内容提供程序管理对中央数据存储库的访问。提供程序是 Android 应用程序的一部分,该应用程序通常提供其自己的 UI 用于处理数据。但是,内容提供程序主要由其他应用程序使用,这些应用程序使用提供程序客户端对象访问提供程序。提供程序和提供程序客户端共同为数据提供一致的标准接口,该接口还处理进程间通信和安全数据访问。
通常,您会在以下两种情况下使用内容提供程序之一:实现代码以访问另一个应用程序中现有的内容提供程序,或在您的应用程序中创建新的内容提供程序以与其他应用程序共享数据。
此页面介绍了使用现有内容提供程序的基础知识。要了解如何在您自己的应用程序中实现内容提供程序,请参阅 创建内容提供程序。
本主题介绍以下内容:
- 内容提供程序的工作原理。
- 用于从内容提供程序检索数据的 API。
- 用于在内容提供程序中插入、更新或删除数据的 API。
- 促进与提供程序协作的其他 API 功能。
概述
内容提供程序将数据以一个或多个表的形式呈现给外部应用程序,这些表类似于关系数据库中的表。一行表示提供程序收集的某种类型数据的实例,并且行中的每一列表示为实例收集的单个数据。
内容提供程序协调您应用程序中多个不同 API 和组件对数据存储层的访问。如图 1 所示,这些包括:
- 与其他应用程序共享对您应用程序数据的访问
- 向小部件发送数据
- 使用
SearchRecentSuggestionsProvider通过搜索框架返回您应用程序的自定义搜索建议 - 使用
AbstractThreadedSyncAdapter的实现将应用程序数据与您的服务器同步 - 使用
CursorLoader在您的 UI 中加载数据
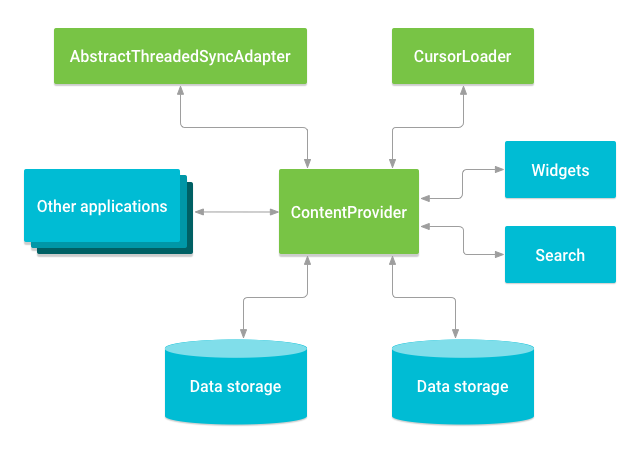
图 1. 内容提供程序与其他组件之间的关系。
访问提供程序
当您要访问内容提供程序中的数据时,请使用应用程序 Context 中的 ContentResolver 对象作为客户端与提供程序进行通信。ContentResolver 对象与提供程序对象(实现 ContentProvider 的类的实例)进行通信。
提供程序对象接收来自客户端的数据请求,执行请求的操作并返回结果。此对象具有调用提供程序对象中同名方法的方法,提供程序对象是ContentProvider的具体子类之一的实例。ContentResolver方法提供持久性存储的基本“CRUD”(创建、检索、更新和删除)功能。
从您的 UI 访问ContentProvider 的一种常见模式是使用CursorLoader在后台运行异步查询。UI 中的Activity或Fragment调用CursorLoader进行查询,后者又使用ContentResolver获取ContentProvider。
这允许 UI 在查询运行时继续对用户可用。此模式涉及许多不同对象以及底层存储机制的交互,如图 2 所示。
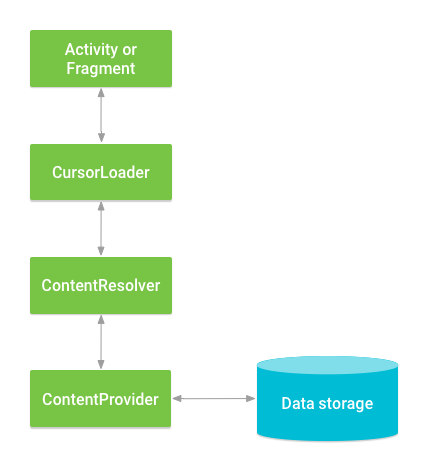
图 2.ContentProvider、其他类和存储之间的交互。
注意:要访问提供程序,您的应用程序通常必须在其清单文件中请求特定权限。此开发模式在内容提供程序权限部分中进行了更详细的描述。
Android 平台内置的提供程序之一是用户词典提供程序,它存储用户想要保留的非标准单词。表 1 说明了此提供程序表中的数据可能是什么样子。
表 1:用户词典表示例。
| 单词 | 应用 ID | 频率 | 语言环境 | _ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
mapreduce |
user1 | 100 | en_US | 1 |
precompiler |
user14 | 200 | fr_FR | 2 |
applet |
user2 | 225 | fr_CA | 3 |
const |
user1 | 255 | pt_BR | 4 |
int |
user5 | 100 | en_UK | 5 |
在表 1 中,每一行都代表标准词典中找不到的一个单词实例。每一列都代表该单词的一段数据,例如首次遇到它的语言环境。列标题是存储在提供程序中的列名。因此,例如,要引用行的语言环境,您需要引用其locale列。对于此提供程序,_ID列用作提供程序自动维护的主键列。
要获取用户词典提供程序中的单词及其语言环境列表,您可以调用ContentResolver.query()。query()方法调用用户词典提供程序定义的ContentProvider.query()方法。以下几行代码显示了ContentResolver.query()调用
Kotlin
// Queries the UserDictionary and returns results cursor = contentResolver.query( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The content URI of the words table projection, // The columns to return for each row selectionClause, // Selection criteria selectionArgs.toTypedArray(), // Selection criteria sortOrder // The sort order for the returned rows )
Java
// Queries the UserDictionary and returns results cursor = getContentResolver().query( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The content URI of the words table projection, // The columns to return for each row selectionClause, // Selection criteria selectionArgs, // Selection criteria sortOrder); // The sort order for the returned rows
表 2 显示了query(Uri,projection,selection,selectionArgs,sortOrder)的参数如何与 SQL SELECT 语句匹配。
表 2:query()与 SQL 查询的比较。
query()参数 |
SELECT 关键字/参数 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|
Uri |
FROM table_name |
Uri映射到提供程序中名为table_name的表。 |
projection |
col,col,col,... |
projection是为检索到的每一行包含的列数组。 |
selection |
WHERE col = value |
selection指定选择行的条件。 |
selectionArgs |
没有完全等效的项。选择参数替换?选择子句中的占位符。 |
|
sortOrder |
ORDER BY col,col,... |
sortOrder指定返回的Cursor中行出现的顺序。 |
内容 URI
