共享元素过渡是一种在具有内容一致的可组合项之间进行无缝过渡的方式。它们通常用于导航,允许您在用户在屏幕之间导航时视觉上连接不同的屏幕。
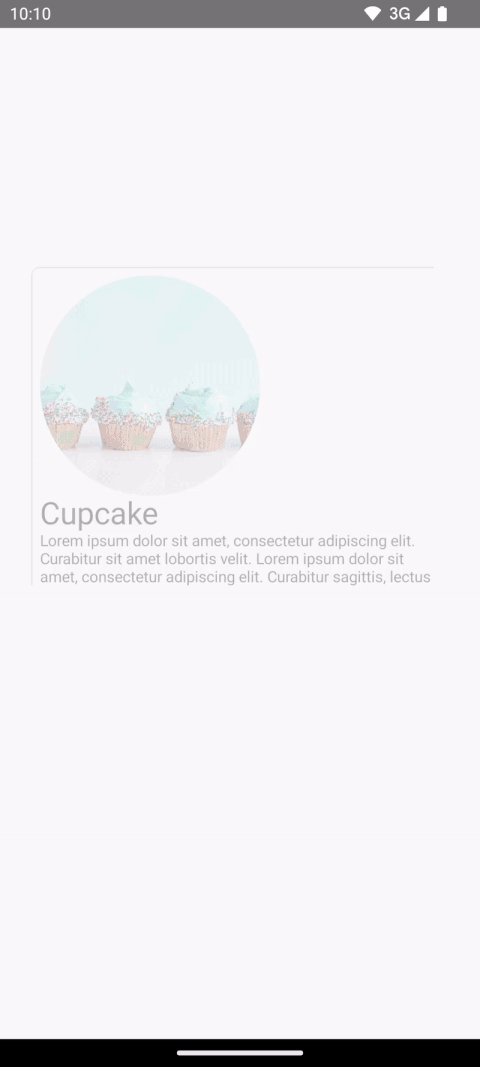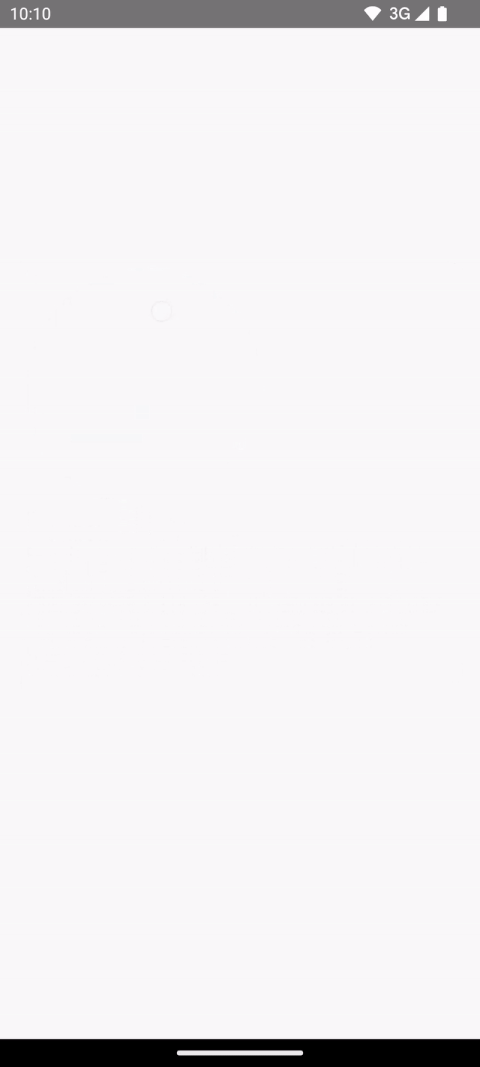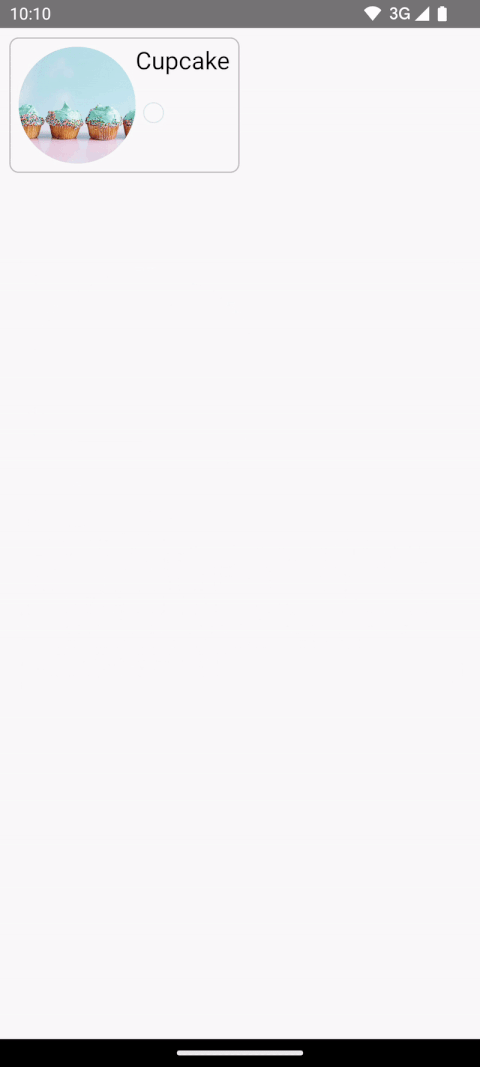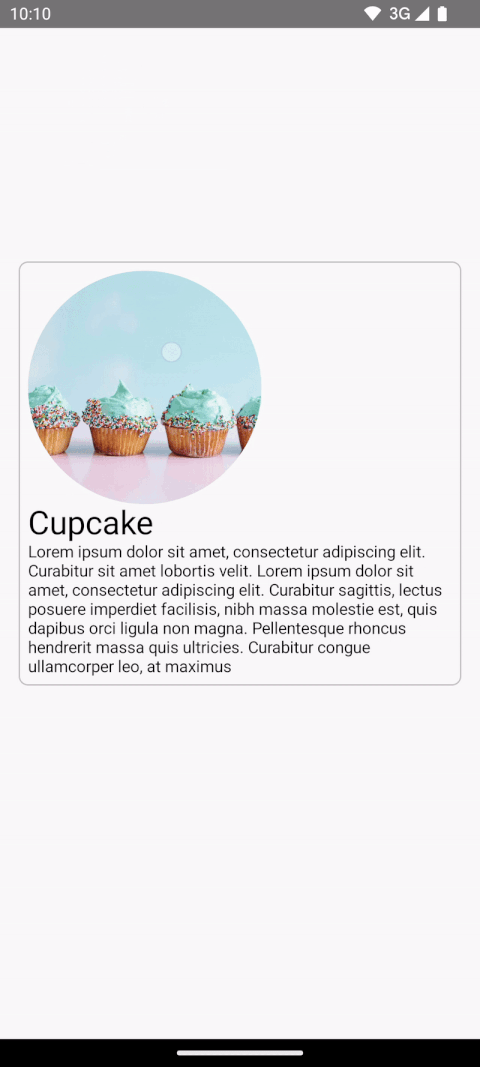
例如,在下面的视频中,您可以看到零食的图像和标题从列表页共享到详情页。
在 Compose 中,有一些高级 API 可以帮助您创建共享元素
SharedTransitionLayout:实现共享元素过渡所需的外部布局。它提供了一个SharedTransitionScope。可组合项需要位于SharedTransitionScope中才能使用共享元素修饰符。Modifier.sharedElement():向SharedTransitionScope标记应与另一个可组合项匹配的可组合项的修饰符。Modifier.sharedBounds():向SharedTransitionScope标记此可组合项的边界应作为过渡发生位置的容器边界的修饰符。与sharedElement()相比,sharedBounds()专为视觉上不同的内容而设计。
在 Compose 中创建共享元素时,一个重要的概念是它们如何与叠加层和剪裁配合使用。请查看剪裁和叠加层部分,以了解有关此重要主题的更多信息。
基本用法
本节将构建以下过渡,从较小的“列表”项过渡到较大的详细项

使用Modifier.sharedElement() 的最佳方法是结合使用AnimatedContent、AnimatedVisibility或NavHost,因为这会自动为您管理可组合项之间的过渡。
在添加共享元素之前,起点是一个现有的基本AnimatedContent,它具有MainContent和DetailsContent可组合项
AnimatedContent。为了使共享元素在两个布局之间进行动画处理,请使用
SharedTransitionLayout包围AnimatedContent可组合项。SharedTransitionLayout和AnimatedContent的范围传递给MainContent和DetailsContentvar showDetails by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } SharedTransitionLayout { AnimatedContent( showDetails, label = "basic_transition" ) { targetState -> if (!targetState) { MainContent( onShowDetails = { showDetails = true }, animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent, sharedTransitionScope = this@SharedTransitionLayout ) } else { DetailsContent( onBack = { showDetails = false }, animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent, sharedTransitionScope = this@SharedTransitionLayout ) } } }
将
