当需要在你的应用中显示静态图像时,可以使用Drawable类及其子类来绘制形状和图像。Drawable是对可以绘制的内容的通用抽象。各种子类有助于处理特定的图像场景,并且可以扩展它们来定义具有独特行为的自定义可绘制对象。
除了使用类构造函数之外,还有两种方法可以定义和实例化Drawable
- 膨胀保存在项目中的图像资源(位图文件)。
- 膨胀定义可绘制属性的 XML 资源。
注意:你可能更倾向于使用矢量可绘制对象,它使用一组点、线和曲线以及相关的颜色信息来定义图像。这允许矢量可绘制对象在不同的尺寸下进行缩放而不会损失质量。有关更多信息,请参阅矢量可绘制对象概述。
从资源图像创建可绘制对象
可以通过引用项目资源中的图像文件向应用添加图形。支持的文件类型为 PNG(首选)、JPG(可接受)和 GIF(不推荐)。应用图标、徽标以及其他图形(例如游戏中使用的图形)非常适合此技术。
要使用图像资源,请将文件添加到项目的res/drawable/目录。添加到项目后,可以从代码或 XML 布局中引用图像资源。无论哪种方式,它都是使用资源 ID 来引用的,资源 ID 是不包含文件类型扩展名的文件名。例如,将my_image.png引用为my_image。
注意:放在res/drawable/目录中的图像资源可能会在构建过程中由aapt工具使用无损图像压缩自动优化。例如,不需要超过 256 种颜色的真彩色 PNG 可能会转换为具有调色板的 8 位 PNG。这将生成质量相同但内存占用更少的图像。因此,此目录中放置的图像二进制文件在构建时可能会发生变化。如果你计划将图像作为比特流读取以便将其转换为位图,请将图像放在res/raw/文件夹中,因为aapt工具不会修改这些图像。
以下代码片段演示了如何构建使用从可绘制资源创建的图像的ImageView并将其添加到布局中
Kotlin
private lateinit var constraintLayout: ConstraintLayout override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // Instantiate an ImageView and define its properties val i = ImageView(this).apply { setImageResource(R.drawable.my_image) contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.my_image_desc) // set the ImageView bounds to match the Drawable's dimensions adjustViewBounds = true layoutParams = ViewGroup.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) } // Create a ConstraintLayout in which to add the ImageView constraintLayout = ConstraintLayout(this).apply { // Add the ImageView to the layout. addView(i) } // Set the layout as the content view. setContentView(constraintLayout) }
Java
ConstraintLayout constraintLayout; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Create a ConstraintLayout in which to add the ImageView constraintLayout = new ConstraintLayout(this); // Instantiate an ImageView and define its properties ImageView i = new ImageView(this); i.setImageResource(R.drawable.my_image); i.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.my_image_desc)); // set the ImageView bounds to match the Drawable's dimensions i.setAdjustViewBounds(true); i.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams( ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT)); // Add the ImageView to the layout and set the layout as the content view. constraintLayout.addView(i); setContentView(constraintLayout); }
在其他情况下,你可能希望将图像资源作为Drawable对象处理,如下例所示
Kotlin
val myImage: Drawable = ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(context.resources, R.drawable.my_image, null)
Java
Resources res = context.getResources(); Drawable myImage = ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(res, R.drawable.my_image, null);
警告:项目中的每个唯一资源只能维护一个状态,无论为此实例化多少个不同的对象。例如,如果从同一个图像资源实例化两个Drawable对象并更改一个对象的属性(例如 alpha),则它也会影响另一个对象。在处理图像资源的多个实例时,不应直接转换Drawable对象,而应执行补间动画。
下面的 XML 代码片段显示了如何在 XML 布局中向ImageView添加可绘制资源
<ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/my_image" android:contentDescription="@string/my_image_desc" />
有关使用项目资源的更多信息,请参阅资源和资产。
