你可以为应用提供基于网页的内容(例如 HTML、JavaScript 和 CSS),这些内容将静态编译到应用中,而无需通过互联网获取。
应用内内容无需互联网访问,也不会消耗用户带宽。如果内容专为 WebView 设计(即依赖于与原生应用通信),那么用户就不会在网页浏览器中意外加载它。
然而,应用内内容也有一些缺点。更新基于网页的内容需要发布新的应用更新,并且如果用户使用的是过时应用版本,网站上的内容与设备应用中的内容可能会不匹配。
WebViewAssetLoader
WebViewAssetLoader 是一种灵活且高性能的方式,可在 WebView 对象中加载应用内内容。此类支持以下功能:
- 通过 HTTP(S) URL 加载内容,以便与同源政策兼容。
- 加载子资源,例如 JavaScript、CSS、图片和 iframe。
在你的主要 Activity 文件中包含 WebViewAssetLoader。以下是一个从 assets 文件夹加载简单网页内容的示例:
Kotlin
private class LocalContentWebViewClient(private val assetLoader: WebViewAssetLoader) : WebViewClientCompat() { @RequiresApi(21) override fun shouldInterceptRequest( view: WebView, request: WebResourceRequest ): WebResourceResponse? { return assetLoader.shouldInterceptRequest(request.url) } // To support API < 21. override fun shouldInterceptRequest( view: WebView, url: String ): WebResourceResponse? { return assetLoader.shouldInterceptRequest(Uri.parse(url)) } }
Java
private static class LocalContentWebViewClient extends WebViewClientCompat { private final WebViewAssetLoader mAssetLoader; LocalContentWebViewClient(WebViewAssetLoader assetLoader) { mAssetLoader = assetLoader; } @Override @RequiresApi(21) public WebResourceResponse shouldInterceptRequest(WebView view, WebResourceRequest request) { return mAssetLoader.shouldInterceptRequest(request.getUrl()); } @Override @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") // To support API < 21. public WebResourceResponse shouldInterceptRequest(WebView view, String url) { return mAssetLoader.shouldInterceptRequest(Uri.parse(url)); } }
你的应用必须配置 WebViewAssetLoader 实例以满足其需求。下一节提供了示例。
创建应用内 assets 和 resources
WebViewAssetLoader 依靠 PathHandler 实例加载与给定资源路径对应的资源。虽然你可以实现此接口以根据应用需要检索资源,但 Webkit 库捆绑了 AssetsPathHandler 和 ResourcesPathHandler,分别用于加载 Android assets 和 resources。
首先,为你的应用创建 assets 和 resources。通常适用以下规则:
- HTML、JavaScript 和 CSS 等文本文件应放在 assets 中。
- 图片和其他二进制文件应放在 resources 中。
要向项目添加基于文本的网页文件,请执行以下操作:
- 在 Android Studio 中,右键点击 app > src > main 文件夹,然后选择 New > Directory。
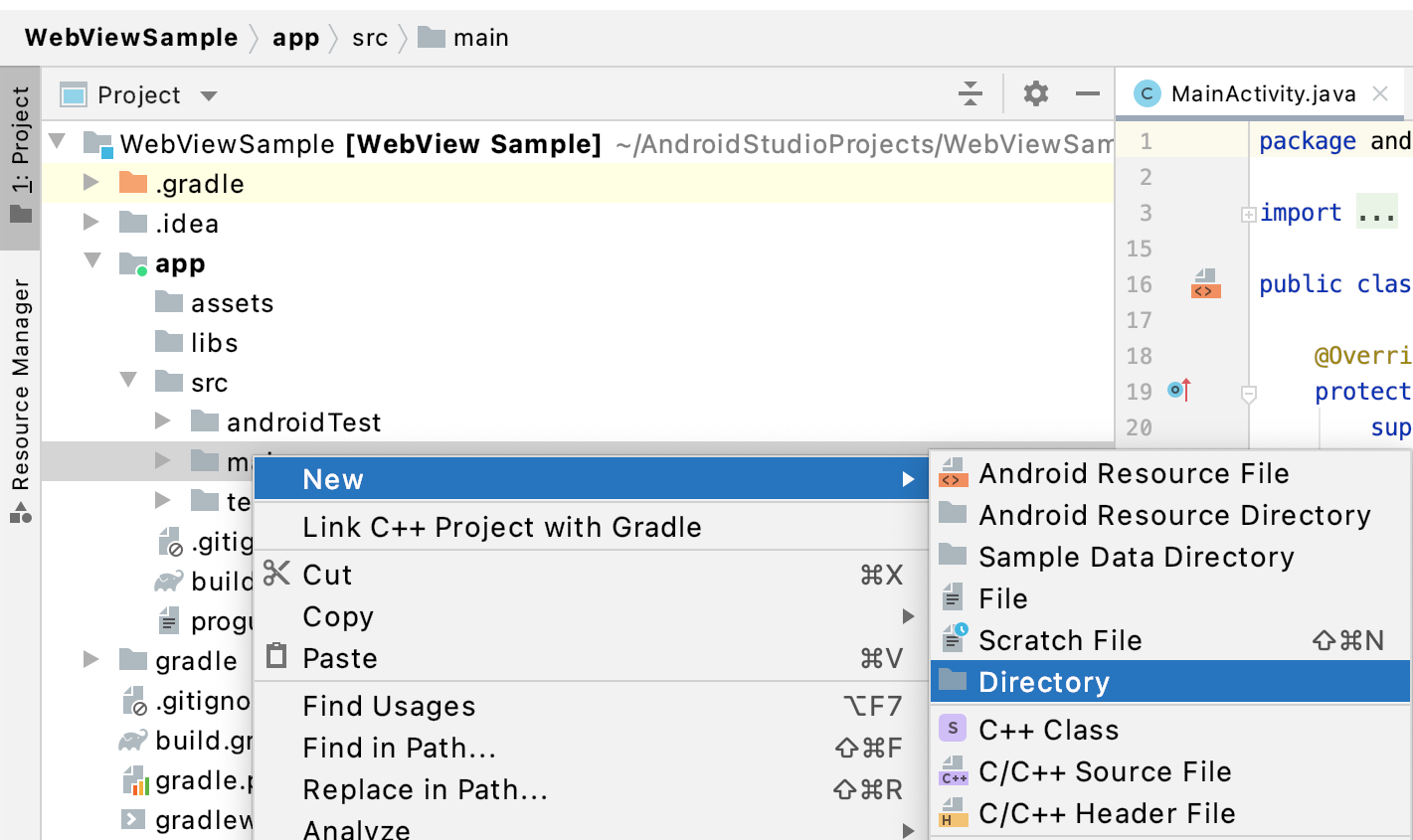
图 1. 为项目创建 assets 文件夹。 - 将文件夹命名为“assets”。
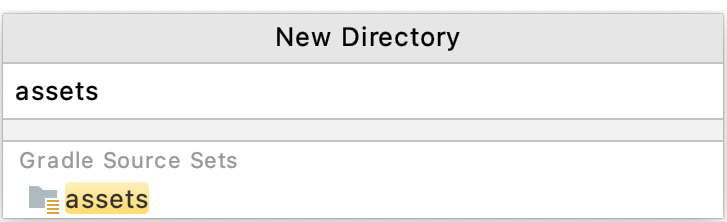
图 2. 为 assets 文件夹命名。 - 右键点击 assets 文件夹,然后点击 New > File。输入
index.html并按 Return 或 Enter 键。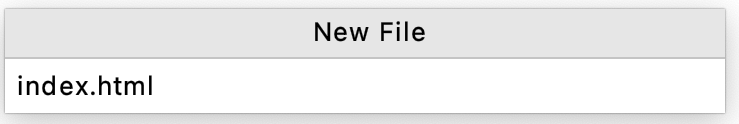
图 3. 创建 index.html文件。 - 重复上一步,创建
stylesheet.css的空文件。 - 用接下来的两个代码示例中的内容填充你创建的空文件。
```html
<!-- index.html content -->
<html>
<head>