Modifier.sharedElement()添加到两个匹配的可组合项上的可组合修饰符链中。创建一个SharedContentState对象并使用rememberSharedContentState()记住它。SharedContentState对象存储确定共享元素的唯一键。提供一个唯一键来标识内容,并为要记住的项目使用rememberSharedContentState()。AnimatedContentScope传递到修饰符中,用于协调动画。@Composable private fun MainContent( onShowDetails: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { Row( // ... ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.cupcake), contentDescription = "Cupcake", modifier = Modifier .sharedElement( rememberSharedContentState(key = "image"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope ) .size(100.dp) .clip(CircleShape), contentScale = ContentScale.Crop ) // ... } } } @Composable private fun DetailsContent( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, onBack: () -> Unit, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { Column( // ... ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.cupcake), contentDescription = "Cupcake", modifier = Modifier .sharedElement( rememberSharedContentState(key = "image"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope ) .size(200.dp) .clip(CircleShape), contentScale = ContentScale.Crop ) // ... } } }
要获取有关是否已发生共享元素匹配的信息,请将rememberSharedContentState()提取到变量中,并查询isMatchFound。
这将产生以下自动动画

您可能会注意到,整个容器的背景颜色和大小仍然使用默认的AnimatedContent设置。
共享边界与共享元素
Modifier.sharedBounds()类似于Modifier.sharedElement()。但是,修饰符在以下方面有所不同
sharedBounds()用于视觉上不同但应在状态之间共享相同区域的内容,而sharedElement()期望内容相同。- 使用
sharedBounds(),在两种状态之间的过渡过程中,进入和退出屏幕的内容是可见的,而使用sharedElement(),只有目标内容在转换边界中呈现。Modifier.sharedBounds()具有enter和exit参数,用于指定内容应如何过渡,类似于AnimatedContent的工作方式。 sharedBounds()最常见的用例是容器转换模式,而对于sharedElement(),示例用例是英雄过渡。- 使用
Text可组合项时,建议使用sharedBounds()来支持字体更改,例如在斜体和粗体之间或颜色更改之间进行过渡。
从前面的示例中,将Modifier.sharedBounds()添加到两种不同情况下的Row和Column将允许我们共享两者的边界并执行过渡动画,从而允许它们相互增长
