使用 WindowInsetsCompat,您的应用可以像与系统栏交互一样查询和控制屏幕键盘(也称为 IME)。您的应用还可以使用 WindowInsetsAnimationCompat 在软件键盘打开或关闭时创建无缝过渡效果。
前提条件
在设置软件键盘的控制和动画之前,请配置您的应用以实现端到端显示。这样可以处理系统窗口边衬区,例如系统栏和屏幕键盘。
检查软件键盘可见性
使用 WindowInsets 检查软件键盘可见性。
Kotlin
val insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view) ?: return val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom
Java
WindowInsetsCompat insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view); boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom;
或者,您可以使用 ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener 观察软件键盘可见性的变化。
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { _, insets -> val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom insets }
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view, (v, insets) -> { boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom; return insets; });
与软件键盘同步动画
用户点按文本输入字段时,键盘会从屏幕底部滑入到位,如下图所示
图 2 中标有“未同步”的示例显示了 Android 10(API 级别 29)中的默认行为,其中文本字段和应用内容会快速到位,而不是与键盘动画同步,这可能会造成视觉上的不适。
在 Android 11(API 级别 30)及更高版本中,您可以使用
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat将应用过渡与键盘从屏幕底部上下滑动的动画同步。这看起来更流畅,如图 2 中标有“同步”的示例所示。
使用要与键盘动画同步的视图配置 WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback。
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback( view, object : WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback(DISPATCH_MODE_STOP) { // Override methods. } )
Java
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback( view, new WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback( WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback.DISPATCH_MODE_STOP ) { // Override methods. });
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback 中有几种方法可以覆写,即 onPrepare()、onStart()、onProgress() 和 onEnd()。首先在任何布局更改之前调用 onPrepare()。
当边衬区动画开始且在由于动画重新布局视图之前,会调用 onPrepare。您可以使用它来保存起始状态,在这种情况下是视图的底部坐标。
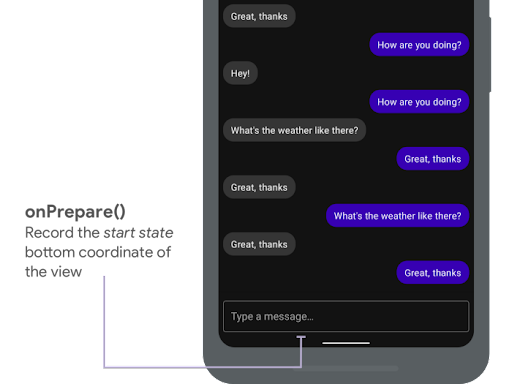
onPrepare() 记录起始状态。以下代码段显示了 onPrepare 的示例调用
Kotlin
var startBottom = 0f override fun onPrepare( animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat ) { startBottom = view.bottom.toFloat() }
Java
float startBottom; @Override public void onPrepare( @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation ) { startBottom = view.getBottom(); }
当边衬区动画开始时,会调用 onStart。您可以使用它将所有视图属性设置为布局更改的最终状态。如果为任何视图设置了 OnApplyWindowInsetsListener 回调,则此时已调用它。这是保存视图属性最终状态的好时机。
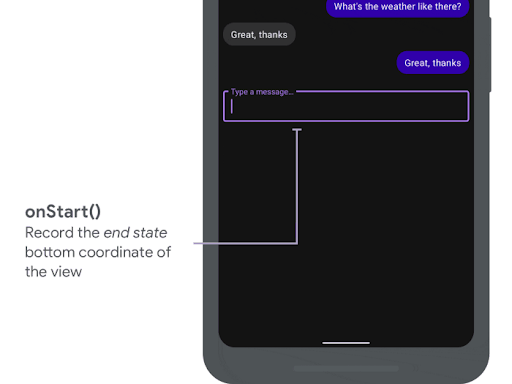
onStart() 记录最终状态。以下代码段显示了 onStart 的示例调用
Kotlin
var endBottom = 0f override fun onStart( animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat, bounds: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat ): WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat { // Record the position of the view after the IME transition. endBottom = view.bottom.toFloat() return bounds }
Java
float endBottom; @NonNull @Override public WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat onStart( @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation, @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat bounds ) { endBottom = view.getBottom(); return bounds; }
当边衬区作为运行动画的一部分发生变化时,会调用 onProgress,因此您可以覆写它并在键盘动画期间的每一帧收到通知。更新视图属性,使视图与键盘同步动画。
此时所有布局更改均已完成。例如,如果您使用 View.translationY 移动视图,则每次调用此方法时该值会逐渐减小,并最终达到 0,回到原始布局位置。
onProgress() 同步动画。以下代码段显示了 onProgress 的示例调用
Kotlin
override fun onProgress( insets: WindowInsetsCompat, runningAnimations: MutableList<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> ): WindowInsetsCompat { // Find an IME animation. val imeAnimation = runningAnimations.find { it.typeMask and WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime() != 0 } ?: return insets // Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation. view.translationY = (startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.interpolatedFraction) return insets }
Java
@NonNull @Override public WindowInsetsCompat onProgress( @NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets, @NonNull List<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> runningAnimations ) { // Find an IME animation. WindowInsetsAnimationCompat imeAnimation = null; for (WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation : runningAnimations) { if ((animation.getTypeMask() & WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) != 0) { imeAnimation = animation; break; } } if (imeAnimation != null) { // Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation. view.setTranslationY((startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.getInterpolatedFraction())); } return insets; }
或者,您可以覆写 onEnd。此方法在动画结束后调用。这是清理任何临时更改的好时机。
其他资源
- GitHub 上的 WindowInsetsAnimation。

