一个常见的误解是使用基本布局结构可以获得最有效的布局。然而,您添加到应用中的每个微件和布局都需要初始化、布局和绘制。例如,嵌套使用 LinearLayout 的实例可能会导致视图层次结构过深。此外,嵌套多个使用 layout_weight 参数的 LinearLayout 实例可能会特别耗费性能,因为每个子视图都需要测量两次。当布局被重复膨胀时(例如在 RecyclerView 中使用时),这一点尤为重要。
本文档展示了如何使用 布局检查器 和 lint 来检查和优化您的布局。
检查您的布局
Android SDK 工具包含 布局检查器 工具,它可以让您在应用运行时分析布局。使用此工具有助于您发现布局性能中的低效之处。
布局检查器允许您选择连接的设备或模拟器上正在运行的进程,然后显示布局树。每个块上的红绿灯表示其测量、布局和绘制性能,帮助您识别潜在问题。
例如,图 1 显示了一个在 RecyclerView 中用作项目的布局。此布局在左侧显示一个小型位图图像,在右侧显示两个堆叠的文本项。对于像这样多次膨胀的布局,进行优化尤为重要,因为性能优势会成倍增加。

RecyclerView 中项目的概念布局。布局检查器显示可用设备及其运行中的组件列表。从 Windows 标签页中选择您的组件,然后点击 Layout Inspector 以查看所选组件的布局层次结构。例如,图 2 显示了图 1 所示列表项的布局。
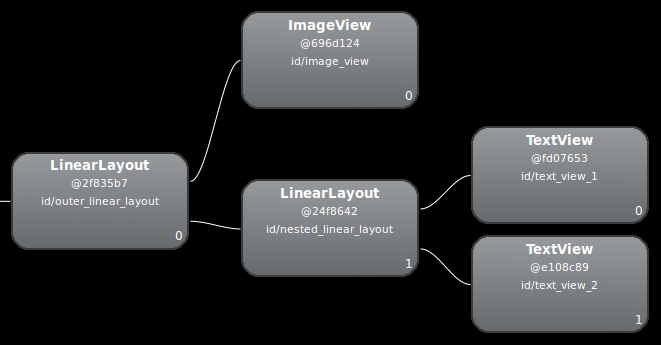
LinearLayout 实例的布局层次结构。修改您的布局
由于前述布局性能因嵌套的 LinearLayout 而变慢,您可以通过展平布局来提高性能——换句话说,使布局扁平化而非狭窄而深层。作为根节点的 ConstraintLayout 允许实现此类布局。当您将此设计转换为使用 ConstraintLayout 时,布局将变为两层层次结构。
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/root" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="52dp" android:background="#e4e6e4" android:padding="4dp"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image" android:layout_width="48dp" android:layout_height="48dp" android:background="#5c5c74" android:contentDescription="An example box" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/title" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_marginStart="4dp" android:background="#745c74" app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/subtitle" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@id/image" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/subtitle" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" android:background="#7e8d6e" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@id/title" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/title" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
新布局的检查结果如下:
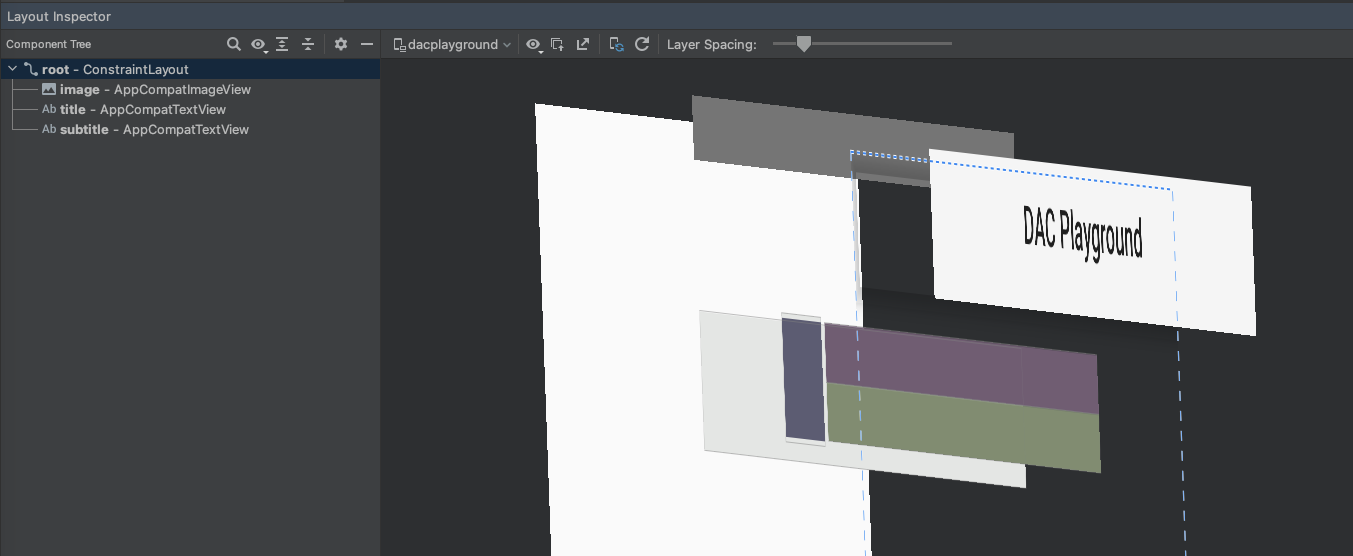
其好处是成倍增加的,因为此布局用于列表中的每个项目。
大部分差异是由于 LinearLayout 设计中使用了 layout_weight,这会减慢测量速度。这是每种布局都有其适当用途的一个示例。仔细考虑使用布局权重是否必要。
在某些复杂布局中,系统可能会浪费精力多次测量同一 UI 元素。这种现象称为双重征税(double taxation)。有关双重征税以及如何预防它的更多信息,请参阅性能和视图层次结构。
使用 lint
在布局文件上运行 lint 工具来搜索可能的视图层次结构优化是很好的实践。Lint 取代了 layoutopt 工具并具有更强大的功能。以下是 lint 规则的示例:
- 使用复合 Drawable。包含
ImageView和TextView的LinearLayout可以更高效地作为复合 Drawable 进行处理。 - 合并根 Frame。如果布局的根是一个不提供背景或内边距的
FrameLayout,您可以将其替换为 merge 标签,这会稍微更高效。 - 移除无用的叶子。您可以移除没有子项或没有背景的布局(因为它是不可见的),以获得更扁平、更高效的布局层次结构。
- 移除无用的父项。您可以移除只有一个子项且没有兄弟姐妹、不是
ScrollView或根布局且没有背景的布局。您还可以将子视图直接移到父项中,以获得更扁平、更高效的布局层次结构。 - 避免深度布局。嵌套过多的布局不利于性能。考虑使用更扁平的布局(例如
ConstraintLayout)来提高性能。lint 检查的默认最大深度是 10。
lint 工具的另一个优点是它与 Android Studio 的集成。只要您编译程序,lint 就会自动运行。使用 Android Studio,您还可以针对特定的构建变体或所有构建变体运行 lint 检查。
您还可以使用 File > Settings > Project Settings 选项在 Android Studio 中管理检查配置文件和配置检查。此时会出现检查配置页面,其中包含支持的检查:
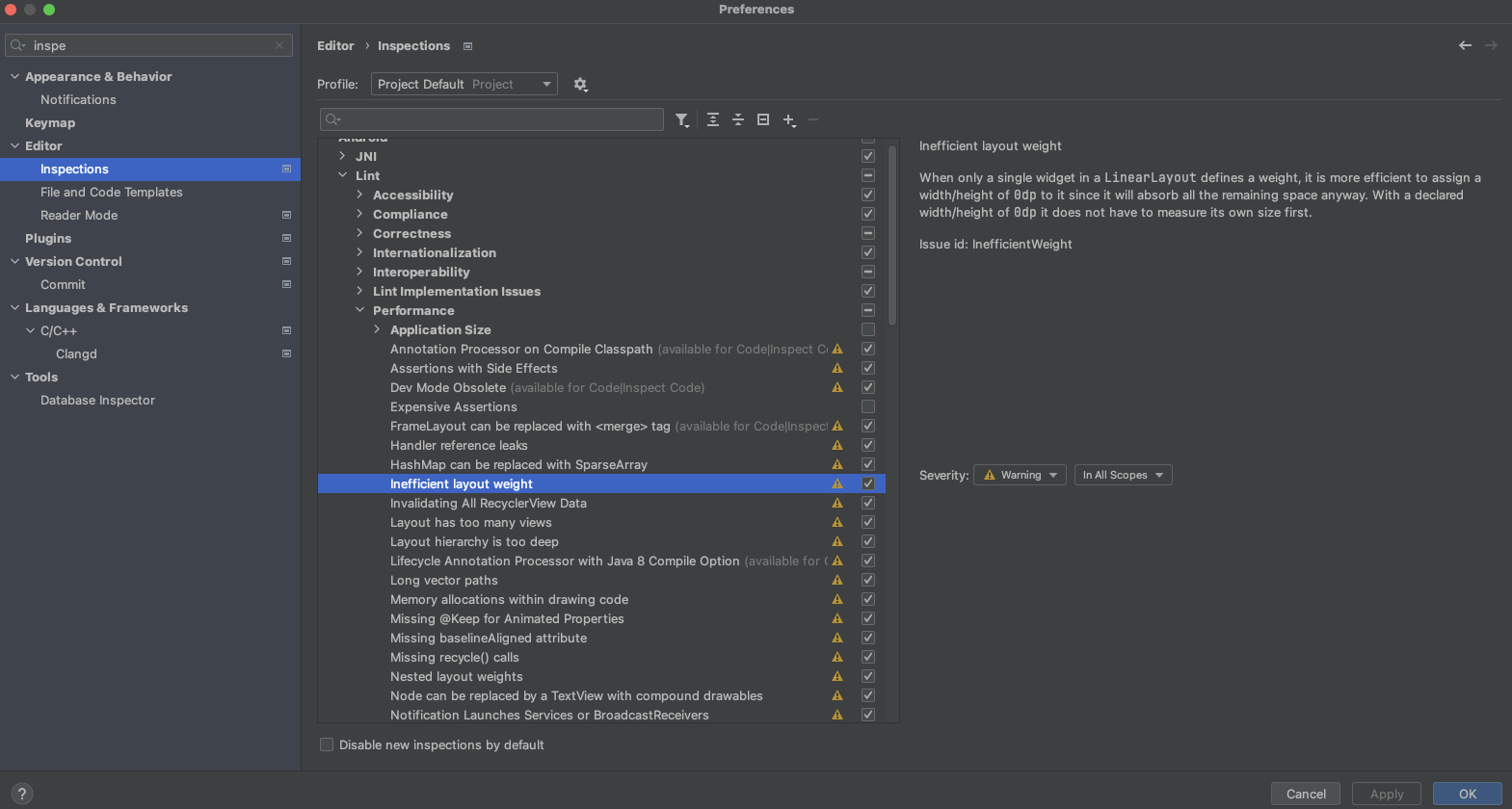
Lint 可以自动修复一些问题,为其他问题提供建议,并直接跳转到有问题代码供审查。

