Compose 具有许多内置的动画机制,选择哪一种可能会让人不知所措。以下是常见动画用例的列表。有关您可以使用的完整 API 选项集的更多详细信息,请阅读完整的 Compose 动画文档。
动画常见可组合属性
Compose 提供了方便的 API,使您可以解决许多常见的动画用例。本节演示如何为可组合对象的常见属性设置动画。
动画出现/消失

使用 AnimatedVisibility 来隐藏或显示可组合对象。AnimatedVisibility 内部的子元素可以使用 Modifier.animateEnterExit() 来进行其自身的进入或退出过渡。
var visible by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } // Animated visibility will eventually remove the item from the composition once the animation has finished. AnimatedVisibility(visible) { // your composable here // ... }
AnimatedVisibility 的进入和退出参数允许您配置可组合对象在出现和消失时的行为。阅读 完整文档 以了解更多信息。
为可组合对象的可见性设置动画的另一种方法是使用 animateFloatAsState 随时间推移来为 alpha 设置动画。
var visible by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val animatedAlpha by animateFloatAsState( targetValue = if (visible) 1.0f else 0f, label = "alpha" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(200.dp) .graphicsLayer { alpha = animatedAlpha } .clip(RoundedCornerShape(8.dp)) .background(colorGreen) .align(Alignment.TopCenter) ) { }
但是,更改 alpha 会带来一个缺点,即可组合对象 **仍然保留在组合中** 并继续占据其布局中的空间。这可能会导致屏幕阅读器和其他辅助功能机制仍然认为该项目在屏幕上。另一方面,AnimatedVisibility 最终会将项目从组合中移除。

动画背景颜色
val animatedColor by animateColorAsState( if (animateBackgroundColor) colorGreen else colorBlue, label = "color" ) Column( modifier = Modifier.drawBehind { drawRect(animatedColor) } ) { // your composable here }