<!-- Tip: Use relative URLs when referring to other in-app content to give
your app code the flexibility to change the scheme or domain as
necessary. -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/assets/stylesheet.css">
</head>
<body>
<p>This file is loaded from in-app content.</p>
<p><img src="/res/drawable/android_robot.png" alt="Android robot" width="100"></p>
</body>
</html>
```
```css
<!-- stylesheet.css content -->
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
```
要向项目添加基于图片的网页文件,请执行以下操作:
将
Android_symbol_green_RGB.png文件下载到本地计算机。将文件重命名为
android_robot.png。手动将文件移动到你硬盘上的项目
main/res/drawable目录中。
图 4 显示了你在应用中添加的图片和渲染的文本(来自前面的代码示例)。

要完成应用,请执行以下操作:
将以下代码添加到
onCreate()方法中,以注册处理程序并配置AssetLoaderKotlin
val assetLoader = WebViewAssetLoader.Builder() .addPathHandler("/assets/", AssetsPathHandler(this)) .addPathHandler("/res/", ResourcesPathHandler(this)) .build() webView.webViewClient = LocalContentWebViewClient(assetLoader)
Java
final WebViewAssetLoader assetLoader = new WebViewAssetLoader.Builder() .addPathHandler("/assets/", new WebViewAssetLoader.AssetsPathHandler(this)) .addPathHandler("/res/", new WebViewAssetLoader.ResourcesPathHandler(this)) .build(); mWebView.setWebViewClient(new LocalContentWebViewClient(assetLoader));
将以下代码添加到
onCreate()方法中,以加载内容Kotlin
webView.loadUrl("https://appassets.androidplatform.net/assets/index.html")
Java
mWebView.loadUrl("https://appassets.androidplatform.net/assets/index.html");
将应用内内容与网站资源混合使用
你的应用可能需要混合加载应用内内容和互联网内容,例如使用你网站的 CSS 设置样式的应用内 HTML 页面。WebViewAssetLoader 支持此用例。如果没有已注册的 PathHandler 实例可以找到给定路径的资源,WebView 将回退到从互联网加载内容。如果你将应用内内容与网站资源混合使用,请为应用内资源预留目录路径,例如 /assets/ 或 /resources/。避免将网站上的任何资源存储在这些位置。
Kotlin
val assetLoader = WebViewAssetLoader.Builder() .setDomain("example.com") // Replace this with your website's domain. .addPathHandler("/assets/", AssetsPathHandler(this)) .build() webView.webViewClient = LocalContentWebViewClient(assetLoader) val inAppHtmlUrl = "https://example.com/assets/index.html" webView.loadUrl(inAppHtmlUrl) val websiteUrl = "https://example.com/website/data.json" // JavaScript code to fetch() content from the same origin. val jsCode = "fetch('$websiteUrl')" + ".then(resp => resp.json())" + ".then(data => console.log(data));" webView.evaluateJavascript(jsCode, null)
Java
final WebViewAssetLoader assetLoader = new WebViewAssetLoader.Builder() .setDomain("example.com") // Replace this with your website's domain. .addPathHandler("/assets/", new AssetsPathHandler(this)) .build(); mWebView.setWebViewClient(new LocalContentWebViewClient(assetLoader)); String inAppHtmlUrl = "https://example.com/assets/index.html"; mWebView.loadUrl(inAppHtmlUrl); String websiteUrl = "https://example.com/website/data.json"; // JavaScript code to fetch() content from the same origin. String jsCode = "fetch('" + websiteUrl + "')" + ".then(resp => resp.json())" + ".then(data => console.log(data));"; mWebView.evaluateJavascript(jsCode, null);
请参阅 GitHub 上的 WebView 演示,了解应用内 HTML 页面获取 Web 托管 JSON 数据的示例。
loadDataWithBaseURL
当你的应用只需要加载 HTML 页面而无需拦截子资源时,可以考虑使用 loadDataWithBaseURL(),它不需要应用 assets。你可以按以下代码示例所示使用它:
Kotlin
val html = "<html><body><p>Hello world</p></body></html>" val baseUrl = "https://example.com/" webView.loadDataWithBaseURL(baseUrl, html, "text/html", null, baseUrl)
Java
String html = "<html><body><p>Hello world</p></body></html>"; String baseUrl = "https://example.com/"; mWebView.loadDataWithBaseURL(baseUrl, html, "text/html", null, baseUrl);
请谨慎选择参数值。请考虑以下几点:
baseUrl:这是你的 HTML 内容加载为的 URL。这必须是一个 HTTP(S) URL。data:这是你想要显示的 HTML 内容,作为字符串。mimeType:这通常必须设置为text/html。encoding:当baseUrl是 HTTP(S) URL 时,此参数未使用,因此可以设置为null。historyUrl:这设置为与baseUrl相同的值。
强烈建议将 HTTP(S) URL 用作 baseUrl,因为这有助于确保你的应用符合同源政策。
如果你找不到适合你的内容的 baseUrl 并更喜欢使用 loadData(),你必须对内容进行编码,使用百分比编码或Base64 编码。强烈建议选择 Base64 编码并使用 Android API 以编程方式进行编码,如以下代码示例所示:
Kotlin
val encodedHtml: String = Base64.encodeToString(html.toByteArray(), Base64.NO_PADDING) webView.loadData(encodedHtml, mimeType, "base64")
Java
String encodedHtml = Base64.encodeToString(html.getBytes(), Base64.NO_PADDING); mWebView.loadData(encodedHtml, mimeType, "base64");
应避免的事项
还有其他几种加载应用内内容的方式,但我们强烈建议避免使用它们:
file://URL 和data:URL 被认为是不透明来源,这意味着它们无法利用强大的 Web API,例如fetch()或XMLHttpRequest。loadData()内部使用data:URL,因此我们鼓励使用WebViewAssetLoader或loadDataWithBaseURL()代替。- 虽然
WebSettings.setAllowFileAccessFromFileURLs()和WebSettings.setAllowUniversalAccessFromFileURLs()可以解决file://URL 的问题,但我们不建议将这些设置为true,因为这样做会使你的应用容易受到基于文件的攻击。为了获得最强的安全性,我们建议在所有 API 级别上明确将这些设置为false。 - 出于同样的原因,我们不建议使用
file://android_assets/和file://android_res/URL。AssetsHandler和ResourcesHandler类旨在作为直接替换。 - 避免使用
MIXED_CONTENT_ALWAYS_ALLOW。此设置通常不是必需的,并且会削弱你的应用安全性。我们建议通过与你网站资源相同的方案(HTTP 或 HTTPS)加载应用内内容,并酌情使用MIXED_CONTENT_COMPATIBILITY_MODE或MIXED_CONTENT_NEVER_ALLOW。