注意:当使用图像资源作为可绘制对象的来源时,请确保图像的大小适合各种像素密度。如果图像不正确,则会将其缩放以适应,这可能会导致可绘制对象出现伪像。有关更多信息,请阅读支持不同的像素密度。
从 XML 资源创建可绘制对象
如果你想要创建Drawable对象,而该对象最初不依赖于代码或用户交互定义的变量,则在 XML 中定义Drawable是一个不错的选择。即使你期望Drawable在用户与应用交互期间更改其属性,也应该考虑在 XML 中定义该对象,因为可以在实例化对象后修改属性。
在 XML 中定义Drawable后,将文件保存在项目的res/drawable/目录中。以下示例显示了定义继承自Drawable的TransitionDrawable资源的 XML。
<!-- res/drawable/expand_collapse.xml --> <transition xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/image_expand"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/image_collapse"/> </transition>
然后,通过调用Resources#getDrawable()并传递 XML 文件的资源 ID 来检索和实例化该对象。任何支持inflate()方法的Drawable子类都可以在 XML 中定义并由应用实例化。
每个支持 XML 膨胀的可绘制类都使用特定的 XML 属性来帮助定义对象属性。以下代码实例化TransitionDrawable并将其设置为ImageView对象的內容
Kotlin
val transition= ResourcesCompat.getDrawable( context.resources, R.drawable.expand_collapse, null ) as TransitionDrawable val image: ImageView = findViewById(R.id.toggle_image) image.setImageDrawable(transition) // Description of the initial state that the drawable represents. image.contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.collapsed) // Then you can call the TransitionDrawable object's methods. transition.startTransition(1000) // After the transition is complete, change the image's content description // to reflect the new state.
Java
Resources res = context.getResources(); TransitionDrawable transition = (TransitionDrawable) ResourcesCompat.getDrawable(res, R.drawable.expand_collapse, null); ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.toggle_image); image.setImageDrawable(transition); // Description of the initial state that the drawable represents. image.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.collapsed)); // Then you can call the TransitionDrawable object's methods. transition.startTransition(1000); // After the transition is complete, change the image's content description // to reflect the new state.
有关支持的 XML 属性的更多信息,请参考上面列出的类。
形状可绘制对象
当想要动态绘制二维图形时,ShapeDrawable对象可能是一个不错的选择。可以在ShapeDrawable对象上以编程方式绘制基本形状,并应用应用所需的样式。
ShapeDrawable是Drawable的子类。因此,可以在任何需要Drawable的地方使用ShapeDrawable。例如,可以通过将其传递给视图的setBackgroundDrawable()方法来使用ShapeDrawable对象设置视图的背景。还可以将形状绘制为其自己的自定义视图,并将其添加到应用中的布局。
因为ShapeDrawable有其自己的draw()方法,所以可以创建一个View的子类,该子类在onDraw()事件期间绘制ShapeDrawable对象,如下面的代码示例所示
Kotlin
class CustomDrawableView(context: Context) : View(context) { private val drawable: ShapeDrawable = run { val x = 10 val y = 10 val width = 300 val height = 50 contentDescription = context.resources.getString(R.string.my_view_desc) ShapeDrawable(OvalShape()).apply { // If the color isn't set, the shape uses black as the default. paint.color = 0xff74AC23.toInt() // If the bounds aren't set, the shape can't be drawn. setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height) } } override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas) { drawable.draw(canvas) } }
Java
