在系统层面,Android 将游戏控制器的输入事件代码报告为 Android 键代码和轴值。在游戏中,你可以接收这些代码和值,并将其转换为特定的游戏内操作。
当玩家通过物理连接或无线配对将游戏控制器连接到他们的 Android 设备时,系统会自动检测到控制器作为输入设备并开始报告其输入事件。你的游戏可以通过在活跃的 Activity 或聚焦的 View 中实现以下回调方法来接收这些输入事件(你应该为 Activity 或 View 实现回调,但不能同时实现):
- 来自
ActivitydispatchGenericMotionEvent(android.view. MotionEvent)调用此方法以处理通用运动事件,例如操纵杆移动。
dispatchKeyEvent(android.view.KeyEvent)调用此方法以处理按键事件,例如手柄或方向键按钮的按下或释放。
- 来自
ViewonGenericMotionEvent(android.view.MotionEvent)调用此方法以处理通用运动事件,例如操纵杆移动。
onKeyDown(int, android.view.KeyEvent)调用此方法以处理物理按键的按下,例如手柄或方向键按钮。
onKeyUp(int, android.view.KeyEvent)调用此方法以处理物理按键的释放,例如手柄或方向键按钮。
推荐的方法是从用户与之交互的特定 View 对象捕获事件。检查回调提供的以下对象,以获取接收到的输入事件类型的信息:
KeyEvent- 一个描述方向键 (D-pad) 和游戏手柄按钮事件的对象。按键事件伴随一个*键代码*,表示触发了哪个特定按钮,例如
DPAD_DOWN或BUTTON_A。你可以通过调用getKeyCode()或从onKeyDown()等按键事件回调中获取键代码。 MotionEvent- 一个描述操纵杆和肩部触发器移动的输入事件对象。运动事件伴随一个动作代码和一组*轴值*。动作代码指定发生的状态变化,例如操纵杆被移动。轴值描述了特定物理控制的位置和其他移动属性,例如
AXIS_X或AXIS_RTRIGGER。你可以通过调用getAction()获取动作代码,通过调用getAxisValue()获取轴值。
本课程重点介绍如何在游戏屏幕中处理最常见类型的物理控制(游戏手柄按钮、方向键和操纵杆)的输入,方法是实现上述 View 回调方法并处理 KeyEvent 和 MotionEvent 对象。
验证游戏控制器是否已连接
在报告输入事件时,Android 不区分来自非游戏控制器设备和来自游戏控制器的事件。例如,触摸屏操作会生成一个 AXIS_X 事件,表示触摸表面的 X 坐标,但操纵杆会生成一个 AXIS_X 事件,表示操纵杆的 X 位置。如果你的游戏需要处理游戏控制器输入,你应该首先检查输入事件是否来自相关的源类型。
为了验证连接的输入设备是游戏控制器,调用 getSources() 获取该设备支持的输入源类型的组合位字段。然后你可以测试以下字段是否已设置:
- 源类型为
SOURCE_GAMEPAD表示输入设备具有游戏手柄按钮(例如BUTTON_A)。请注意,此源类型并不严格指示游戏控制器是否具有方向键按钮,尽管大多数游戏手柄通常都有方向控制。 - 源类型为
SOURCE_DPAD表示输入设备具有方向键按钮(例如DPAD_UP)。 - 源类型为
SOURCE_JOYSTICK表示输入设备具有模拟控制杆(例如,记录沿AXIS_X和AXIS_Y移动的操纵杆)。
以下代码段展示了一个辅助方法,可让你检查连接的输入设备是否为游戏控制器。如果是,该方法会检索游戏控制器的设备 ID。然后,你可以将每个设备 ID 与游戏中的玩家关联起来,并分别为每个连接的玩家处理游戏操作。要了解如何在同一 Android 设备上同时连接多个控制器的更多信息,请参阅支持多个游戏控制器。
Kotlin
fun getGameControllerIds(): List<Int> { val gameControllerDeviceIds = mutableListOf<Int>() val deviceIds = InputDevice.getDeviceIds() deviceIds.forEach { deviceId -> InputDevice.getDevice(deviceId).apply { // Verify that the device has gamepad buttons, control sticks, or both. if (sources and InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD == InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD || sources and InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK == InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK) { // This device is a game controller. Store its device ID. gameControllerDeviceIds .takeIf { !it.contains(deviceId) } ?.add(deviceId) } } } return gameControllerDeviceIds }
Java
public ArrayList<Integer> getGameControllerIds() { ArrayList<Integer> gameControllerDeviceIds = new ArrayList<Integer>(); int[] deviceIds = InputDevice.getDeviceIds(); for (int deviceId : deviceIds) { InputDevice dev = InputDevice.getDevice(deviceId); int sources = dev.getSources(); // Verify that the device has gamepad buttons, control sticks, or both. if (((sources & InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD) == InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD) || ((sources & InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK) == InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK)) { // This device is a game controller. Store its device ID. if (!gameControllerDeviceIds.contains(deviceId)) { gameControllerDeviceIds.add(deviceId); } } } return gameControllerDeviceIds; }
此外,你可能想检查连接的游戏控制器支持的各个输入功能。例如,如果你的游戏只想使用它能理解的物理控制输入,这可能会很有用。
要检测连接的游戏控制器是否支持特定的键代码或轴代码,请使用以下技术:
- 在 Android 4.4(API 级别 19)或更高版本中,你可以通过调用
hasKeys(int...)来确定连接的游戏控制器是否支持某个键代码。 - 在 Android 3.1(API 级别 12)或更高版本中,你可以先调用
getMotionRanges()查找连接的游戏控制器支持的所有可用轴。然后,在返回的每个InputDevice.MotionRange对象上,调用getAxis()获取其轴 ID。
处理游戏手柄按钮按下
图 1 显示了 Android 如何将键代码和轴值映射到大多数游戏控制器上的物理控制。
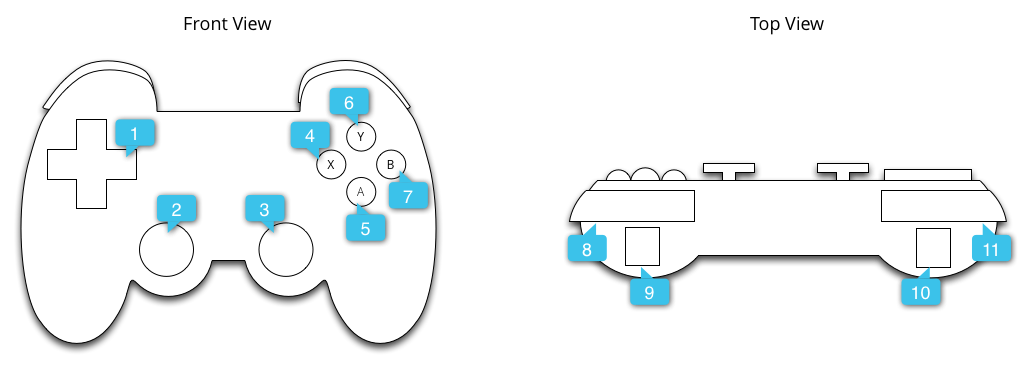
图中标注的内容如下:
游戏手柄按钮按下生成的常见键代码包括 BUTTON_A、BUTTON_B、BUTTON_SELECT 和 BUTTON_START。某些游戏控制器在按下方向键中心时也会触发 DPAD_CENTER 键代码。你的游戏可以通过调用 getKeyCode() 或从 onKeyDown() 等按键事件回调中检查键代码,如果它表示与你的游戏相关的事件,则将其作为游戏操作进行处理。表 1 列出了最常见的游戏手柄按钮的推荐游戏操作。
表 1. 游戏手柄按钮的推荐游戏操作。
| 游戏操作 | 按钮键代码 |
|---|---|
| 在主菜单中开始游戏,或在游戏过程中暂停/取消暂停 | BUTTON_START* |
| 显示菜单 | BUTTON_SELECT* 和 KEYCODE_MENU* |
| 与导航设计指南中描述的 Android *返回*导航行为相同。 | KEYCODE_BACK |
| 在菜单中导航回上一项 | BUTTON_B |
| 确认选择,或执行主要游戏操作 | BUTTON_A 和 DPAD_CENTER |
* 你的游戏不应依赖于 Start、Select 或 Menu 按钮的存在。
提示:考虑在游戏中提供配置屏幕,让用户为游戏操作个性化设置自己的游戏控制器映射。
以下代码段展示了如何覆盖 onKeyDown(),将 BUTTON_A 和 DPAD_CENTER 按钮按下与游戏操作关联起来。
Kotlin
class GameView(...) : View(...) { ... override fun onKeyDown(keyCode: Int, event: KeyEvent): Boolean { var handled = false if (event.source and InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD == InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD) { if (event.repeatCount == 0) { when (keyCode) { // Handle gamepad and D-pad button presses to navigate the ship ... else -> { keyCode.takeIf { isFireKey(it) }?.run { // Update the ship object to fire lasers ... handled = true } } } } if (handled) { return true } } return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event) } // Here we treat Button_A and DPAD_CENTER as the primary action // keys for the game. private fun isFireKey(keyCode: Int): Boolean = keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER || keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BUTTON_A }
Java
public class GameView extends View { ... @Override public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) { boolean handled = false; if ((event.getSource() & InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD) == InputDevice.SOURCE_GAMEPAD) { if (event.getRepeatCount() == 0) { switch (keyCode) { // Handle gamepad and D-pad button presses to // navigate the ship ... default: if (isFireKey(keyCode)) { // Update the ship object to fire lasers ... handled = true; } break; } } if (handled) { return true; } } return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event); } private static boolean isFireKey(int keyCode) { // Here we treat Button_A and DPAD_CENTER as the primary action // keys for the game. return keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER || keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BUTTON_A; } }
注意:在 Android 4.2(API 级别 17)及更低版本中,系统默认将 BUTTON_A 视为 Android 的*返回*键。如果你的应用支持这些 Android 版本,请确保将 BUTTON_A 视为主要游戏操作。要确定设备上的当前 Android SDK 版本,请参阅 Build.VERSION.SDK_INT 值。
处理方向键输入