内容 URI 是标识提供程序中数据的 URI。内容 URI 包括整个提供程序的符号名称(其授权)和指向表的名称(路径)。当您调用客户端方法访问提供程序中的表时,表的 content URI 是参数之一。
在前面的代码行中,常量CONTENT_URI包含用户词典提供程序的Words表的 content URI。ContentResolver对象解析 URI 的授权并使用它通过将授权与已知提供程序的系统表进行比较来解析提供程序。ContentResolver然后可以将查询参数分派到正确的提供程序。
ContentProvider使用 content URI 的路径部分来选择要访问的表。提供程序通常为其公开的每个表都有一个路径。
在前面的代码行中,Words表的完整 URI 为
content://user_dictionary/words
content://字符串是方案,它始终存在并将其标识为 content URI。user_dictionary字符串是提供程序的授权。words字符串是表的路径。
许多提供程序允许您通过将 ID 值附加到 URI 的末尾来访问表中的一行。例如,要从用户词典提供程序检索其_ID为4的行,您可以使用此 content URI
Kotlin
val singleUri: Uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, 4)
Java
Uri singleUri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI,4);
当您检索一组行然后想要更新或删除其中一行时,通常会使用 ID 值。
注意:Uri和Uri.Builder类包含用于从字符串构造格式良好的 URI 对象的便捷方法。ContentUris类包含用于将 ID 值附加到 URI 的便捷方法。前面的代码片段使用withAppendedId()将 ID 附加到用户词典提供程序 content URI。
从提供程序检索数据
本节介绍如何使用用户词典提供程序为例从提供程序检索数据。
为了清晰起见,本节中的代码片段在 UI 线程上调用ContentResolver.query()。但是,在实际代码中,请在单独的线程上异步执行查询。您可以使用CursorLoader类,这在加载器指南中有更详细的描述。此外,代码行仅是代码片段。它们没有显示完整的应用程序。
要从提供程序检索数据,请遵循以下基本步骤
- 请求对提供程序的读取访问权限。
- 定义将查询发送到提供程序的代码。
请求读取访问权限
要从提供程序检索数据,您的应用程序需要对提供程序的读取访问权限。您不能在运行时请求此权限。相反,您必须使用<uses-permission>元素和提供程序定义的确切权限名称,在清单中指定您需要此权限。
在清单中指定此元素时,您是在为您的应用程序请求此权限。当用户安装您的应用程序时,他们会隐式授予此请求。
要查找您正在使用的提供程序的读取访问权限的确切名称以及提供程序使用的其他访问权限的名称,请查看提供程序的文档。
访问提供程序中权限的作用在内容提供程序权限部分中进行了更详细的描述。
用户词典提供程序在其清单文件中定义了权限android.permission.READ_USER_DICTIONARY,因此想要从此提供程序读取的应用程序必须请求此权限。
构造查询
从提供程序检索数据的下一步是构造查询。以下代码片段定义了一些用于访问用户词典提供程序的变量
Kotlin
// A "projection" defines the columns that are returned for each row private val mProjection: Array<String> = arrayOf( UserDictionary.Words._ID, // Contract class constant for the _ID column name UserDictionary.Words.WORD, // Contract class constant for the word column name UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE // Contract class constant for the locale column name ) // Defines a string to contain the selection clause private var selectionClause: String? = null // Declares an array to contain selection arguments private lateinit var selectionArgs: Array<String>
Java
// A "projection" defines the columns that are returned for each row String[] mProjection = { UserDictionary.Words._ID, // Contract class constant for the _ID column name UserDictionary.Words.WORD, // Contract class constant for the word column name UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE // Contract class constant for the locale column name }; // Defines a string to contain the selection clause String selectionClause = null; // Initializes an array to contain selection arguments String[] selectionArgs = {""};
以下代码片段显示了如何使用ContentResolver.query(),以用户词典提供程序为例。提供程序客户端查询类似于 SQL 查询,它包含一组要返回的列、一组选择条件和排序顺序。
查询返回的列集称为投影,变量为mProjection。
指定要检索的行的表达式被拆分为选择子句和选择参数。选择子句是逻辑和布尔表达式、列名和值的组合。变量是mSelectionClause。如果您指定可替换参数?而不是值,则查询方法会从选择参数数组(变量为mSelectionArgs)中检索该值。
在下一个代码片段中,如果用户未输入单词,则选择子句设置为null,并且查询返回提供程序中的所有单词。如果用户输入了一个单词,则选择子句设置为UserDictionary.Words.WORD + " = ?",并且选择参数数组的第一个元素设置为用户输入的单词。
Kotlin
/* * This declares a String array to contain the selection arguments. */ private lateinit var selectionArgs: Array<String> // Gets a word from the UI searchString = searchWord.text.toString() // Insert code here to check for invalid or malicious input // If the word is the empty string, gets everything selectionArgs = searchString?.takeIf { it.isNotEmpty() }?.let { selectionClause = "${UserDictionary.Words.WORD} = ?" arrayOf(it) } ?: run { selectionClause = null emptyArray<String>() } // Does a query against the table and returns a Cursor object mCursor = contentResolver.query( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The content URI of the words table projection, // The columns to return for each row selectionClause, // Either null or the word the user entered selectionArgs, // Either empty or the string the user entered sortOrder // The sort order for the returned rows ) // Some providers return null if an error occurs, others throw an exception when (mCursor?.count) { null -> { /* * Insert code here to handle the error. Be sure not to use the cursor! * You might want to call android.util.Log.e() to log this error. */ } 0 -> { /* * Insert code here to notify the user that the search is unsuccessful. This isn't * necessarily an error. You might want to offer the user the option to insert a new * row, or re-type the search term. */ } else -> { // Insert code here to do something with the results } }
Java
/* * This defines a one-element String array to contain the selection argument. */ String[] selectionArgs = {""}; // Gets a word from the UI searchString = searchWord.getText().toString(); // Remember to insert code here to check for invalid or malicious input // If the word is the empty string, gets everything if (TextUtils.isEmpty(searchString)) { // Setting the selection clause to null returns all words selectionClause = null; selectionArgs[0] = ""; } else { // Constructs a selection clause that matches the word that the user entered selectionClause = UserDictionary.Words.WORD + " = ?"; // Moves the user's input string to the selection arguments selectionArgs[0] = searchString; } // Does a query against the table and returns a Cursor object mCursor = getContentResolver().query( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The content URI of the words table projection, // The columns to return for each row selectionClause, // Either null or the word the user entered selectionArgs, // Either empty or the string the user entered sortOrder); // The sort order for the returned rows // Some providers return null if an error occurs, others throw an exception if (null == mCursor) { /* * Insert code here to handle the error. Be sure not to use the cursor! You can * call android.util.Log.e() to log this error. * */ // If the Cursor is empty, the provider found no matches } else if (mCursor.getCount() < 1) { /* * Insert code here to notify the user that the search is unsuccessful. This isn't necessarily * an error. You can offer the user the option to insert a new row, or re-type the * search term. */ } else { // Insert code here to do something with the results }
此查询类似于以下 SQL 语句
SELECT _ID, word, locale FROM words WHERE word = <userinput> ORDER BY word ASC;
在此 SQL 语句中,使用实际的列名而不是契约类常量。
防止恶意输入
如果内容提供程序管理的数据位于 SQL 数据库中,则将外部不受信任的数据包含到原始 SQL 语句中可能会导致 SQL 注入。
考虑以下选择子句
Kotlin
// Constructs a selection clause by concatenating the user's input to the column name var selectionClause = "var = $mUserInput"
Java
// Constructs a selection clause by concatenating the user's input to the column name String selectionClause = "var = " + userInput;
如果您这样做,您可能会允许用户将恶意的 SQL 连接到您的 SQL 语句。例如,用户可以为mUserInput输入“nothing; DROP TABLE *;”,这将导致选择子句var = nothing; DROP TABLE *;。
由于选择子句被视为 SQL 语句,这可能会导致提供程序擦除底层 SQLite 数据库中的所有表,除非提供程序设置为捕获SQL 注入尝试。
为避免此问题,请使用将?用作可替换参数的选择子句和单独的选择参数数组。这样,用户输入将直接绑定到查询,而不是被解释为 SQL 语句的一部分。因为它不被视为 SQL,所以用户输入无法注入恶意的 SQL。不要使用连接来包含用户输入,请使用此选择子句
Kotlin
// Constructs a selection clause with a replaceable parameter var selectionClause = "var = ?"
Java
// Constructs a selection clause with a replaceable parameter String selectionClause = "var = ?";
像这样设置选择参数数组
Kotlin
// Defines a mutable list to contain the selection arguments var selectionArgs: MutableList<String> = mutableListOf()
Java
// Defines an array to contain the selection arguments String[] selectionArgs = {""};
像这样在选择参数数组中放入一个值
Kotlin
// Adds the user's input to the selection argument selectionArgs += userInput
Java
// Sets the selection argument to the user's input selectionArgs[0] = userInput;
即使提供程序不是基于 SQL 数据库,使用?作为可替换参数和选择参数数组的选择子句也是指定选择的首选方法。
显示查询结果
客户端方法 ContentResolver.query() 始终返回一个包含查询投影指定的列的 Cursor 对象,这些列对应于匹配查询选择条件的行。 Cursor 对象提供对其中包含的行和列的随机读取访问。
使用 Cursor 方法,您可以迭代结果中的行,确定每一列的数据类型,获取列中的数据以及检查结果的其他属性。
某些 Cursor 实现会在提供程序的数据发生更改时自动更新对象,在 Cursor 发生更改时触发观察者对象中的方法,或者同时执行这两项操作。
注意:提供程序可以根据进行查询的对象的性质来限制对列的访问。例如,联系人提供程序会限制某些列对同步适配器的访问,因此不会将其返回给活动或服务。
如果没有行与选择条件匹配,提供程序将返回一个 Cursor 对象,其中 Cursor.getCount() 为 0,即空游标。
如果发生内部错误,查询的结果取决于特定的提供程序。它可能会返回 null,或者抛出 Exception。
由于 Cursor 是行的列表,因此显示 Cursor 内容的一种好方法是使用 SimpleCursorAdapter 将其链接到 ListView。
以下代码段延续了前面代码段中的代码。它创建一个包含由查询检索到的 Cursor 的 SimpleCursorAdapter 对象,并将此对象设置为 ListView 的适配器。
Kotlin
// Defines a list of columns to retrieve from the Cursor and load into an output row val wordListColumns : Array<String> = arrayOf( UserDictionary.Words.WORD, // Contract class constant containing the word column name UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE // Contract class constant containing the locale column name ) // Defines a list of View IDs that receive the Cursor columns for each row val wordListItems = intArrayOf(R.id.dictWord, R.id.locale) // Creates a new SimpleCursorAdapter cursorAdapter = SimpleCursorAdapter( applicationContext, // The application's Context object R.layout.wordlistrow, // A layout in XML for one row in the ListView mCursor, // The result from the query wordListColumns, // A string array of column names in the cursor wordListItems, // An integer array of view IDs in the row layout 0 // Flags (usually none are needed) ) // Sets the adapter for the ListView wordList.setAdapter(cursorAdapter)
Java
// Defines a list of columns to retrieve from the Cursor and load into an output row String[] wordListColumns = { UserDictionary.Words.WORD, // Contract class constant containing the word column name UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE // Contract class constant containing the locale column name }; // Defines a list of View IDs that receive the Cursor columns for each row int[] wordListItems = { R.id.dictWord, R.id.locale}; // Creates a new SimpleCursorAdapter cursorAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter( getApplicationContext(), // The application's Context object R.layout.wordlistrow, // A layout in XML for one row in the ListView mCursor, // The result from the query wordListColumns, // A string array of column names in the cursor wordListItems, // An integer array of view IDs in the row layout 0); // Flags (usually none are needed) // Sets the adapter for the ListView wordList.setAdapter(cursorAdapter);
注意:要使用 Cursor 支持 ListView,游标必须包含名为 _ID 的列。因此,前面显示的查询检索 Words 表的 _ID 列,即使 ListView 不显示它。此限制也解释了为什么大多数提供程序都为其每个表都具有 _ID 列。
从查询结果获取数据
除了显示查询结果外,您还可以将它们用于其他任务。例如,您可以从用户词典提供程序检索拼写,然后在其他提供程序中查找它们。为此,您可以迭代 Cursor 中的行,如下例所示
Kotlin
/* * Only executes if the cursor is valid. The User Dictionary Provider returns null if * an internal error occurs. Other providers might throw an Exception instead of returning null. */ mCursor?.apply { // Determine the column index of the column named "word" val index: Int = getColumnIndex(UserDictionary.Words.WORD) /* * Moves to the next row in the cursor. Before the first movement in the cursor, the * "row pointer" is -1, and if you try to retrieve data at that position you get an * exception. */ while (moveToNext()) { // Gets the value from the column newWord = getString(index) // Insert code here to process the retrieved word ... // End of while loop } }
Java
// Determine the column index of the column named "word" int index = mCursor.getColumnIndex(UserDictionary.Words.WORD); /* * Only executes if the cursor is valid. The User Dictionary Provider returns null if * an internal error occurs. Other providers might throw an Exception instead of returning null. */ if (mCursor != null) { /* * Moves to the next row in the cursor. Before the first movement in the cursor, the * "row pointer" is -1, and if you try to retrieve data at that position you get an * exception. */ while (mCursor.moveToNext()) { // Gets the value from the column newWord = mCursor.getString(index); // Insert code here to process the retrieved word ... // End of while loop } } else { // Insert code here to report an error if the cursor is null or the provider threw an exception }
Cursor 实现包含多种“获取”方法,用于从对象中检索不同类型的数据。例如,前面的代码段使用 getString()。它们还有一个 getType() 方法,该方法返回一个指示列数据类型的数值。
释放查询结果资源
如果不再需要 Cursor 对象,则必须关闭它们,以便更快地释放与其关联的资源。这可以通过调用 close() 来完成,也可以在 Java 编程语言中使用 try-with-resources 语句或在 Kotlin 编程语言中使用 use() 函数来完成。
内容提供程序权限
提供程序的应用程序可以指定其他应用程序必须拥有的权限才能访问提供程序的数据。这些权限使用户了解应用程序尝试访问哪些数据。根据提供程序的要求,其他应用程序会请求它们访问提供程序所需的权限。最终用户在安装应用程序时会看到请求的权限。
如果提供程序的应用程序未指定任何权限,则其他应用程序将无法访问提供程序的数据,除非提供程序已导出。此外,提供程序应用程序中的组件始终具有完全的读写访问权限,而不管指定的权限如何。
用户词典提供程序需要 android.permission.READ_USER_DICTIONARY 权限才能从中检索数据。该提供程序具有单独的 android.permission.WRITE_USER_DICTIONARY 权限,用于插入、更新或删除数据。
要获得访问提供程序所需的权限,应用程序会在其清单文件中使用 <uses-permission> 元素请求这些权限。当 Android 包管理器安装应用程序时,用户必须批准应用程序请求的所有权限。如果用户批准了这些权限,包管理器将继续安装。如果用户未批准这些权限,包管理器将停止安装。
以下示例 <uses-permission> 元素请求对用户词典提供程序的读取访问权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_USER_DICTIONARY">权限对提供程序访问的影响将在 安全提示 中更详细地解释。
插入、更新和删除数据
与从提供程序检索数据的方式相同,您还可以使用提供程序客户端与提供程序的 ContentProvider 之间的交互来修改数据。您可以调用 ContentResolver 的方法,其参数将传递给 ContentProvider 的相应方法。提供程序和提供程序客户端会自动处理安全性和进程间通信。
插入数据
要将数据插入提供程序,您可以调用 ContentResolver.insert() 方法。此方法会将新行插入提供程序并返回该行的内容 URI。以下代码段显示了如何将新单词插入用户词典提供程序
Kotlin
// Defines a new Uri object that receives the result of the insertion lateinit var newUri: Uri ... // Defines an object to contain the new values to insert val newValues = ContentValues().apply { /* * Sets the values of each column and inserts the word. The arguments to the "put" * method are "column name" and "value". */ put(UserDictionary.Words.APP_ID, "example.user") put(UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE, "en_US") put(UserDictionary.Words.WORD, "insert") put(UserDictionary.Words.FREQUENCY, "100") } newUri = contentResolver.insert( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The UserDictionary content URI newValues // The values to insert )
Java
// Defines a new Uri object that receives the result of the insertion Uri newUri; ... // Defines an object to contain the new values to insert ContentValues newValues = new ContentValues(); /* * Sets the values of each column and inserts the word. The arguments to the "put" * method are "column name" and "value". */ newValues.put(UserDictionary.Words.APP_ID, "example.user"); newValues.put(UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE, "en_US"); newValues.put(UserDictionary.Words.WORD, "insert"); newValues.put(UserDictionary.Words.FREQUENCY, "100"); newUri = getContentResolver().insert( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The UserDictionary content URI newValues // The values to insert );
新行的数据将进入单个 ContentValues 对象,其形式类似于单行游标。此对象中的列不需要具有相同的数据类型,如果您根本不想指定值,则可以使用 ContentValues.putNull() 将列设置为 null。
前面的代码段没有添加 _ID 列,因为此列是自动维护的。提供程序会为添加的每一行分配唯一的 _ID 值。提供程序通常使用此值作为表的主键。
newUri 中返回的内容 URI 使用以下格式标识新添加的行
content://user_dictionary/words/<id_value>
<id_value> 是新行的 _ID 的内容。大多数提供程序可以自动检测此形式的内容 URI,然后对该特定行执行请求的操作。
要从返回的 Uri 获取 _ID 的值,请调用 ContentUris.parseId()。
更新数据
要更新行,您可以使用包含更新值的 ContentValues 对象(就像插入一样),以及选择条件(就像查询一样)。您使用的客户端方法是 ContentResolver.update()。您只需要为要更新的列向 ContentValues 对象添加值。如果要清除列的内容,请将值设置为 null。
以下代码段将所有语言区域为 "en" 的行更改为语言区域为 null。返回值是已更新的行数。
Kotlin
// Defines an object to contain the updated values val updateValues = ContentValues().apply { /* * Sets the updated value and updates the selected words. */ putNull(UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE) } // Defines selection criteria for the rows you want to update val selectionClause: String = UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE + "LIKE ?" val selectionArgs: Array<String> = arrayOf("en_%") // Defines a variable to contain the number of updated rows var rowsUpdated: Int = 0 ... rowsUpdated = contentResolver.update( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The UserDictionary content URI updateValues, // The columns to update selectionClause, // The column to select on selectionArgs // The value to compare to )
Java
// Defines an object to contain the updated values ContentValues updateValues = new ContentValues(); // Defines selection criteria for the rows you want to update String selectionClause = UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE + " LIKE ?"; String[] selectionArgs = {"en_%"}; // Defines a variable to contain the number of updated rows int rowsUpdated = 0; ... /* * Sets the updated value and updates the selected words. */ updateValues.putNull(UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE); rowsUpdated = getContentResolver().update( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The UserDictionary content URI updateValues, // The columns to update selectionClause, // The column to select on selectionArgs // The value to compare to );
调用 ContentResolver.update() 时,请清理用户输入。要了解有关此内容的更多信息,请阅读 防止恶意输入 部分。
删除数据
删除行类似于检索行数据。您可以为要删除的行指定选择条件,客户端方法将返回已删除的行数。以下代码段删除应用程序 ID 与 "user" 匹配的行。该方法返回已删除的行数。
Kotlin
// Defines selection criteria for the rows you want to delete val selectionClause = "${UserDictionary.Words.APP_ID} LIKE ?" val selectionArgs: Array<String> = arrayOf("user") // Defines a variable to contain the number of rows deleted var rowsDeleted: Int = 0 ... // Deletes the words that match the selection criteria rowsDeleted = contentResolver.delete( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The UserDictionary content URI selectionClause, // The column to select on selectionArgs // The value to compare to )
Java
// Defines selection criteria for the rows you want to delete String selectionClause = UserDictionary.Words.APP_ID + " LIKE ?"; String[] selectionArgs = {"user"}; // Defines a variable to contain the number of rows deleted int rowsDeleted = 0; ... // Deletes the words that match the selection criteria rowsDeleted = getContentResolver().delete( UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, // The UserDictionary content URI selectionClause, // The column to select on selectionArgs // The value to compare to );
调用 ContentResolver.delete() 时,请清理用户输入。要了解有关此内容的更多信息,请阅读 防止恶意输入 部分。
提供程序数据类型
内容提供程序可以提供许多不同的数据类型。用户词典提供程序仅提供文本,但提供程序还可以提供以下格式
- 整数
- 长整数 (long)
- 浮点数
- 长浮点数 (double)
提供程序经常使用的另一种数据类型是作为 64 KB 字节数组实现的二进制大对象 (BLOB)。您可以通过查看 Cursor 类的“获取”方法来查看可用的数据类型。
提供程序中每一列的数据类型通常在其文档中列出。用户词典提供程序的数据类型列在其契约类的参考文档 UserDictionary.Words 中。契约类在 契约类 部分中进行了描述。您还可以通过调用 Cursor.getType() 来确定数据类型。
提供程序还维护其定义的每个内容 URI 的 MIME 数据类型信息。您可以使用 MIME 类型信息来了解您的应用程序是否可以处理提供程序提供的或根据 MIME 类型选择处理类型的数据。当您使用包含复杂数据结构或文件的提供程序时,通常需要 MIME 类型。
例如,联系人提供程序中的 ContactsContract.Data 表使用 MIME 类型来标记存储在每一行中的联系人数据的类型。要获取与内容 URI 对应的 MIME 类型,请调用 ContentResolver.getType()。
MIME 类型参考 部分描述了标准和自定义 MIME 类型的语法。
提供程序访问的替代形式
在应用程序开发中,提供程序访问的三个替代形式非常重要
-
批量访问:您可以使用
ContentProviderOperation类中的方法创建一批访问调用,然后使用ContentResolver.applyBatch()应用它们。 - 异步查询:在单独的线程中执行查询。您可以使用
CursorLoader对象。 加载器指南中的示例演示了如何执行此操作。 - 使用Intent进行数据访问:虽然您不能直接向提供程序发送Intent,但您可以向提供程序的应用程序发送Intent,该应用程序通常最适合修改提供程序的数据。
使用Intent进行批量访问和修改将在以下部分中介绍。
批量访问
批量访问提供程序对于插入大量行、在同一方法调用中插入多个表中的行以及通常在进程边界上执行一组操作作为事务(称为原子操作)非常有用。
要批量访问提供程序,请创建ContentProviderOperation对象的数组,然后使用ContentResolver.applyBatch()将它们分派到内容提供程序。您向此方法传递内容提供程序的权限,而不是特定的内容URI。
这允许数组中的每个ContentProviderOperation对象针对不同的表工作。ContentResolver.applyBatch()调用返回结果数组。
ContactsContract.RawContacts契约类的描述包含一个演示批量插入的代码片段。
使用Intent进行数据访问
Intent可以提供对内容提供程序的间接访问。即使您的应用程序没有访问权限,您也可以让用户访问提供程序中的数据,方法是从具有权限的应用程序获取结果Intent,或激活具有权限的应用程序并让用户在其中完成工作。
获取具有临时权限的访问权限
即使您没有正确的访问权限,也可以通过向具有权限的应用程序发送Intent并接收包含URI权限的结果Intent来访问内容提供程序中的数据。这些是特定内容URI的权限,持续时间直到接收它们的活动结束。具有永久权限的应用程序通过在结果Intent中设置标志来授予临时权限。
注意:这些标志不会授予对内容URI中包含的权限的提供程序的一般读取或写入访问权限。访问仅限于URI本身。