public class CustomDrawableView extends View { private ShapeDrawable drawable; public CustomDrawableView(Context context) { super(context); int x = 10; int y = 10; int width = 300; int height = 50; setContentDescription(context.getResources().getString( R.string.my_view_desc)); drawable = new ShapeDrawable(new OvalShape()); // If the color isn't set, the shape uses black as the default. drawable.getPaint().setColor(0xff74AC23); // If the bounds aren't set, the shape can't be drawn. drawable.setBounds(x, y, x + width, y + height); } protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { drawable.draw(canvas); } }
您可以像使用其他任何自定义视图一样使用上面代码示例中的CustomDrawableView类。例如,您可以通过编程方式将其添加到应用程序中的活动中,如下例所示。
Kotlin
private lateinit var customDrawableView: CustomDrawableView override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) customDrawableView = CustomDrawableView(this) setContentView(customDrawableView) }
Java
CustomDrawableView customDrawableView; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); customDrawableView = new CustomDrawableView(this); setContentView(customDrawableView); }
如果您想在XML布局中使用自定义视图,则CustomDrawableView类必须重写View(Context, AttributeSet)构造函数,该构造函数在从XML膨胀类时调用。以下示例演示如何在XML布局中声明CustomDrawableView。
<com.example.shapedrawable.CustomDrawableView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
ShapeDrawable类,与android.graphics.drawable包中的许多其他可绘制类型一样,允许您使用公共方法定义对象的各种属性。您可能想要调整的一些示例属性包括alpha透明度、颜色过滤器、抖动、不透明度和颜色。
您还可以使用XML资源定义原始可绘制形状。有关更多信息,请参阅形状可绘制对象(位于可绘制资源类型中)。
九宫格可绘制对象
NinePatchDrawable图形是可以作为视图背景使用的可拉伸位图图像。Android会自动调整图形大小以适应视图的内容。NinePatch图像的一个示例用法是标准Android按钮使用的背景——按钮必须拉伸以适应不同长度的字符串。NinePatch图形是包含额外1像素边框的标准PNG图像。它必须使用9.png扩展名保存在项目的res/drawable/目录中。
使用边框定义图像的可拉伸区域和静态区域。您可以通过在边框的左侧和顶部绘制一条(或多条)1像素宽的黑色线来指示可拉伸区域(其他边框像素应完全透明或白色)。您可以根据需要设置任意数量的可拉伸区域。可拉伸区域的相对大小保持不变,因此最大的区域始终保持最大。
您还可以通过在右侧和底部绘制线条来定义图像的可选可绘制区域(实际上是填充线)。如果View对象将其NinePatch图形设置为其背景,然后指定视图的文本,它会自行拉伸,以便所有文本仅占据由右侧和底部线条(如果包含)指定的区域。如果没有包含填充线,Android将使用左侧和顶线来定义此可绘制区域。
为了阐明线条之间的区别,左侧和顶线定义允许复制图像的哪些像素以拉伸图像。底部和右侧线条定义视图内容允许占据的图像内相对区域。
图1显示了用于定义按钮的NinePatch图形示例。
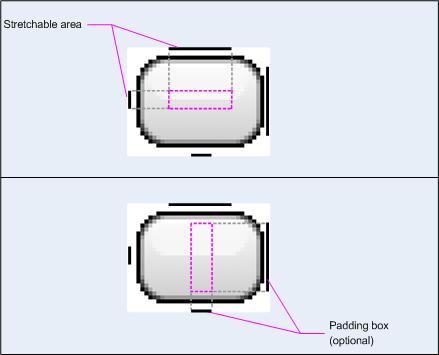
图1:定义按钮的NinePatch图形示例
此NinePatch图形使用左侧和顶线定义一个可拉伸区域,并使用底部和右侧线条定义可绘制区域。在上图中,虚线灰线标识为了拉伸图像而复制的图像区域。下图中的粉红色矩形标识视图内容允许所在的区域。如果内容不适合此区域,则图像将被拉伸以使其适合。
Draw 9-patch工具提供了一种非常方便的方法来创建您的NinePatch图像,它使用所见即所得的图形编辑器。如果由于像素复制导致您为可拉伸区域定义的区域有产生绘图瑕疵的风险,它甚至会发出警告。
以下示例布局XML演示了如何将NinePatch图形添加到几个按钮中。NinePatch图像保存到res/drawable/my_button_background.9.png。
<Button android:id="@+id/tiny" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="Tiny" android:textSize="8sp" android:background="@drawable/my_button_background"/> <Button android:id="@+id/big" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="Biiiiiiig text!" android:textSize="30sp" android:background="@drawable/my_button_background"/>
请注意,layout_width和layout_height属性设置为wrap_content,以使按钮整齐地围绕文本。
图2显示了从上面显示的XML和NinePatch图像渲染的两个按钮。请注意按钮的宽度和高度如何随文本变化,以及背景图像如何拉伸以适应它。