@Composable private fun MainContent( onShowDetails: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Row( modifier = Modifier .padding(8.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState(key = "bounds"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope, enter = fadeIn(), exit = fadeOut(), resizeMode = SharedTransitionScope.ResizeMode.ScaleToBounds() ) // ... ) { // ... } } } @Composable private fun DetailsContent( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, onBack: () -> Unit, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Column( modifier = Modifier .padding(top = 200.dp, start = 16.dp, end = 16.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState(key = "bounds"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope, enter = fadeIn(), exit = fadeOut(), resizeMode = SharedTransitionScope.ResizeMode.ScaleToBounds() ) // ... ) { // ... } } }
了解范围
要使用Modifier.sharedElement(),可组合项需要位于SharedTransitionScope中。SharedTransitionLayout可组合项提供SharedTransitionScope。确保将其放在包含要共享的元素的 UI 层次结构的相同顶层位置。
通常,可组合项也应放置在AnimatedVisibilityScope内。这通常通过使用AnimatedContent在可组合项之间切换或直接使用AnimatedVisibility,或者通过NavHost可组合函数来提供,除非您手动管理可见性。为了使用多个范围,请将所需的范围保存在CompositionLocal中,使用Kotlin 中的上下文接收器,或将范围作为参数传递给您的函数。
在您需要跟踪多个范围或具有深度嵌套层次结构的情况下,使用CompositionLocals。CompositionLocal允许您选择要保存和使用的确切范围。另一方面,当您使用上下文接收器时,层次结构中的其他布局可能会意外地覆盖提供的范围。例如,如果您有多个嵌套的AnimatedContent,则可能会覆盖范围。
val LocalNavAnimatedVisibilityScope = compositionLocalOf<AnimatedVisibilityScope?> { null } val LocalSharedTransitionScope = compositionLocalOf<SharedTransitionScope?> { null } @Composable private fun SharedElementScope_CompositionLocal() { // An example of how to use composition locals to pass around the shared transition scope, far down your UI tree. // ... SharedTransitionLayout { CompositionLocalProvider( LocalSharedTransitionScope provides this ) { // This could also be your top-level NavHost as this provides an AnimatedContentScope AnimatedContent(state, label = "Top level AnimatedContent") { targetState -> CompositionLocalProvider(LocalNavAnimatedVisibilityScope provides this) { // Now we can access the scopes in any nested composables as follows: val sharedTransitionScope = LocalSharedTransitionScope.current ?: throw IllegalStateException("No SharedElementScope found") val animatedVisibilityScope = LocalNavAnimatedVisibilityScope.current ?: throw IllegalStateException("No AnimatedVisibility found") } // ... } } } }
或者,如果您的层次结构没有深度嵌套,您可以将范围作为参数向下传递
@Composable fun MainContent( animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope ) { } @Composable fun Details( animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope ) { }
使用AnimatedVisibility的共享元素
之前的示例展示了如何将共享元素与AnimatedContent一起使用,但共享元素也适用于AnimatedVisibility。
例如,在此惰性网格示例中,每个元素都包装在AnimatedVisibility中。当单击该项目时,内容具有从 UI 中拉出到对话框式组件的视觉效果。
var selectedSnack by remember { mutableStateOf<Snack?>(null) } SharedTransitionLayout(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { LazyColumn( // ... ) { items(listSnacks) { snack -> AnimatedVisibility( visible = snack != selectedSnack, enter = fadeIn() + scaleIn(), exit = fadeOut() + scaleOut(), modifier = Modifier.animateItem() ) { Box( modifier = Modifier .sharedBounds( sharedContentState = rememberSharedContentState(key = "${snack.name}-bounds"), // Using the scope provided by AnimatedVisibility animatedVisibilityScope = this, clipInOverlayDuringTransition = OverlayClip(shapeForSharedElement) ) .background(Color.White, shapeForSharedElement) .clip(shapeForSharedElement) ) { SnackContents( snack = snack, modifier = Modifier.sharedElement( state = rememberSharedContentState(key = snack.name), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedVisibility ), onClick = { selectedSnack = snack } ) } } } } // Contains matching AnimatedContent with sharedBounds modifiers. SnackEditDetails( snack = selectedSnack, onConfirmClick = { selectedSnack = null } ) }
