如果您有一个现有的基于 View 的应用,您可能不想一次性重写其整个 UI。本页面可帮助您将新的 Compose 组件添加到现有应用中。如需开始在您的应用中使用 Compose,请参阅为现有应用设置 Compose。
Jetpack Compose 从一开始就设计为与 View 互操作。此功能意味着您可以将现有的基于 View 的应用迁移到 Compose,同时仍能构建新功能。为了迁移到 Compose,我们建议采用增量迁移方式,让 Compose 和 View 在您的代码库中并存,直到您的应用完全采用 Compose。
要将您的应用迁移到 Compose,请遵循以下步骤
- 使用 Compose 构建新屏幕。
- 在构建功能时,识别可重用元素并开始创建常用 UI 组件库。
- 一次替换一个屏幕的现有功能。
使用 Compose 构建新屏幕
使用 Compose 构建包含整个屏幕的新功能是推动您采用 Compose 的最佳方式。通过此策略,您可以添加功能并利用 Compose 的优势,同时仍满足公司的业务需求。

当您在现有应用中使用 Compose 构建新屏幕时,您仍受应用架构的限制。如果您使用 Fragment 和 Navigation 组件,则必须创建一个新的 Fragment 并将其内容置于 Compose 中。
要在 Fragment 中使用 Compose,请在 Fragment 的 onCreateView() 生命周期方法中返回一个 ComposeView。ComposeView 有一个 setContent() 方法,您可以在其中提供一个可组合函数。
class NewFeatureFragment : Fragment() { override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View { return ComposeView(requireContext()).apply { setViewCompositionStrategy(ViewCompositionStrategy.DisposeOnViewTreeLifecycleDestroyed) setContent { NewFeatureScreen() } } } }
如需了解详情,请参阅Fragment 中的 ComposeView。
在现有屏幕中添加新功能

如果新添加的功能是现有屏幕的一部分,您还可以在现有的基于 View 的屏幕中使用 Compose。为此,只需像添加任何其他 View 一样,将 ComposeView 添加到 View 层次结构中。
例如,假设您要将子视图添加到 LinearLayout。您可以在 XML 中执行以下操作:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <androidx.compose.ui.platform.ComposeView android:id="@+id/compose_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </LinearLayout>
膨胀视图后,您可以在层次结构中引用 ComposeView 并调用 setContent()。
如需了解有关 ComposeView 的更多信息,请查阅互操作性 API。
构建常用 UI 组件库
当您使用 Compose 构建功能时,您会很快发现自己最终会构建一个组件库。创建常用 UI 组件库可以让您在应用中为这些组件提供单一事实来源,并促进可重用性。您构建的功能可以依赖此库。如果您正在在 Compose 中构建自定义设计系统,此技术特别有用。
根据您的应用大小,此库可以是单独的软件包、模块或库模块。如需了解有关在应用中组织模块的更多信息,请查阅Android 应用模块化指南。
用 Compose 替换现有功能
除了使用 Compose 构建新功能之外,您还需要逐步将应用中的现有功能迁移到 Compose,以利用其优势。
让您的应用仅使用 Compose 可以加快开发速度,并减少应用的 APK 大小和构建时间。如需了解详情,请参阅比较 Compose 和 View 性能。
简单屏幕
在将现有功能迁移到 Compose 时,首先要关注的是简单屏幕。简单屏幕可以是欢迎屏幕、确认屏幕或设置屏幕,其中 UI 中显示的数据相对静态。
以以下 XML 文件为例
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/title_text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/title" android:textAppearance="?attr/textAppearanceHeadline2" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/subtitle_text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/subtitle" android:textAppearance="?attr/textAppearanceHeadline6" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/body_text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="@string/body" android:textAppearance="?attr/textAppearanceBody1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/confirm_button" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/confirm"/> </LinearLayout>
该 XML 文件可以用 Compose 在几行内重写
@Composable fun SimpleScreen() { Column(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { Text( text = stringResource(R.string.title), style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineMedium ) Text( text = stringResource(R.string.subtitle), style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall ) Text( text = stringResource(R.string.body), style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium ) Spacer(modifier = Modifier.weight(1f)) Button(onClick = { /* Handle click */ }, Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { Text(text = stringResource(R.string.confirm)) } } }
视图和 Compose 混合屏幕
已经包含一些 Compose 代码的屏幕是完全迁移到 Compose 的另一个良好选择。根据屏幕的复杂性,您可以将其完全迁移到 Compose,或者分阶段进行。如果屏幕在 UI 层次结构的子树中开始使用 Compose,您将继续迁移 UI 元素,直到整个屏幕都使用 Compose。这种方法也称为自下而上的方法。
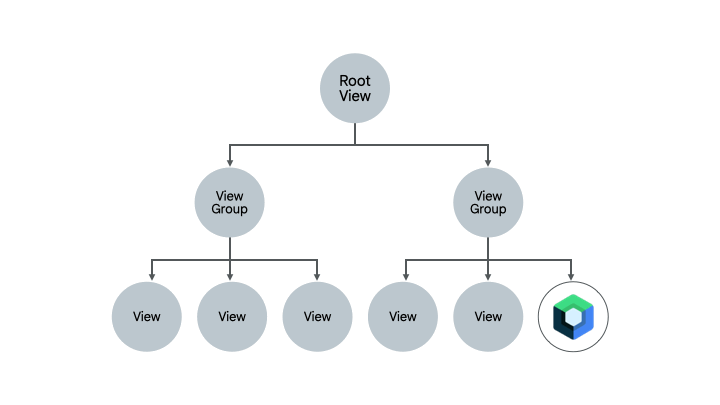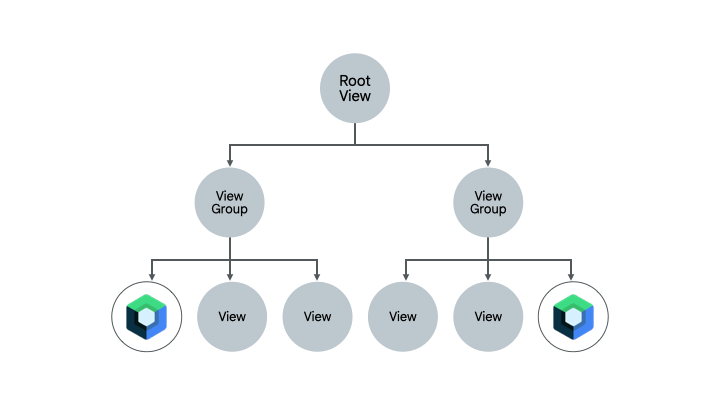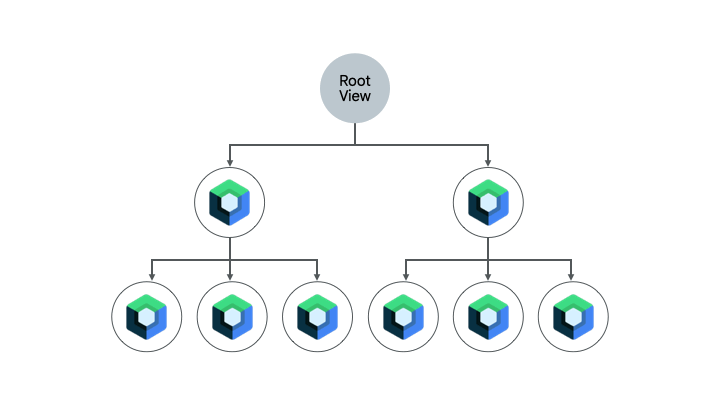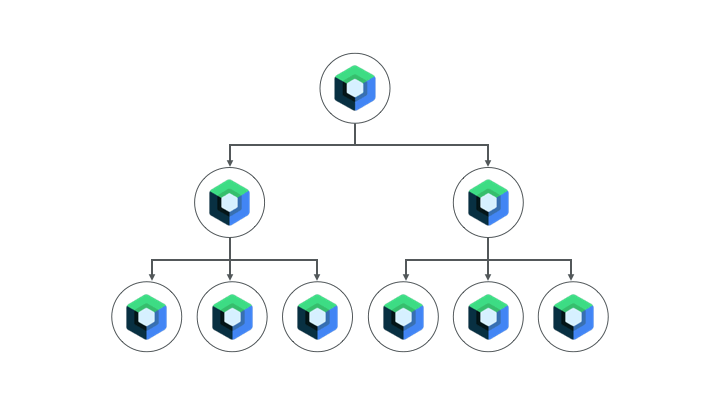
移除 Fragment 和 Navigation 组件
一旦您能够移除所有 Fragment 并将其替换为相应的屏幕级可组合项,您就可以迁移到Navigation Compose。屏幕级可组合项可以包含Compose 和 View 内容的混合,但所有导航目标都必须是可组合项才能启用 Navigation Compose 迁移。在此之前,您应该继续在混合 View 和 Compose 代码库中使用基于 Fragment 的 Navigation 组件。如需了解更多信息,请参阅将 Jetpack Navigation 迁移到 Navigation Compose。
更多资源
请查阅以下额外资源,了解更多关于将现有基于 View 的应用迁移到 Compose 的信息
- Codelab
- 迁移到 Jetpack Compose:在此 Codelab 中了解如何将 Sunflower 应用的某些部分迁移到 Compose。
- 博文
- 将 Sunflower 迁移到 Jetpack Compose:了解如何使用本页面中描述的策略将 Sunflower 迁移到 Compose。
- Jetpack Compose 互操作:在 RecyclerView 中使用 Compose:了解如何在
RecyclerView中高效使用 Compose。
后续步骤
现在您已了解将现有基于 View 的应用迁移到 Compose 的策略,请探索互操作性 API 以了解更多信息。
为您推荐
- 注意:当 JavaScript 关闭时,会显示链接文本
- 在视图中使用 Compose
- 滚动
- 将
RecyclerView迁移到 Lazy list
