一旦您在运行 Android 15 或更高版本的设备上将 SDK 靶向 35 或更高版本,您的应用就会以边缘到边缘的方式显示。窗口通过在系统栏后面绘制来跨越显示器的整个宽度和高度。系统栏包括状态栏、标题栏和导航栏。
许多应用都有一个顶部应用栏。顶部应用栏应延伸到屏幕顶部边缘并在状态栏后面显示。可选地,当内容滚动时,顶部应用栏可以缩小到状态栏的高度。
许多应用还具有底部应用栏或底部导航栏。这些栏也应延伸到屏幕底部边缘并在导航栏后面显示。否则,应用应在导航栏后面显示滚动内容。
在您的应用中实现边缘到边缘布局时,请记住以下几点
- 启用边缘到边缘显示
- 处理任何视觉重叠。
- 考虑在系统栏后面显示遮罩。
启用边缘到边缘显示
如果您的应用以 SDK 35 或更高版本为目标,则会自动为 Android 15 或更高版本的设备启用边缘到边缘。
要在以前的 Android 版本上启用边缘到边缘,请执行以下操作
在应用或模块的
build.gradle文件中添加对androidx.activity库的依赖项Kotlin
dependencies { val activity_version =
activity_version// Java language implementation implementation("androidx.activity:activity:$activity_version") // Kotlin implementation("androidx.activity:activity-ktx:$activity_version") }Groovy
dependencies { def activity_version =
activity_version// Java language implementation implementation 'androidx.activity:activity:$activity_version' // Kotlin implementation 'androidx.activity:activity-ktx:$activity_version' }将
enableEdgeToEdge扩展函数导入到您的应用中
通过在 Activity 的 onCreate 中调用 enableEdgeToEdge 来手动启用边缘到边缘。它应该在 setContentView 之前调用。
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { enableEdgeToEdge() super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) ... }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { EdgeToEdge.enable(this); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); ... }
默认情况下,enableEdgeToEdge() 使系统栏透明,但在三键导航模式下,状态栏会获得半透明遮罩。系统图标和遮罩的颜色会根据系统的浅色或深色主题进行调整。
enableEdgeToEdge() 函数会自动声明应用应以边缘到边缘的方式进行布局,并调整系统栏的颜色。
要启用您的应用中的边缘到边缘显示,而不使用 enableEdgeToEdge() 函数,请参阅 手动设置边缘到边缘显示。
使用内边距处理重叠
您应用中的一些视图可能会在系统栏后面绘制,如图 3 所示。
您可以通过对内边距做出反应来解决重叠问题,内边距指定屏幕的哪些部分与系统 UI(例如导航栏或状态栏)相交。相交可能意味着显示在内容之上,但也可能通知您的应用有关系统手势的信息。
适用于以边缘到边缘方式显示您的应用的内边距类型包括:
系统栏内边距:最适合可点击且必须不会被系统栏视觉遮挡的视图。
显示切口内边距:对于由于设备形状而可能存在屏幕切口的情况。
系统手势内边距:对于系统使用的优先于您的应用的手势导航区域。
系统栏内边距
系统栏内边距是最常用的内边距类型。它们表示系统 UI 在 Z 轴上显示在您的应用之上的区域。它们最适合移动或填充应用中可点击且不应被系统栏视觉遮挡的视图。
例如,图 3 中的浮动操作按钮(FAB) 部分被导航栏遮挡

