洁的短语,描述快捷方式的用途。如果可能,请将此简短说明限制在 10 个字符以内。
如需了解详情,请参阅
setShortLabel()。 -
android:shortcutLongLabel -
一个较长的短语,描述快捷方式的用途。如果空间充足,启动器会显示此值,而不是
android:shortcutShortLabel。如果可能,请将此长说明限制在 25 个字符以内。如需了解详情,请参阅
setLongLabel()。 -
android:shortcutDisabledMessage -
当用户尝试启动已停用的快捷方式时,在受支持的启动器中显示的消息。该消息必须向用户说明快捷方式为何被停用。如果
android:enabled的值为true,则此属性的值无效。 -
android:enabled -
确定用户是否可以从受支持的启动器与快捷方式互动。
android:enabled的默认值为true。如果您将其设置为false,请设置一个android:shortcutDisabledMessage来解释您停用此快捷方式的原因。如果您认为无需提供此类消息,请将快捷方式从 XML 文件中完全移除。 -
android:icon -
启动器向用户显示快捷方式时使用的位图或自适应图标。此值可以是图像的路径,也可以是包含图像的资源文件。尽可能使用自适应图标以提高性能和一致性。
配置内部元素
列出应用的静态快捷方式的 XML 文件支持在每个 <shortcut> 元素内使用以下元素。您必须为您定义的每个静态快捷方式包含一个 intent 内部元素。
-
intent -
用户选择快捷方式时系统启动的操作。此 Intent 必须为
android:action属性提供一个值。您可以为一个快捷方式提供多个 Intent。如需了解详情,请参阅管理多个 Intent 和 Activity、设置 Intent 以及
TaskStackBuilder类参考文档。 -
categories -
提供应用快捷方式执行的操作类型的分组,例如创建新的聊天消息。
如需受支持的快捷方式类别的列表,请参阅
ShortcutInfo类参考文档。 -
capability-binding -
声明与快捷方式相关联的功能。
在上一个示例中,快捷方式与为
CREATE_MESSAGE声明的功能关联,这是一个 App Actions 内置 Intent。此功能绑定让用户可以通过 Google Assistant 使用语音命令来调用快捷方式。
创建动态快捷方式
动态快捷方式提供指向应用内特定的、与上下文相关的操作的链接。这些操作可以在应用使用之间或应用运行时发生变化。动态快捷方式的良好用途包括呼叫特定联系人、导航到特定位置以及从用户的上一个保存点加载游戏。您还可以使用动态快捷方式打开对话。
The ShortcutManagerCompat Jetpack 库是 ShortcutManager API 的帮助程序,可让您在应用中管理动态快捷方式。使用 ShortcutManagerCompat 库可减少样板代码,并有助于确保您的快捷方式在不同 Android 版本中保持一致。此库也是推送动态快捷方式所必需的,以便它们能够通过 Google 快捷方式集成库显示在 Google Surface(例如 Assistant)上。
ShortcutManagerCompat API 允许您的应用对动态快捷方式执行以下操作
-
推送和更新: 使用
pushDynamicShortcut()发布和更新动态快捷方式。如果已存在 ID 相同的动态或固定快捷方式,则每个可变的快捷方式都会更新。 -
移除: 使用
removeDynamicShortcuts()移除一组动态快捷方式。使用removeAllDynamicShortcuts()移除所有动态快捷方式。
如需详细了解如何对快捷方式执行操作,请参阅管理快捷方式和 ShortcutManagerCompat 参考文档。
以下是创建动态快捷方式并将其关联到应用的示例
Kotlin
val shortcut = ShortcutInfoCompat.Builder(context, "id1") .setShortLabel("Website") .setLongLabel("Open the website") .setIcon(IconCompat.createWithResource(context, R.drawable.icon_website)) .setIntent(Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("https://www.mysite.example.com/"))) .build() ShortcutManagerCompat.pushDynamicShortcut(context, shortcut)
Java
ShortcutInfoCompat shortcut = new ShortcutInfoCompat.Builder(context, "id1") .setShortLabel("Website") .setLongLabel("Open the website") .setIcon(IconCompat.createWithResource(context, R.drawable.icon_website)) .setIntent(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("https://www.mysite.example.com/"))) .build(); ShortcutManagerCompat.pushDynamicShortcut(context, shortcut);
添加 Google 快捷方式集成库
Google 快捷方式集成库是一个可选的 Jetpack 库。它让您可以推送动态快捷方式,这些快捷方式可以显示在 Android Surface(例如启动器)和 Google Surface(例如 Assistant)上。使用此库有助于用户发现您的快捷方式,从而快速访问特定内容或重播应用中的操作。
例如,消息应用可以在用户向联系人“Alex”发送消息后,为此联系人推送一个动态快捷方式。推送动态快捷方式后,如果用户询问 Assistant:“Hey Google, message Alex on ExampleApp”,Assistant 就可以启动 ExampleApp 并自动将其配置为向 Alex 发送消息。
使用此库推送的动态快捷方式不受按设备执行的快捷方式限制的约束。这样,您的应用就可以在用户每次完成应用中的相关操作时推送快捷方式。通过这种方式频繁推送快捷方式,Google 可以了解用户的行为模式,并向他们推荐上下文相关的快捷方式。
例如,Assistant 可以从您的健身追踪应用推送的快捷方式中了解到用户通常在早晨跑步,并在用户早晨拿起手机时主动建议一个“开始跑步”的快捷方式。
Google 快捷方式集成库本身不提供任何可寻址的功能。将此库添加到应用后,Google Surface 即可接收您的应用使用 ShortcutManagerCompat 推送的快捷方式。
要在您的应用中使用此库,请按以下步骤操作
-
更新您的
gradle.properties文件以支持AndroidX 库android.useAndroidX=true # Automatically convert third-party libraries to use AndroidX android.enableJetifier=true
-
在
app/build.gradle中,添加 Google 快捷方式集成库和ShortcutManagerCompat的依赖项dependencies { implementation "androidx.core:core:1.6.0" implementation 'androidx.core:core-google-shortcuts:1.0.0' ... }
将库依赖项添加到您的 Android 项目后,您的应用就可以使用 ShortcutManagerCompat 中的 pushDynamicShortcut() 方法推送可在启动器和参与的 Google Surface 上显示的动态快捷方式。
创建固定快捷方式
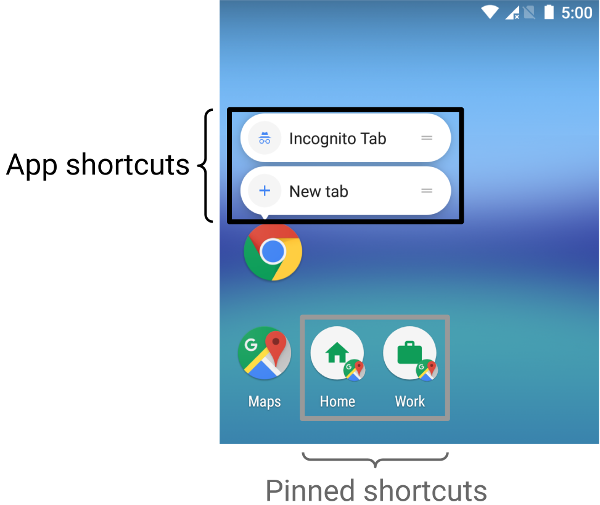
在 Android 8.0(API 级别 26)及更高版本上,您可以创建固定快捷方式。与静态快捷方式和动态快捷方式不同,固定快捷方式在受支持的启动器中显示为单独的图标。图 1 显示了这两种类型快捷方式之间的区别。
要使用您的应用将快捷方式固定到受支持的启动器,请完成以下步骤
- 使用
isRequestPinShortcutSupported()验证设备的默认启动器是否支持应用内固定快捷方式。 -
根据快捷方式是否存在,通过以下两种方式之一创建
ShortcutInfo对象- 如果快捷方式已存在,则创建仅包含现有快捷方式 ID 的
ShortcutInfo对象。系统会自动查找并固定与该快捷方式相关的所有其他信息。 - 如果要固定新的快捷方式,则创建包含新快捷方式的 ID、Intent 和短标签的
ShortcutInfo对象。
- 如果快捷方式已存在,则创建仅包含现有快捷方式 ID 的
-
通过调用
requestPinShortcut()将快捷方式固定到设备的启动器。在此过程中,您可以传入一个PendingIntent对象,该对象仅在快捷方式成功固定后通知您的应用。快捷方式固定后,您的应用可以使用
updateShortcuts()方法更新其内容。如需了解详情,请阅读更新快捷方式。
以下代码片段演示了如何创建固定快捷方式。
Kotlin
val shortcutManager = getSystemService(ShortcutManager::class.java) if (shortcutManager!!.isRequestPinShortcutSupported) { // Enable the existing shortcut with the ID "my-shortcut". val pinShortcutInfo = ShortcutInfo.Builder(context, "my-shortcut").build() // Create the PendingIntent object only if your app needs to be notified // that the user let the shortcut be pinned. If the pinning operation