四向方向键 (D-pad) 是许多游戏控制器中常见的物理控制。Android 将方向键的 UP 和 DOWN 按下报告为 AXIS_HAT_Y 事件,范围从 -1.0(上)到 1.0(下),将方向键的 LEFT 或 RIGHT 按下报告为 AXIS_HAT_X 事件,范围从 -1.0(左)到 1.0(右)。
有些控制器会使用键代码报告方向键按下。如果你的游戏关注方向键按下,你应该将帽子轴事件和方向键键代码视为相同的输入事件,如表 2 所推荐。
表 2. 方向键键代码和帽子轴值的推荐默认游戏操作。
| 游戏操作 | 方向键键代码 | 帽子轴代码 |
|---|---|---|
| 向上移动 | KEYCODE_DPAD_UP |
AXIS_HAT_Y(对于 0 到 -1.0 的值) |
| 向下移动 | KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN |
AXIS_HAT_Y(对于 0 到 1.0 的值) |
| 向左移动 | KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT |
AXIS_HAT_X(对于 0 到 -1.0 的值) |
| 向右移动 | KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT |
AXIS_HAT_X(对于 0 到 1.0 的值) |
以下代码片段展示了一个辅助类,可让你从输入事件中检查帽子轴和键代码值,以确定方向键方向。
Kotlin
class Dpad { private var directionPressed = -1 // initialized to -1 fun getDirectionPressed(event: InputEvent): Int { if (!isDpadDevice(event)) { return -1 } // If the input event is a MotionEvent, check its hat axis values. (event as? MotionEvent)?.apply { // Use the hat axis value to find the D-pad direction val xaxis: Float = event.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_X) val yaxis: Float = event.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_Y) directionPressed = when { // Check if the AXIS_HAT_X value is -1 or 1, and set the D-pad // LEFT and RIGHT direction accordingly. xaxis.compareTo(-1.0f) == 0 -> Dpad.LEFT xaxis.compareTo(1.0f) == 0 -> Dpad.RIGHT // Check if the AXIS_HAT_Y value is -1 or 1, and set the D-pad // UP and DOWN direction accordingly. yaxis.compareTo(-1.0f) == 0 -> Dpad.UP yaxis.compareTo(1.0f) == 0 -> Dpad.DOWN else -> directionPressed } } // If the input event is a KeyEvent, check its key code. (event as? KeyEvent)?.apply { // Use the key code to find the D-pad direction. directionPressed = when(event.keyCode) { KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT -> Dpad.LEFT KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT -> Dpad.RIGHT KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP -> Dpad.UP KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN -> Dpad.DOWN KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER -> Dpad.CENTER else -> directionPressed } } return directionPressed } companion object { internal const val UP = 0 internal const val LEFT = 1 internal const val RIGHT = 2 internal const val DOWN = 3 internal const val CENTER = 4 fun isDpadDevice(event: InputEvent): Boolean = // Check that input comes from a device with directional pads. event.source and InputDevice.SOURCE_DPAD != InputDevice.SOURCE_DPAD } }
Java
public class Dpad { final static int UP = 0; final static int LEFT = 1; final static int RIGHT = 2; final static int DOWN = 3; final static int CENTER = 4; int directionPressed = -1; // initialized to -1 public int getDirectionPressed(InputEvent event) { if (!isDpadDevice(event)) { return -1; } // If the input event is a MotionEvent, check its hat axis values. if (event instanceof MotionEvent) { // Use the hat axis value to find the D-pad direction MotionEvent motionEvent = (MotionEvent) event; float xaxis = motionEvent.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_X); float yaxis = motionEvent.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_Y); // Check if the AXIS_HAT_X value is -1 or 1, and set the D-pad // LEFT and RIGHT direction accordingly. if (Float.compare(xaxis, -1.0f) == 0) { directionPressed = Dpad.LEFT; } else if (Float.compare(xaxis, 1.0f) == 0) { directionPressed = Dpad.RIGHT; } // Check if the AXIS_HAT_Y value is -1 or 1, and set the D-pad // UP and DOWN direction accordingly. else if (Float.compare(yaxis, -1.0f) == 0) { directionPressed = Dpad.UP; } else if (Float.compare(yaxis, 1.0f) == 0) { directionPressed = Dpad.DOWN; } } // If the input event is a KeyEvent, check its key code. else if (event instanceof KeyEvent) { // Use the key code to find the D-pad direction. KeyEvent keyEvent = (KeyEvent) event; if (keyEvent.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT) { directionPressed = Dpad.LEFT; } else if (keyEvent.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT) { directionPressed = Dpad.RIGHT; } else if (keyEvent.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP) { directionPressed = Dpad.UP; } else if (keyEvent.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN) { directionPressed = Dpad.DOWN; } else if (keyEvent.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER) { directionPressed = Dpad.CENTER; } } return directionPressed; } public static boolean isDpadDevice(InputEvent event) { // Check that input comes from a device with directional pads. if ((event.getSource() & InputDevice.SOURCE_DPAD) != InputDevice.SOURCE_DPAD) { return true; } else { return false; } } }
你可以在游戏中任何需要处理方向键输入的地方使用此辅助类(例如,在 onGenericMotionEvent() 或 onKeyDown() 回调中)。
例如:
Kotlin
private val dpad = Dpad() ... override fun onGenericMotionEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { if (Dpad.isDpadDevice(event)) { when (dpad.getDirectionPressed(event)) { Dpad.LEFT -> { // Do something for LEFT direction press ... return true } Dpad.RIGHT -> { // Do something for RIGHT direction press ... return true } Dpad.UP -> { // Do something for UP direction press ... return true } ... } } // Check if this event is from a joystick movement and process accordingly. ... }
Java
Dpad dpad = new Dpad(); ... @Override public boolean onGenericMotionEvent(MotionEvent event) { // Check if this event if from a D-pad and process accordingly. if (Dpad.isDpadDevice(event)) { int press = dpad.getDirectionPressed(event); switch (press) { case LEFT: // Do something for LEFT direction press ... return true; case RIGHT: // Do something for RIGHT direction press ... return true; case UP: // Do something for UP direction press ... return true; ... } } // Check if this event is from a joystick movement and process accordingly. ... }
处理操纵杆移动
当玩家移动游戏控制器上的操纵杆时,Android 会报告一个 MotionEvent,其中包含 ACTION_MOVE 动作代码和操纵杆轴的更新位置。你的游戏可以使用 MotionEvent 提供的数据来确定是否发生了游戏关注的操纵杆移动。
请注意,操纵杆运动事件可能会将多个运动样本批量处理到一个对象中。 MotionEvent 对象包含每个操纵杆轴的当前位置以及每个轴的多个历史位置。当报告带有 ACTION_MOVE 动作代码(例如操纵杆移动)的运动事件时,Android 为了效率会批量处理轴值。轴的历史值由一组不同于当前轴值但比之前任何运动事件报告的值更近期值的集合组成。有关详细信息,请参阅 MotionEvent 参考文档。
你可以使用历史信息更准确地根据操纵杆输入渲染游戏对象的移动。要检索当前值和历史值,请调用 getAxisValue() 或 getHistoricalAxisValue()。你还可以通过调用 getHistorySize() 查找操纵杆事件中的历史点数量。
以下代码片段展示了如何覆盖 onGenericMotionEvent() 回调来处理操纵杆输入。你应该首先处理轴的历史值,然后处理其当前位置。
Kotlin
class GameView(...) : View(...) { override fun onGenericMotionEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { // Check that the event came from a game controller return if (event.source and InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK == InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK && event.action == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE) { // Process the movements starting from the // earliest historical position in the batch (0 until event.historySize).forEach { i -> // Process the event at historical position i processJoystickInput(event, i) } // Process the current movement sample in the batch (position -1) processJoystickInput(event, -1) true } else { super.onGenericMotionEvent(event) } } }
Java
public class GameView extends View { @Override public boolean onGenericMotionEvent(MotionEvent event) { // Check that the event came from a game controller if ((event.getSource() & InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK) == InputDevice.SOURCE_JOYSTICK && event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE) { // Process all historical movement samples in the batch final int historySize = event.getHistorySize(); // Process the movements starting from the // earliest historical position in the batch for (int i = 0; i < historySize; i++) { // Process the event at historical position i processJoystickInput(event, i); } // Process the current movement sample in the batch (position -1) processJoystickInput(event, -1); return true; } return super.onGenericMotionEvent(event); } }
在使用操纵杆输入之前,你需要确定操纵杆是否居中,然后相应地计算其轴移动。操纵杆通常有一个*平坦区域*,即在 (0,0) 坐标附近的一个值范围,在该范围内轴被认为是居中的。如果 Android 报告的轴值落在平坦区域内,你应该将控制器视为静止状态(即沿两个轴都无运动)。
以下代码片段显示了一个计算沿每个轴移动的辅助方法。你将在稍后描述的 processJoystickInput() 方法中调用此辅助方法。
Kotlin
private fun getCenteredAxis( event: MotionEvent, device: InputDevice, axis: Int, historyPos: Int ): Float { val range: InputDevice.MotionRange? = device.getMotionRange(axis, event.source) // A joystick at rest does not always report an absolute position of // (0,0). Use the getFlat() method to determine the range of values // bounding the joystick axis center. range?.apply { val value: Float = if (historyPos < 0) { event.getAxisValue(axis) } else { event.getHistoricalAxisValue(axis, historyPos) } // Ignore axis values that are within the 'flat' region of the // joystick axis center. if (Math.abs(value) > flat) { return value } } return 0f }
Java
private static float getCenteredAxis(MotionEvent event, InputDevice device, int axis, int historyPos) { final InputDevice.MotionRange range = device.getMotionRange(axis, event.getSource()); // A joystick at rest does not always report an absolute position of // (0,0). Use the getFlat() method to determine the range of values // bounding the joystick axis center. if (range != null) { final float flat = range.getFlat(); final float value = historyPos < 0 ? event.getAxisValue(axis): event.getHistoricalAxisValue(axis, historyPos); // Ignore axis values that are within the 'flat' region of the // joystick axis center. if (Math.abs(value) > flat) { return value; } } return 0; }