为了避免在手势模式或按钮模式下出现这种视觉重叠,您可以使用 getInsets(int) 和 WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars() 来增加视图的边距。
以下代码示例显示如何实现系统栏内边距
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(fab) { v, windowInsets -> val insets = windowInsets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()) // Apply the insets as a margin to the view. This solution sets // only the bottom, left, and right dimensions, but you can apply whichever // insets are appropriate to your layout. You can also update the view padding // if that's more appropriate. v.updateLayoutParams<MarginLayoutParams> { leftMargin = insets.left, bottomMargin = insets.bottom, rightMargin = insets.right, } // Return CONSUMED if you don't want want the window insets to keep passing // down to descendant views. WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED }
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(fab, (v, windowInsets) -> { Insets insets = windowInsets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()); // Apply the insets as a margin to the view. This solution sets only the // bottom, left, and right dimensions, but you can apply whichever insets are // appropriate to your layout. You can also update the view padding if that's // more appropriate. MarginLayoutParams mlp = (MarginLayoutParams) v.getLayoutParams(); mlp.leftMargin = insets.left; mlp.bottomMargin = insets.bottom; mlp.rightMargin = insets.right; v.setLayoutParams(mlp); // Return CONSUMED if you don't want want the window insets to keep passing // down to descendant views. return WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED; });
如果您将此解决方案应用于图 3 中显示的示例,则在按钮模式下不会出现视觉重叠,如图 4 所示

手势导航模式也是如此,如图 5 所示

显示切口内边距
某些设备具有显示切口。通常,切口位于屏幕顶部并包含在状态栏中。当设备屏幕处于横向模式时,切口可能位于垂直边缘。根据您的应用在屏幕上显示的内容,您应实现填充以避免显示切口,因为默认情况下,应用将在显示切口中绘制。
例如,许多应用屏幕显示项目列表。不要用显示切口或系统栏遮挡列表项。
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(binding.recyclerView) { v, insets -> val bars = insets.getInsets( WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars() or WindowInsetsCompat.Type.displayCutout() ) v.updatePadding( left = bars.left, top = bars.top, right = bars.right, bottom = bars.bottom, ) WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED }
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(mBinding.recyclerView, (v, insets) -> { Insets bars = insets.getInsets( WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars() | WindowInsetsCompat.Type.displayCutout() ); v.setPadding(bars.left, bars.top, bars.right, bars.bottom); return WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED; });
通过获取系统栏和显示切口类型的逻辑或值来确定 WindowInsetsCompat 的值。
将 clipToPadding 设置为 RecyclerView,以便填充与列表项一起滚动。这允许项目在用户滚动时位于系统栏的后面,如下例所示。
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recycler_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:clipToPadding="false"
app:layoutManager="androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager" />
系统手势内边距
系统手势内边距表示窗口中系统手势优先于您的应用的区域。这些区域在图 6 中以橙色显示
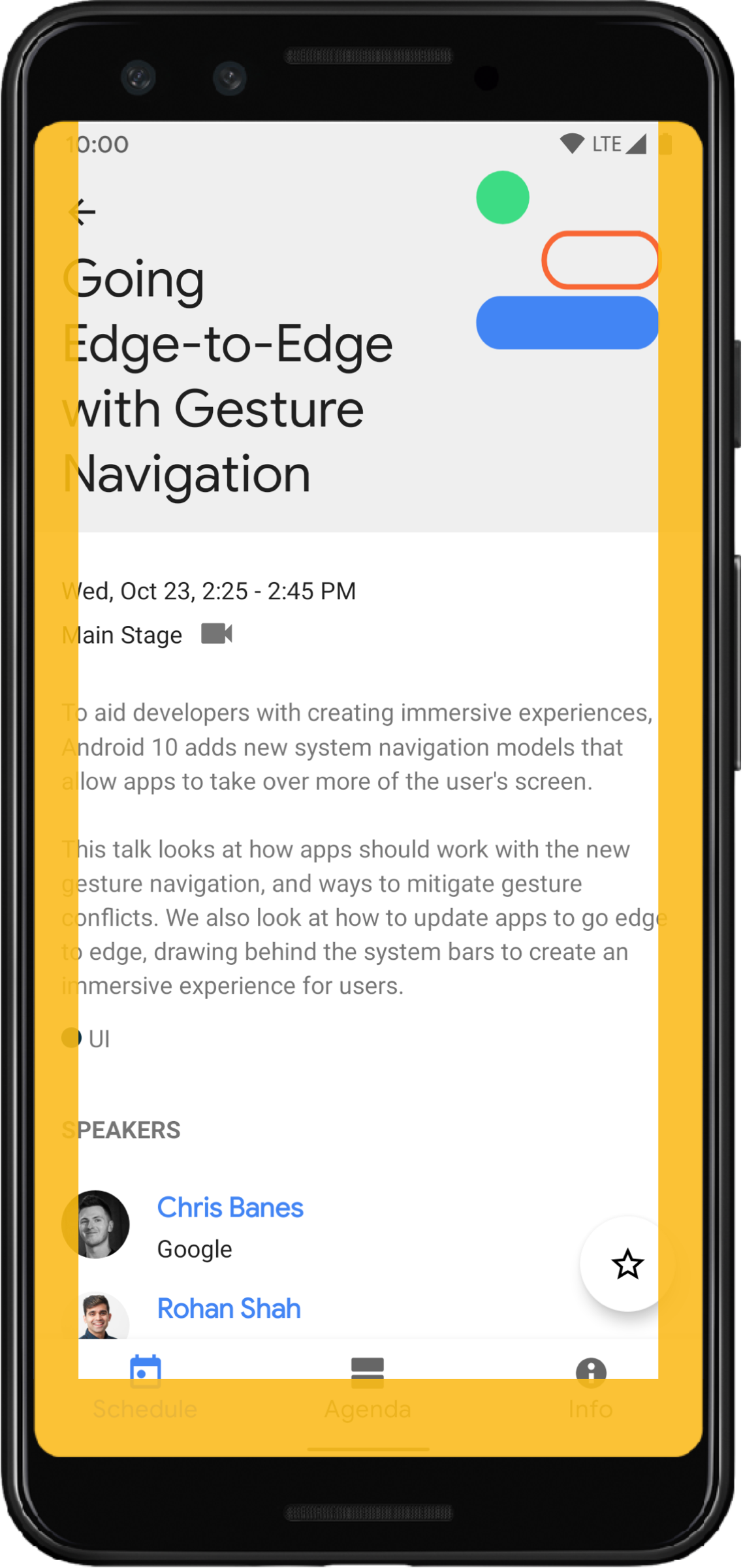
与系统栏内边距一样,您可以使用 getInsets(int) 和 WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemGestures() 来避免与系统手势内边距重叠。
使用这些内边距将可滑动视图从边缘移开或填充。常见的用例包括底部工作表、游戏中滑动以及使用 ViewPager2 实现的轮播。
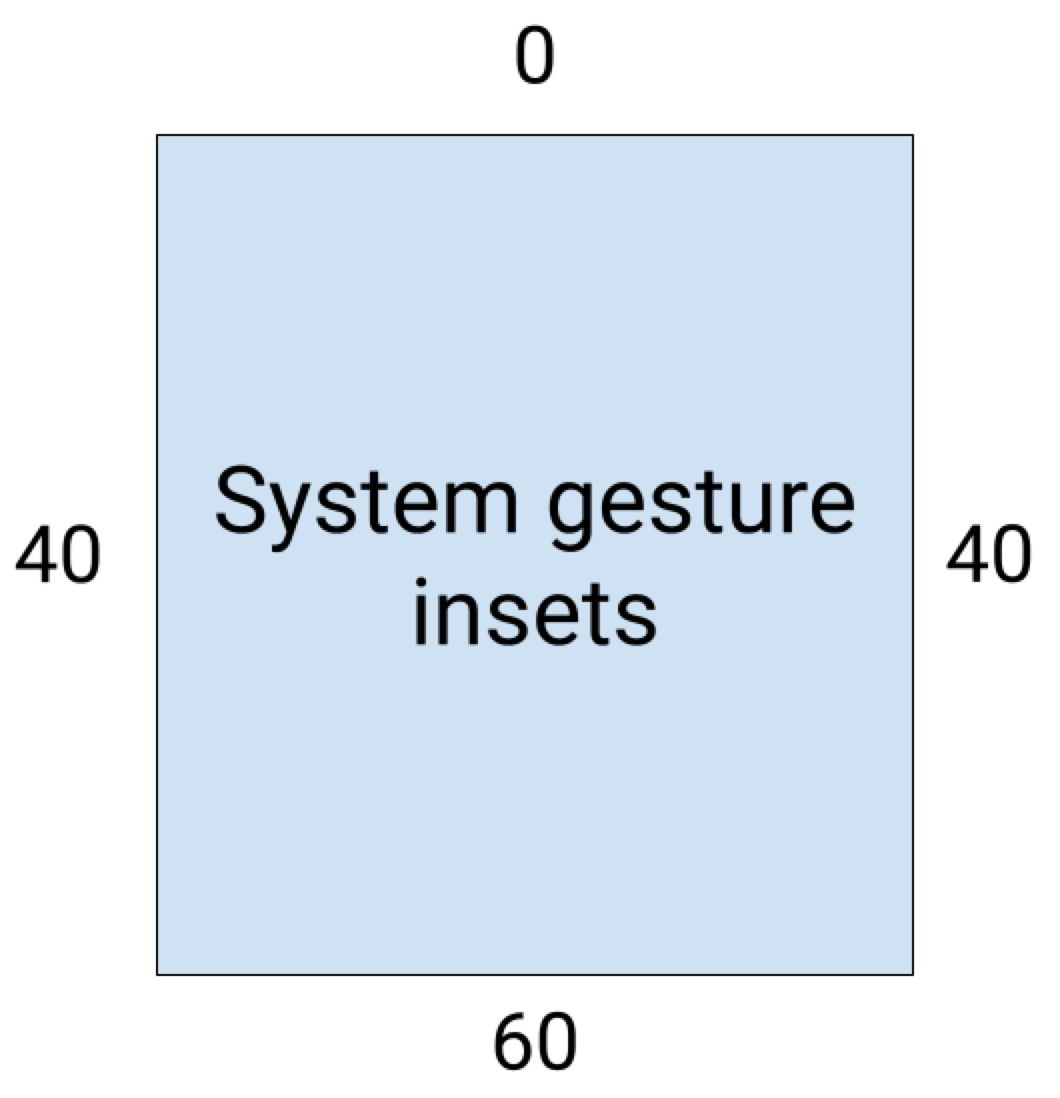
在 Android 10 或更高版本上,系统手势内边距包含主屏幕手势的底部内边距,以及后退手势的左侧和右侧内边距
以下代码示例显示如何实现系统手势内边距
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { view, windowInsets -> val insets = windowInsets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemGestures()) // Apply the insets as padding to the view. Here, set all the dimensions // as appropriate to your layout. You can also update the view's margin if // more appropriate. view.updatePadding(insets.left, insets.top, insets.right, insets.bottom) // Return CONSUMED if you don't want the window insets to keep passing down // to descendant views. WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED }
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view, (v, windowInsets) -> { Insets insets = windowInsets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemGestures()); // Apply the insets as padding to the view. Here, set all the dimensions // as appropriate to your layout. You can also update the view's margin if // more appropriate. view.setPadding(insets.left, insets.top, insets.right, insets.bottom); // Return CONSUMED if you don't want the window insets to keep passing down // to descendant views. return WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED; });
Material 组件
许多基于视图的 Android Material 组件 (com.google.android.material){:.external} 会自动处理内边距,包括 BottomAppBar、BottomNavigationView、NavigationRailView 和 NavigationView
但是,AppBarLayout 不会自动处理内边距。添加 android:fitsSystemWindows="true" 以处理顶部内边距。
阅读如何在 Compose 中使用 Material 组件 处理内边距。
沉浸式模式
某些内容最好在全屏模式下体验,这可以为用户提供更身临其境的体验。您可以使用 WindowInsetsController 和 WindowInsetsControllerCompat 库来隐藏系统栏以实现沉浸式模式
Kotlin
val windowInsetsController = WindowCompat.getInsetsController(window, window.decorView) // Hide the system bars. windowInsetsController.hide(Type.systemBars()) // Show the system bars. windowInsetsController.show(Type.systemBars())
Java
Window window = getWindow(); WindowInsetsControllerCompat windowInsetsController = WindowCompat.getInsetsController(window, window.getDecorView()); if (windowInsetsController == null) { return; } // Hide the system bars. windowInsetsController.hide(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()); // Show the system bars. windowInsetsController.show(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars());
请参阅 隐藏系统栏以实现沉浸式模式,了解更多关于实现此功能的信息。
系统栏保护
一旦您的应用以 SDK 35 或更高版本为目标,边缘到边缘就会强制执行。系统状态栏和手势导航栏是透明的,但三键导航栏是半透明的。
要移除默认的半透明三键导航背景保护,请将Window.setNavigationBarContrastEnforced设置为false。
更多资源
请参阅以下参考资料,了解更多关于WindowInsets、手势导航以及内边距工作原理的信息