AnimatedVisibility的共享元素。修饰符顺序
对于Modifier.sharedElement()和Modifier.sharedBounds(),修饰符的顺序与 Compose 的其余部分一样重要。不正确放置影响大小的修饰符会导致共享元素匹配期间出现意外的视觉跳跃。
例如,如果您在两个共享元素上将填充修饰符放在不同的位置,则动画中会出现视觉差异。
var selectFirst by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val key = remember { Any() } SharedTransitionLayout( Modifier .fillMaxSize() .padding(10.dp) .clickable { selectFirst = !selectFirst } ) { AnimatedContent(targetState = selectFirst, label = "AnimatedContent") { targetState -> if (targetState) { Box( Modifier .padding(12.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState(key = key), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent ) .border(2.dp, Color.Red) ) { Text( "Hello", fontSize = 20.sp ) } } else { Box( Modifier .offset(180.dp, 180.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState( key = key, ), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent ) .border(2.dp, Color.Red) // This padding is placed after sharedBounds, but it doesn't match the // other shared elements modifier order, resulting in visual jumps .padding(12.dp) ) { Text( "Hello", fontSize = 36.sp ) } } } }
匹配的边界 |
不匹配的边界:请注意,共享元素动画看起来有点偏离,因为它需要调整到不正确的边界。 |
|---|---|
在共享元素修饰符之前使用的修饰符为共享元素修饰符提供约束,然后将其用于推导出初始和目标边界,以及随后的边界动画。
在共享元素修饰符之后使用的修饰符使用之前的约束来测量和计算子项的目标大小。共享元素修饰符创建一系列动画约束,以逐渐将子项从初始大小转换为目标大小。
例外情况是,如果您为动画使用resizeMode = ScaleToBounds(),或在可组合项上使用Modifier.skipToLookaheadSize()。在这种情况下,Compose 使用目标约束来布局子项,并使用比例因子来执行动画,而不是更改布局大小本身。
唯一键
处理复杂的共享元素时,最好创建一个非字符串键,因为字符串匹配容易出错。每个键必须唯一才能进行匹配。例如,在 Jetsnack 中,我们有以下共享元素
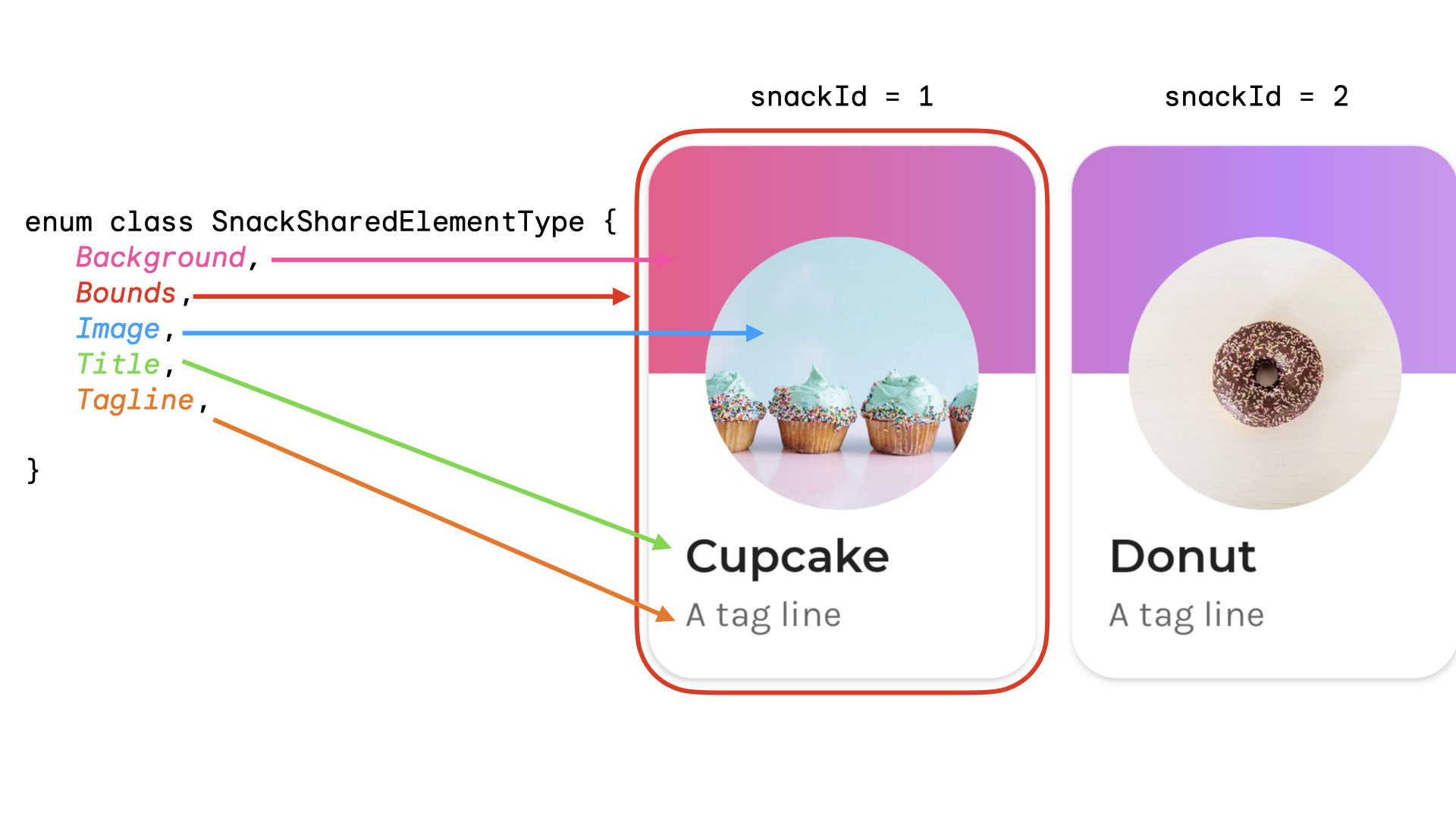