此选项比使用 Modifier.background() 更高效。Modifier.background() 适用于一次性颜色设置,但当随时间推移为颜色设置动画时,这可能会导致比必要更多的重新组合。
要无限期地为背景颜色设置动画,请参阅 重复动画部分。
动画可组合对象的大小
Compose 允许您通过几种不同的方式为可组合对象的大小设置动画。使用 animateContentSize() 来为可组合对象大小更改之间的动画。
例如,如果您有一个包含可以从一行扩展到多行的文本的框,您可以使用 Modifier.animateContentSize() 来实现更平滑的过渡。
var expanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } Box( modifier = Modifier .background(colorBlue) .animateContentSize() .height(if (expanded) 400.dp else 200.dp) .fillMaxWidth() .clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { expanded = !expanded } ) { }
您还可以使用 AnimatedContent,并使用 SizeTransform 来描述大小更改应如何发生。
动画可组合对象的位置
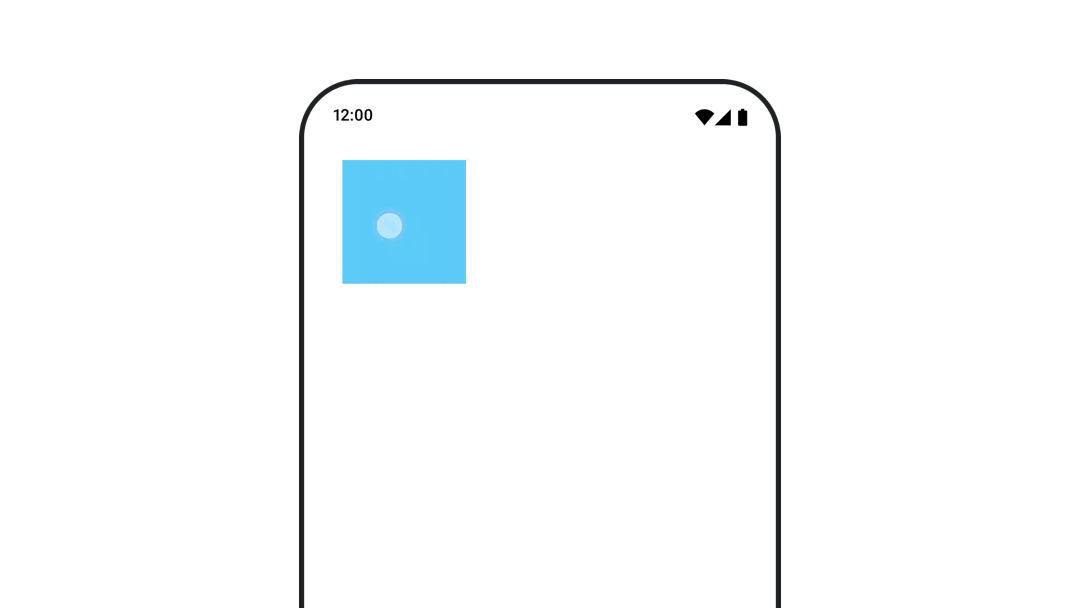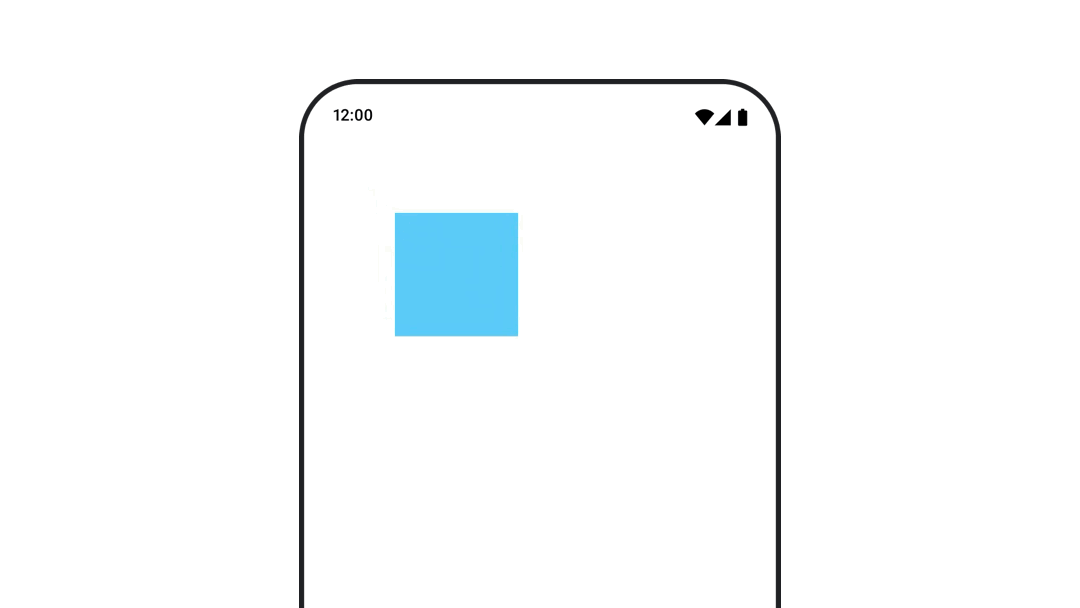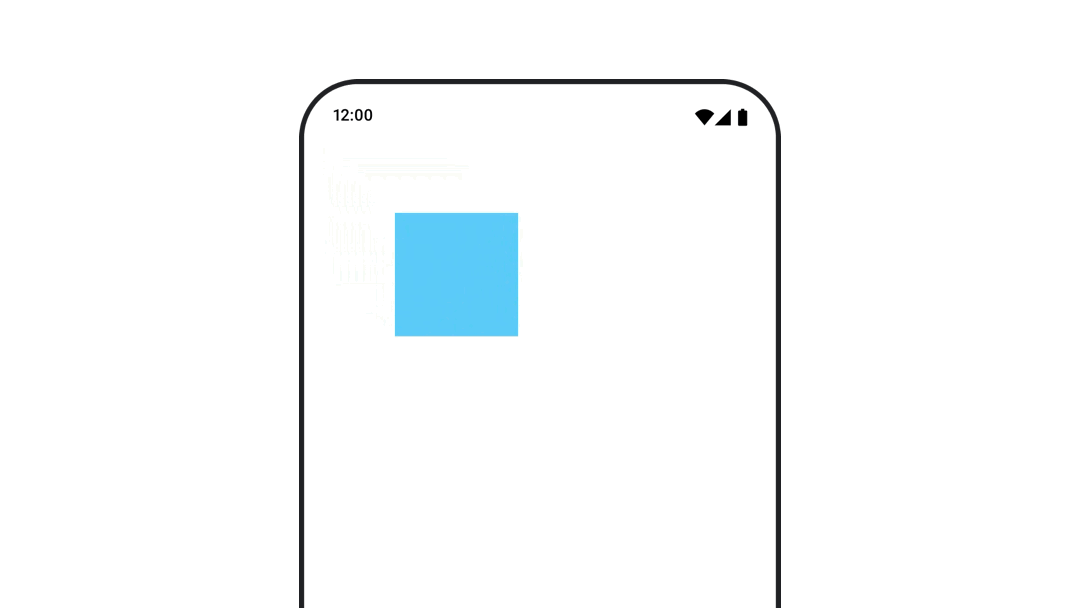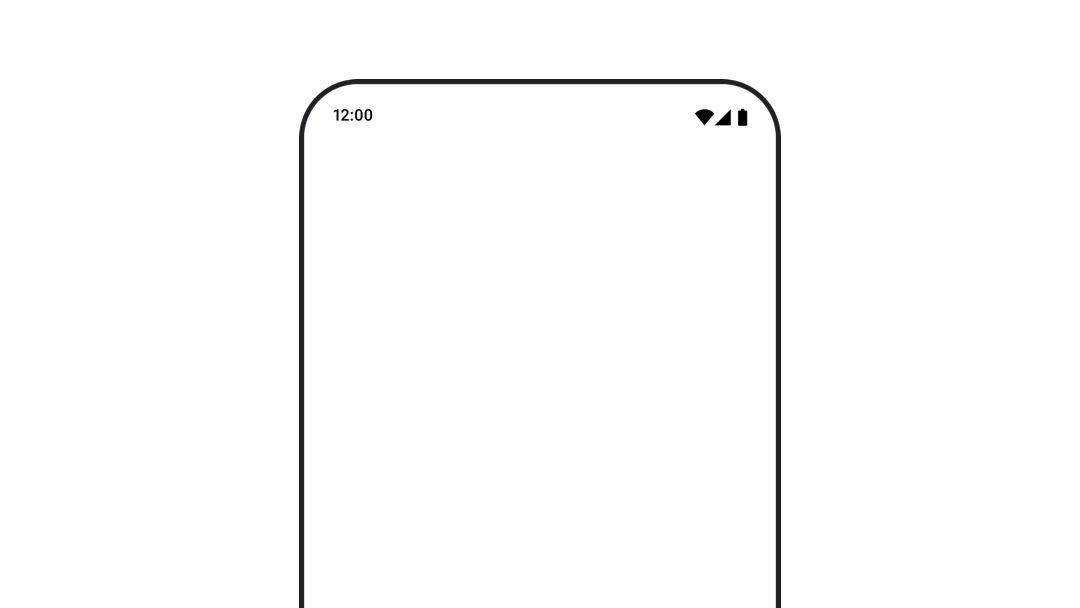
要为可组合对象的位置设置动画,请使用 Modifier.offset{ } 与 animateIntOffsetAsState() 组合使用。
var moved by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val pxToMove = with(LocalDensity.current) { 100.dp.toPx().roundToInt() } val offset by animateIntOffsetAsState( targetValue = if (moved) { IntOffset(pxToMove, pxToMove) } else { IntOffset.Zero }, label = "offset" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .offset { offset } .background(colorBlue) .size(100.dp) .clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { moved = !moved } )
如果您想确保在为位置或大小设置动画时,可组合对象不会相互覆盖,请使用 Modifier.layout{ }。此修饰符会将大小和位置更改传播到父级,然后影响其他子元素。
例如,如果您在一个 Column 中移动一个 Box,并且当 Box 移动时其他子元素也需要移动,请按如下所示包含偏移信息以及 Modifier.layout{ }
var toggled by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() } Column( modifier = Modifier .padding(16.dp) .fillMaxSize() .clickable(indication = null, interactionSource = interactionSource) { toggled = !toggled } ) { val offsetTarget = if (toggled) { IntOffset(150, 150) } else { IntOffset.Zero } val offset = animateIntOffsetAsState( targetValue = offsetTarget, label = "offset" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(100.dp) .background(colorBlue) ) Box( modifier = Modifier .layout { measurable, constraints -> val offsetValue = if (isLookingAhead) offsetTarget else offset.value val placeable = measurable.measure(constraints) layout(placeable.width + offsetValue.x, placeable.height + offsetValue.y) { placeable.placeRelative(offsetValue) } } .size(100.dp) .background(colorGreen) ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(100.dp) .background(colorBlue) ) }
Modifier.layout{ } 设置动画动画可组合对象的填充

要为可组合对象的填充设置动画,请使用 animateDpAsState 与 Modifier.padding() 组合使用。
var toggled by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val animatedPadding by animateDpAsState( if (toggled) { 0.dp } else { 20.dp }, label = "padding" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .aspectRatio(1f) .fillMaxSize() .padding(animatedPadding) .background(Color(0xff53D9A1)) .clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { toggled = !toggled } )
动画可组合对象的海拔高度
要为可组合对象的海拔高度设置动画,请使用 animateDpAsState 与 Modifier.graphicsLayer{ } 组合使用。对于一次性海拔高度更改,请使用 Modifier.shadow()。如果您正在为阴影设置动画,则使用 Modifier.graphicsLayer{ } 修饰符是更高效的选项。
val mutableInteractionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() } val pressed = mutableInteractionSource.collectIsPressedAsState() val elevation = animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (pressed.value) { 32.dp } else { 8.dp }, label = "elevation" ) Box( modifier = Modifier .size(100.dp) .align(Alignment.Center) .graphicsLayer { this.shadowElevation = elevation.value.toPx() } .clickable(interactionSource = mutableInteractionSource, indication = null) { } .background(colorGreen) ) { }
或者,使用 Card 可组合对象,并为每个状态设置不同的 elevation 属性值。
动画文本缩放、平移或旋转

在为文本的缩放、平移或旋转设置动画时,请将 TextStyle 上的 textMotion 参数设置为 TextMotion.Animated。这确保了文本动画之间更平滑的过渡。使用 Modifier.graphicsLayer{ } 来平移、旋转或缩放文本。
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite transition") val scale by infiniteTransition.animateFloat( initialValue = 1f, targetValue = 8f, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(tween(1000), RepeatMode.Reverse), label = "scale" ) Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { Text( text = "Hello", modifier = Modifier .graphicsLayer { scaleX = scale scaleY = scale transformOrigin = TransformOrigin.Center } .align(Alignment.Center), // Text composable does not take TextMotion as a parameter. // Provide it via style argument but make sure that we are copying from current theme style = LocalTextStyle.current.copy(textMotion = TextMotion.Animated) ) }
动画文本颜色
要为文本颜色设置动画,请使用 BasicText 可组合对象上的 color lambda。
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite transition") val animatedColor by infiniteTransition.animateColor( initialValue = Color(0xFF60DDAD), targetValue = Color(0xFF4285F4), animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(tween(1000), RepeatMode.Reverse), label = "color" ) BasicText( text = "Hello Compose", color = { animatedColor }, // ... )
在不同类型的內容之間切換
使用 AnimatedContent 为不同可组合对象之间的动画,如果您只想在可组合对象之间进行标准淡入淡出,请使用 Crossfade。
var state by remember { mutableStateOf(UiState.Loading) } AnimatedContent( state, transitionSpec = { fadeIn( animationSpec = tween(3000) ) togetherWith fadeOut(animationSpec = tween(3000)) }, modifier = Modifier.clickable( interactionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() }, indication = null ) { state = when (state) { UiState.Loading -> UiState.Loaded UiState.Loaded -> UiState.Error UiState.Error -> UiState.Loading } }, label = "Animated Content" ) { targetState -> when (targetState) { UiState.Loading -> { LoadingScreen() } UiState.Loaded -> { LoadedScreen() } UiState.Error -> { ErrorScreen() } } }
AnimatedContent 可以自定义以显示许多不同类型的进入和退出过渡。有关更多信息,请阅读有关 AnimatedContent 的文档,或阅读这篇有关 博客文章 AnimatedContent。
在导航到不同目标时设置动画
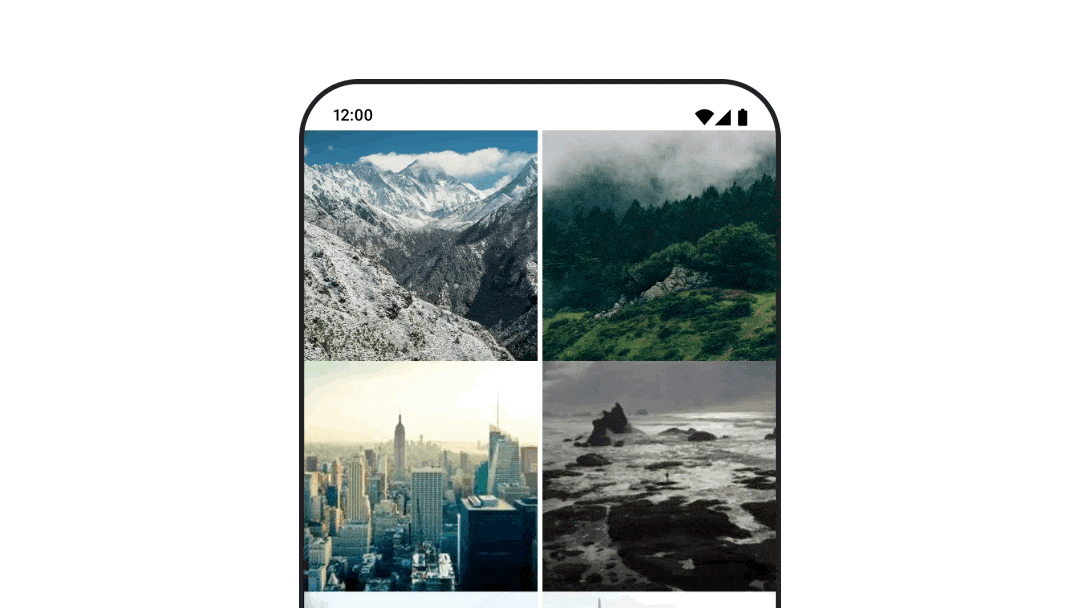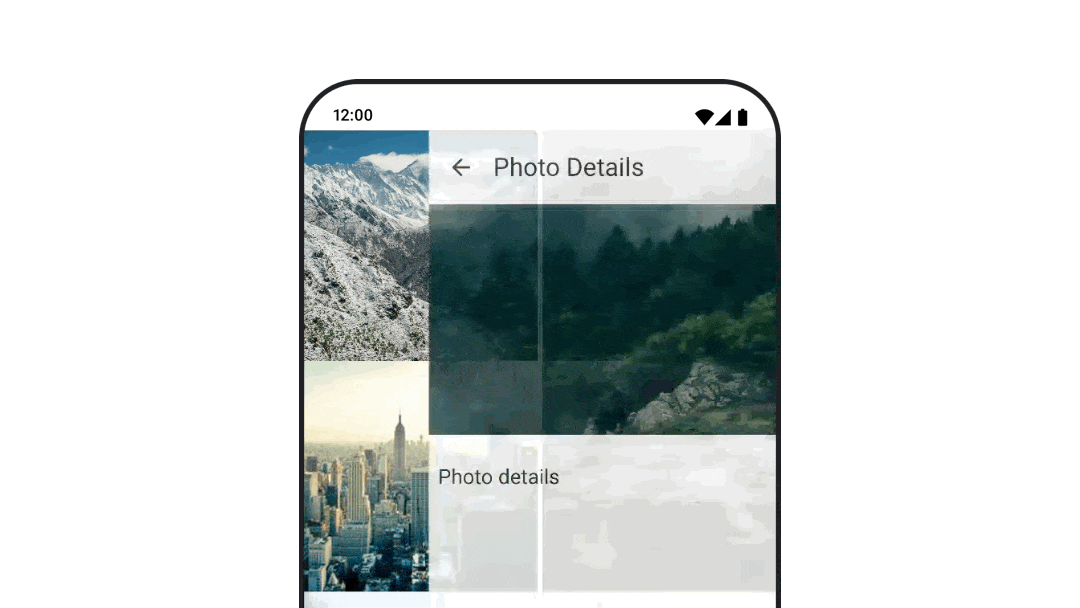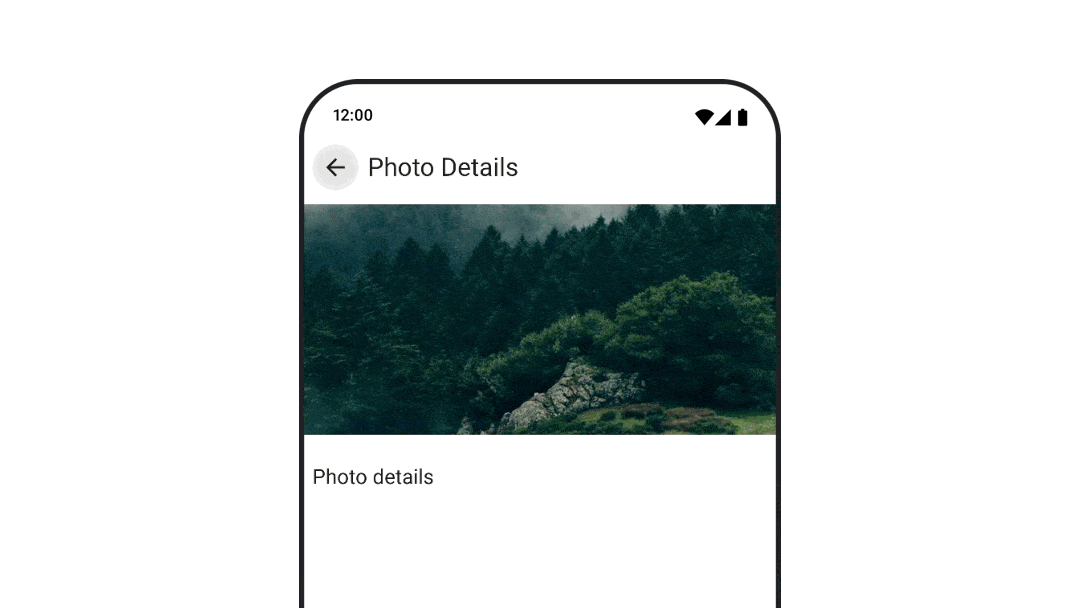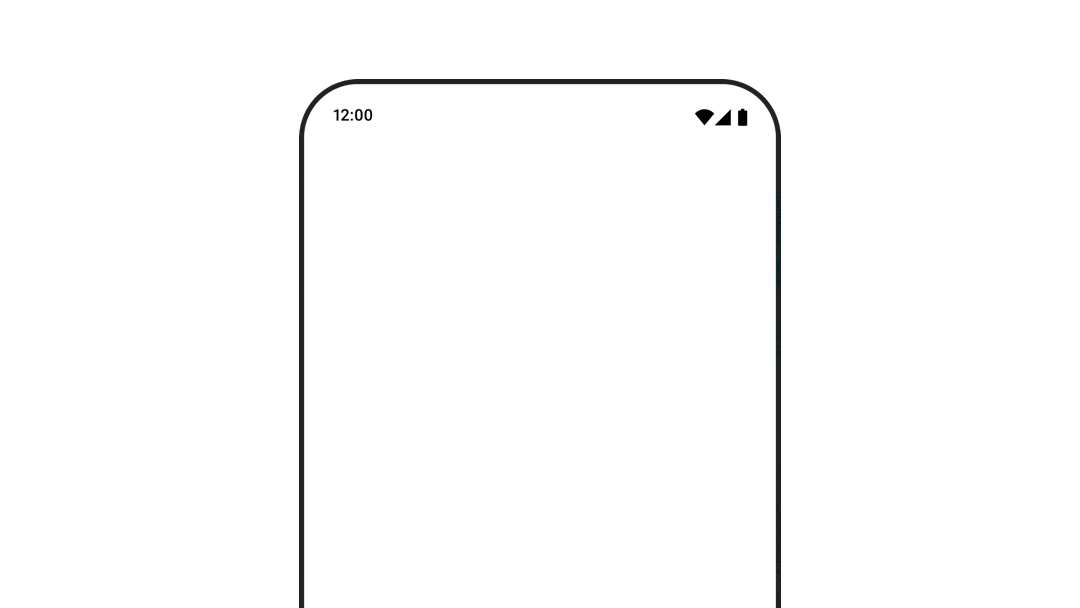
要使用 navigation-compose 工件为可组合对象之间的过渡设置动画,请在可组合对象上指定 enterTransition 和 exitTransition。您还可以设置在顶级 NavHost 中使用的默认动画。
val navController = rememberNavController() NavHost( navController = navController, startDestination = "landing", enterTransition = { EnterTransition.None }, exitTransition = { ExitTransition.None } ) { composable("landing") { ScreenLanding( // ... ) } composable( "detail/{photoUrl}", arguments = listOf(navArgument("photoUrl") { type = NavType.StringType }), enterTransition = { fadeIn( animationSpec = tween( 300, easing = LinearEasing ) ) + slideIntoContainer( animationSpec = tween(300, easing = EaseIn), towards = AnimatedContentTransitionScope.SlideDirection.Start ) }, exitTransition = { fadeOut( animationSpec = tween( 300, easing = LinearEasing ) ) + slideOutOfContainer( animationSpec = tween(300, easing = EaseOut), towards = AnimatedContentTransitionScope.SlideDirection.End ) } ) { backStackEntry -> ScreenDetails( // ... ) } }
有许多不同类型的进入和退出过渡会对传入和传出的内容应用不同的效果,请参阅 文档 以了解更多信息。
重复动画

使用 rememberInfiniteTransition 和 infiniteRepeatable animationSpec 来连续重复您的动画。更改 RepeatModes 以指定它应该如何来回移动。
使用 finiteRepeatable 来重复特定次数。
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infinite") val color by infiniteTransition.animateColor( initialValue = Color.Green, targetValue = Color.Blue, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( animation = tween(1000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse ), label = "color" ) Column( modifier = Modifier.drawBehind { drawRect(color) } ) { // your composable here }
在启动可组合对象时启动动画
LaunchedEffect 在可组合对象进入组合时运行。它在启动可组合对象时启动动画,您可以使用它来驱动动画状态更改。使用 Animatable 和 animateTo 方法来在启动时启动动画。
val alphaAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } LaunchedEffect(Unit) { alphaAnimation.animateTo(1f) } Box( modifier = Modifier.graphicsLayer { alpha = alphaAnimation.value } )
创建顺序动画
使用Animatable协程 API 执行顺序或并发动画。依次在Animatable上调用animateTo会导致每个动画在继续之前等待之前的动画完成。这是因为它是一个挂起函数。
val alphaAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } val yAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } LaunchedEffect("animationKey") { alphaAnimation.animateTo(1f) yAnimation.animateTo(100f) yAnimation.animateTo(500f, animationSpec = tween(100)) }
创建并发动画
使用协程 API(Animatable#animateTo() 或 animate),或Transition API 来实现并发动画。如果在协程上下文中使用多个启动函数,则会同时启动动画。
val alphaAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } val yAnimation = remember { Animatable(0f) } LaunchedEffect("animationKey") { launch { alphaAnimation.animateTo(1f) } launch { yAnimation.animateTo(100f) } }
您可以使用updateTransition API 使用相同的状态来同时驱动许多不同的属性动画。下面的示例动画由状态更改控制的两个属性rect和borderWidth。
var currentState by remember { mutableStateOf(BoxState.Collapsed) } val transition = updateTransition(currentState, label = "transition") val rect by transition.animateRect(label = "rect") { state -> when (state) { BoxState.Collapsed -> Rect(0f, 0f, 100f, 100f) BoxState.Expanded -> Rect(100f, 100f, 300f, 300f) } } val borderWidth by transition.animateDp(label = "borderWidth") { state -> when (state) { BoxState.Collapsed -> 1.dp BoxState.Expanded -> 0.dp } }
优化动画性能
Compose 中的动画可能会导致性能问题。这是因为动画的本质是:快速移动或更改屏幕上的像素,逐帧创建运动的错觉。
考虑Compose的不同阶段:组合、布局和绘制。如果您的动画更改了布局阶段,则需要所有受影响的可组合项重新布局和重绘。如果您的动画发生在绘制阶段,则默认情况下它比在布局阶段运行动画的性能更好,因为它总体上工作量更少。
为了确保您的应用在动画期间尽可能少地执行操作,请尽可能选择Modifier的 lambda 版本。这跳过了重新组合并在组合阶段之外执行动画,否则请使用Modifier.graphicsLayer{ },因为此修饰符始终在绘制阶段运行。有关此方面的更多信息,请参阅性能文档中的延迟读取部分。
更改动画计时
Compose 默认情况下对大多数动画使用弹簧动画。弹簧或基于物理的动画感觉更自然。它们也是可中断的,因为它们考虑了物体的当前速度,而不是固定时间。如果要覆盖默认值,上面演示的所有动画 API 都可以设置animationSpec来自定义动画的运行方式,无论您是想在特定持续时间内执行它还是使其更具弹性。
以下是不同animationSpec选项的摘要
spring:基于物理的动画,所有动画的默认值。您可以更改stiffness或dampingRatio以实现不同的动画外观和感觉。tween(缩写为between):基于持续时间的动画,使用Easing函数在两个值之间进行动画。keyframes:用于在动画的某些关键点指定值的规范。repeatable:基于持续时间的规范,运行特定次数,由RepeatMode指定。infiniteRepeatable:无限运行的基于持续时间的规范。snap:立即跳转到最终值,无需任何动画。

阅读完整文档以获取有关animationSpecs的更多信息。
其他资源
有关 Compose 中更多有趣的动画示例,请查看以下内容