将所有内容整合在一起,下面是你在游戏中处理操纵杆移动的方法:
Kotlin
private fun processJoystickInput(event: MotionEvent, historyPos: Int) { val inputDevice = event.device // Calculate the horizontal distance to move by // using the input value from one of these physical controls: // the left control stick, hat axis, or the right control stick. var x: Float = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_X, historyPos) if (x == 0f) { x = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_X, historyPos) } if (x == 0f) { x = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_Z, historyPos) } // Calculate the vertical distance to move by // using the input value from one of these physical controls: // the left control stick, hat switch, or the right control stick. var y: Float = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_Y, historyPos) if (y == 0f) { y = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_Y, historyPos) } if (y == 0f) { y = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_RZ, historyPos) } // Update the ship object based on the new x and y values }
Java
private void processJoystickInput(MotionEvent event, int historyPos) { InputDevice inputDevice = event.getDevice(); // Calculate the horizontal distance to move by // using the input value from one of these physical controls: // the left control stick, hat axis, or the right control stick. float x = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_X, historyPos); if (x == 0) { x = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_X, historyPos); } if (x == 0) { x = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_Z, historyPos); } // Calculate the vertical distance to move by // using the input value from one of these physical controls: // the left control stick, hat switch, or the right control stick. float y = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_Y, historyPos); if (y == 0) { y = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_HAT_Y, historyPos); } if (y == 0) { y = getCenteredAxis(event, inputDevice, MotionEvent.AXIS_RZ, historyPos); } // Update the ship object based on the new x and y values }
为了支持具有单个操纵杆以外更复杂功能的游戏控制器,请遵循以下最佳实践:
- 处理双操纵杆。许多游戏控制器同时拥有左操纵杆和右操纵杆。对于左操纵杆,Android 将水平移动报告为
AXIS_X事件,将垂直移动报告为AXIS_Y事件。对于右操纵杆,Android 将水平移动报告为AXIS_Z事件,将垂直移动报告为AXIS_RZ事件。确保在代码中处理这两个操纵杆。 -
处理肩部触发器按下(并确保你的游戏支持
AXIS_和KEYCODE_BUTTON_事件)。一些控制器具有左右肩部触发器。当存在这些触发器时,它们会发出AXIS_*TRIGGER或KEYCODE_BUTTON_*2事件,或两者都发出。对于左触发器,这将是AXIS_LTRIGGER和KEYCODE_BUTTON_L2。对于右触发器,这将是AXIS_RTRIGGER和KEYCODE_BUTTON_R2。轴事件仅在触发器发出介于 0 和 1 之间的值范围时发生,并且一些具有模拟输出的控制器除了轴事件外还会发出按钮事件。游戏必须同时支持AXIS_和KEYCODE_BUTTON_事件,以保持与所有常见游戏控制器的兼容性,但如果控制器同时报告这两种事件,则优先处理对你的游戏玩法最有意义的事件。在 Android 4.3(API 级别 18)及更高版本中,产生AXIS_LTRIGGER的控制器也会为AXIS_BRAKE轴报告相同的值。对于AXIS_RTRIGGER和AXIS_GAS也是如此。Android 以 0.0(释放)到 1.0(完全按下)的归一化值报告所有模拟触发器按下。 -
模拟环境中的特定行为和支持可能有所不同。模拟平台(例如 Google Play Games)的行为可能会根据主机操作系统的功能略有不同。例如,某些同时发出
AXIS_和KEYCODE_BUTTON_事件的控制器可能只发出AXIS_事件,并且可能完全缺失对某些控制器的支持。