图2:使用XML资源和NinePatch图形渲染的按钮
自定义可绘制对象
当您想要创建一些自定义绘图时,您可以通过扩展Drawable类(或其任何子类)来实现。
要实现的最重要的方法是draw(Canvas),因为它提供了必须用于提供绘图指令的Canvas对象。
以下代码显示了Drawable的简单子类,它绘制一个圆圈。
Kotlin
class MyDrawable : Drawable() { private val redPaint: Paint = Paint().apply { setARGB(255, 255, 0, 0) } override fun draw(canvas: Canvas) { // Get the drawable's bounds val width: Int = bounds.width() val height: Int = bounds.height() val radius: Float = Math.min(width, height).toFloat() / 2f // Draw a red circle in the center canvas.drawCircle((width / 2).toFloat(), (height / 2).toFloat(), radius, redPaint) } override fun setAlpha(alpha: Int) { // This method is required } override fun setColorFilter(colorFilter: ColorFilter?) { // This method is required } override fun getOpacity(): Int = // Must be PixelFormat.UNKNOWN, TRANSLUCENT, TRANSPARENT, or OPAQUE PixelFormat.OPAQUE }
Java
public class MyDrawable extends Drawable { private final Paint redPaint; public MyDrawable() { // Set up color and text size redPaint = new Paint(); redPaint.setARGB(255, 255, 0, 0); } @Override public void draw(Canvas canvas) { // Get the drawable's bounds int width = getBounds().width(); int height = getBounds().height(); float radius = Math.min(width, height) / 2; // Draw a red circle in the center canvas.drawCircle(width/2, height/2, radius, redPaint); } @Override public void setAlpha(int alpha) { // This method is required } @Override public void setColorFilter(ColorFilter colorFilter) { // This method is required } @Override public int getOpacity() { // Must be PixelFormat.UNKNOWN, TRANSLUCENT, TRANSPARENT, or OPAQUE return PixelFormat.OPAQUE; } }
然后,您可以将可绘制对象添加到任何您想要的地方,例如添加到ImageView,如下所示。
Kotlin
val myDrawing = MyDrawable() val image: ImageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView) image.setImageDrawable(myDrawing) image.contentDescription = resources.getString(R.string.my_image_desc)
Java
MyDrawable mydrawing = new MyDrawable(); ImageView image = findViewById(R.id.imageView); image.setImageDrawable(mydrawing); image.setContentDescription(getResources().getString(R.string.my_image_desc));
在Android 7.0(API级别24)及更高版本中,您还可以通过以下方式使用XML定义自定义可绘制对象的实例。
- 使用完全限定的类名作为XML元素名称。对于这种方法,自定义可绘制类必须是公共顶级类。
<com.myapp.MyDrawable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:color="#ffff0000" />
- 使用
drawable作为XML标记名称,并从class属性指定完全限定的类名。此方法可用于公共顶级类和公共静态内部类。<drawable xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" class="com.myapp.MyTopLevelClass$MyDrawable" android:color="#ffff0000" />
为可绘制对象添加色调
在Android 5.0(API级别21)及更高版本中,您可以为定义为alpha蒙版的位图和九宫格着色。您可以使用颜色资源或解析为颜色资源的主题属性(例如,?android:attr/colorPrimary)对其进行着色。通常,您只需创建一次这些资源,并自动为其着色以匹配您的主题。
您可以使用setTint()方法将色调应用于BitmapDrawable、NinePatchDrawable或VectorDrawable对象。您还可以使用android:tint和android:tintMode属性在布局中设置色调颜色和模式。
从图像中提取突出颜色
Android支持库包括Palette类,它允许您从图像中提取突出颜色。您可以将可绘制对象加载为Bitmap并将其传递给Palette以访问其颜色。有关更多信息,请阅读使用Palette API选择颜色。