向另一个应用发送内容URI时,请至少包含其中一个标志。这些标志为任何接收 Intent 并定位 Android 11(API 级别 30)或更高版本的应用提供了以下功能:
- 根据 Intent 中包含的标志,读取或写入内容 URI 表示的数据。
- 获得对包含与 URI 权限匹配的内容提供程序的应用的包可见性。发送 Intent 的应用和包含内容提供程序的应用可能是两个不同的应用。
提供程序在其清单中为内容 URI 定义 URI 权限,使用android:grantUriPermissions属性<provider>元素以及<grant-uri-permission><provider>元素的子元素。Android 上的权限指南中更详细地解释了 URI 权限机制。
例如,即使您没有READ_CONTACTS权限,您也可以检索通讯录提供程序中的联系人数据。您可能希望在向联系人在其生日那天发送电子贺卡的应用程序中执行此操作。无需请求READ_CONTACTS(这使您可以访问所有用户的联系人及其所有信息),让用户控制您的应用程序使用哪些联系人。为此,请使用以下过程:
- 在您的应用程序中,使用
startActivityForResult()方法发送包含操作ACTION_PICK和“联系人”MIME类型CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE的Intent。 - 由于此Intent与通讯录应用的“选择”活动的Intent过滤器匹配,因此该活动会显示在前台。
- 在选择活动中,用户选择要更新的联系人。发生这种情况时,选择活动调用
setResult(resultcode, intent)来设置要返回给您的应用程序的Intent。Intent包含用户选择的联系人的内容URI和“额外”标志FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION。这些标志授予您的应用读取内容URI指向的联系人的数据的URI权限。然后,选择活动调用finish()以将控制权返回到您的应用程序。 - 您的活动返回前台,系统调用您的活动的
onActivityResult()方法。此方法接收通讯录应用中选择活动创建的结果Intent。 - 使用结果Intent中的内容URI,您可以读取通讯录提供程序中的联系人的数据,即使您没有在清单中请求对提供程序的永久读取访问权限。然后,您可以获取联系人的生日信息或电子邮件地址,然后发送电子贺卡。
使用另一个应用程序
让用户修改您没有访问权限的数据的另一种方法是激活具有权限的应用程序并让用户在那里完成工作。
例如,日历应用程序接受ACTION_INSERT Intent,允许您激活应用程序的插入UI。您可以在此Intent中传递“额外”数据,应用程序使用这些数据来预填充UI。由于定期事件具有复杂的语法,因此将事件插入日历提供程序的首选方法是使用ACTION_INSERT激活日历应用,然后让用户在那里插入事件。
使用辅助应用显示数据
如果您的应用程序确实具有访问权限,您仍然可以使用Intent在另一个应用程序中显示数据。例如,日历应用程序接受ACTION_VIEW Intent,显示特定日期或事件。这使您可以显示日历信息,而无需创建自己的UI。要了解有关此功能的更多信息,请参阅日历提供程序概述。
您发送Intent到的应用程序不必与提供程序关联的应用程序相同。例如,您可以从通讯录提供程序检索联系人,然后向图像查看器发送包含联系人的图像的内容URI的ACTION_VIEW Intent。
契约类
契约类定义常量,帮助应用程序使用内容URI、列名、Intent操作以及内容提供程序的其他功能。契约类不会自动包含在提供程序中。提供程序的开发者必须定义它们,然后才能将它们提供给其他开发者。Android平台中包含的许多提供程序在android.provider包中都有相应的契约类。
例如,用户词典提供程序有一个契约类UserDictionary,其中包含内容URI和列名常量。Words表的內容URI在常量UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI中定义。UserDictionary.Words类还包含列名常量,这些常量在本指南的示例代码段中使用。例如,可以像下面这样定义查询投影:
Kotlin
val projection : Array<String> = arrayOf( UserDictionary.Words._ID, UserDictionary.Words.WORD, UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE )
Java
String[] projection = { UserDictionary.Words._ID, UserDictionary.Words.WORD, UserDictionary.Words.LOCALE };
另一个契约类是通讯录提供程序的ContactsContract。此类的参考文档包含示例代码片段。它的一个子类ContactsContract.Intents.Insert是一个契约类,其中包含Intent和Intent数据的常量。
MIME类型参考
内容提供程序可以返回标准MIME媒体类型、自定义MIME类型字符串或两者兼而有之。
MIME类型具有以下格式:
type/subtype
例如,众所周知的MIME类型text/html具有text类型和html子类型。如果提供程序为URI返回此类型,则表示使用该URI的查询返回包含HTML标签的文本。
自定义MIME类型字符串(也称为厂商特定MIME类型)具有更复杂的type和subtype值。对于多行,type值始终如下:
vnd.android.cursor.dir
对于单行,type值始终如下:
vnd.android.cursor.item
subtype是提供程序特定的。Android内置提供程序通常具有简单的子类型。例如,当通讯录应用程序为电话号码创建一行时,它会在该行中设置以下MIME类型:
vnd.android.cursor.item/phone_v2
子类型值为phone_v2。
其他提供程序开发者可以根据提供程序的权限和表名创建自己的子类型模式。例如,考虑一个包含火车时刻表的提供程序。提供程序的权限是com.example.trains,它包含Line1、Line2和Line3表。对于Line1表的以下内容URI:
content://com.example.trains/Line1
提供程序返回以下MIME类型:
vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.example.line1
对于Line2表中第5行的以下内容URI:
content://com.example.trains/Line2/5
提供程序返回以下MIME类型:
vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.example.line2
大多数内容提供程序都为其使用的MIME类型定义契约类常量。例如,通讯录提供程序契约类ContactsContract.RawContacts定义了单行原始联系人的MIME类型的常量CONTENT_ITEM_TYPE。
单行的内容URI在内容URI部分中进行了描述。