fails, // your app isn't notified. Assume here that the app implements a method // called createShortcutResultIntent() that returns a broadcast intent. val pinnedShortcutCallbackIntent = shortcutManager.createShortcutResultIntent(pinShortcutInfo) // Configure the intent so that your app's broadcast receiver gets the // callback successfully. For details, see PendingIntent.getBroadcast(). val successCallback = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, /* request code */ 0, pinnedShortcutCallbackIntent, /* flags */ 0) shortcutManager.requestPinShortcut(pinShortcutInfo, successCallback.intentSender) }
Java
ShortcutManager shortcutManager = context.getSystemService(ShortcutManager.class); if (shortcutManager.isRequestPinShortcutSupported()) { // Enable the existing shortcut with the ID "my-shortcut". ShortcutInfo pinShortcutInfo = new ShortcutInfo.Builder(context, "my-shortcut").build(); // Create the PendingIntent object only if your app needs to be notified // that the user let the shortcut be pinned. If the pinning operation fails, // your app isn't notified. Assume here that the app implements a method // called createShortcutResultIntent() that returns a broadcast intent. Intent pinnedShortcutCallbackIntent = shortcutManager.createShortcutResultIntent(pinShortcutInfo); // Configure the intent so that your app's broadcast receiver gets the // callback successfully. For details, see PendingIntent.getBroadcast(). PendingIntent successCallback = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, /* request code */ 0, pinnedShortcutCallbackIntent, /* flags */ 0); shortcutManager.requestPinShortcut(pinShortcutInfo, successCallback.getIntentSender()); }
创建自定义快捷方式 Activity
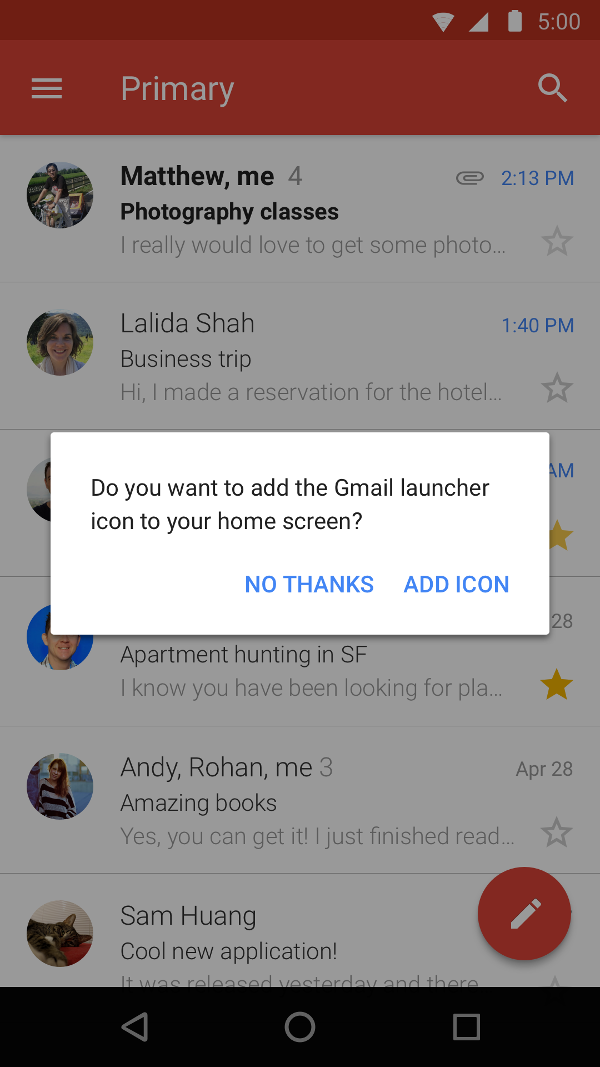
您还可以创建一个专门的 Activity,帮助用户创建快捷方式,其中包含自定义选项和确认按钮。图 2 显示了 Gmail 应用中此类 Activity 的示例。
在应用的 manifest 文件中,将 ACTION_CREATE_SHORTCUT 添加到 Activity 的 <intent-filter> 元素。此声明会在用户尝试创建快捷方式时设置以下行为
- 系统会启动您应用的专门 Activity。
- 用户为快捷方式设置选项。
- 用户选择确认按钮。
- 您的应用使用
createShortcutResultIntent()方法创建快捷方式。此方法返回一个Intent,您的应用可以使用setResult()将其传递回之前执行的 Activity。 - 您的应用对用于创建自定义快捷方式的 Activity 调用
finish()。
同样,您的应用可以在安装后或首次启动时提示用户将固定快捷方式添加到主屏幕。此方法非常有效,因为它有助于用户在其日常工作流程中创建快捷方式。
测试快捷方式
要测试应用的快捷方式,请将应用安装在支持快捷方式的启动器设备上。然后,执行以下操作
- 触摸并按住应用启动器图标,以查看您为应用定义的快捷方式。
- 拖动快捷方式,将其固定到设备的启动器。