您可以创建一个枚举来表示共享元素类型。在这个例子中,整个零食卡片也可以从主屏幕上的多个不同位置出现,例如在“热门”和“推荐”部分。您可以创建一个包含snackId、origin(“热门”/“推荐”)和将要共享的共享元素type的键。
data class SnackSharedElementKey( val snackId: Long, val origin: String, val type: SnackSharedElementType ) enum class SnackSharedElementType { Bounds, Image, Title, Tagline, Background } @Composable fun SharedElementUniqueKey() { // ... Box( modifier = Modifier .sharedElement( rememberSharedContentState( key = SnackSharedElementKey( snackId = 1, origin = "latest", type = SnackSharedElementType.Image ) ), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedVisibility ) ) // ... }
建议使用数据类作为键,因为它们实现了hashCode()和isEquals()。
手动管理共享元素的可见性
如果您可能没有使用AnimatedVisibility或AnimatedContent,您可以自己管理共享元素的可见性。使用Modifier.sharedElementWithCallerManagedVisibility()并提供您自己的条件来确定何时显示或隐藏项目。
var selectFirst by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val key = remember { Any() } SharedTransitionLayout( Modifier .fillMaxSize() .padding(10.dp) .clickable { selectFirst = !selectFirst } ) { Box( Modifier .sharedElementWithCallerManagedVisibility( rememberSharedContentState(key = key), !selectFirst ) .background(Color.Red) .size(100.dp) ) { Text(if (!selectFirst) "false" else "true", color = Color.White) } Box( Modifier .offset(180.dp, 180.dp) .sharedElementWithCallerManagedVisibility( rememberSharedContentState( key = key, ), selectFirst ) .alpha(0.5f) .background(Color.Blue) .size(180.dp) ) { Text(if (selectFirst) "false" else "true", color = Color.White) } }
当前限制
这些 API 有一些限制。最值得注意的是
- 不支持 Views 和 Compose 之间的互操作性。这包括任何包装
AndroidView的可组合项,例如Dialog。 - 以下内容不支持自动动画
- 共享图像可组合项:
ContentScale默认情况下不进行动画处理。它会直接跳转到设置的最终ContentScale。
- 形状裁剪 - 不内置支持形状之间的自动动画 - 例如,在项目转换时将正方形动画化为圆形。
- 对于不支持的情况,请使用
Modifier.sharedBounds()代替sharedElement(),并在项目上添加Modifier.animateEnterExit()。
- 共享图像可组合项:
