导航组件是一个库,可管理应用屏幕之间复杂的导航、过渡动画、深度链接以及编译时检查的参数传递。
本文档作为通用指南,介绍如何将现有应用迁移到 Navigation 组件。
从高层次来看,迁移包括以下步骤
将屏幕专用界面逻辑移出 Activity - 将您的应用界面逻辑移出 Activity,确保每个 Activity 仅拥有全局导航界面组件(例如
Toolbar)的逻辑,同时将每个屏幕的实现委托给 Fragment 或自定义目标。集成 Navigation 组件 - 对于每个 Activity,构建一个导航图,其中包含该 Activity 管理的一个或多个 Fragment。将 Fragment 事务替换为 Navigation 组件操作。
添加 Activity 目标 - 使用 Activity 目标将
startActivity()调用替换为操作。合并 Activity - 在多个 Activity 共享同一布局的情况下合并导航图。
前提条件
本指南假定您已将应用迁移到使用 AndroidX 库。如果您尚未完成此操作,请在继续之前将您的项目迁移到使用 AndroidX。
将屏幕专用界面逻辑移出 Activity
Activity 是系统级组件,可促进您的应用与 Android 之间的图形交互。Activity 在您的应用清单中注册,以便 Android 知道哪些 Activity 可供启动。Activity 类还使您的应用能够对 Android 更改做出反应,例如当您的应用界面进入或离开前台、旋转等。Activity 还可以作为在屏幕之间共享状态的位置。
在您的应用中,Activity 应作为导航宿主,并应包含屏幕之间如何过渡、传递数据等的逻辑和知识。但是,管理界面详细信息最好留给界面中较小的、可重用的部分。此模式的推荐实现是 Fragment。请参阅 单 Activity:原因、时机和方式,详细了解使用 Fragment 的优势。Navigation 通过 navigation-fragment 依赖项支持 Fragment。Navigation 还支持自定义目标类型。
如果您的应用未使用 Fragment,那么您首先需要做的就是将应用中的每个屏幕迁移到使用 Fragment。此时您不会移除 Activity。相反,您正在创建 Fragment 来表示屏幕,并按职责分解您的界面逻辑。
引入 Fragment
为了说明引入 Fragment 的过程,我们从一个包含两个屏幕的应用示例开始:一个产品列表屏幕和一个产品详情屏幕。在列表屏幕中点击产品会将用户带到详情屏幕以了解有关该产品的更多信息。
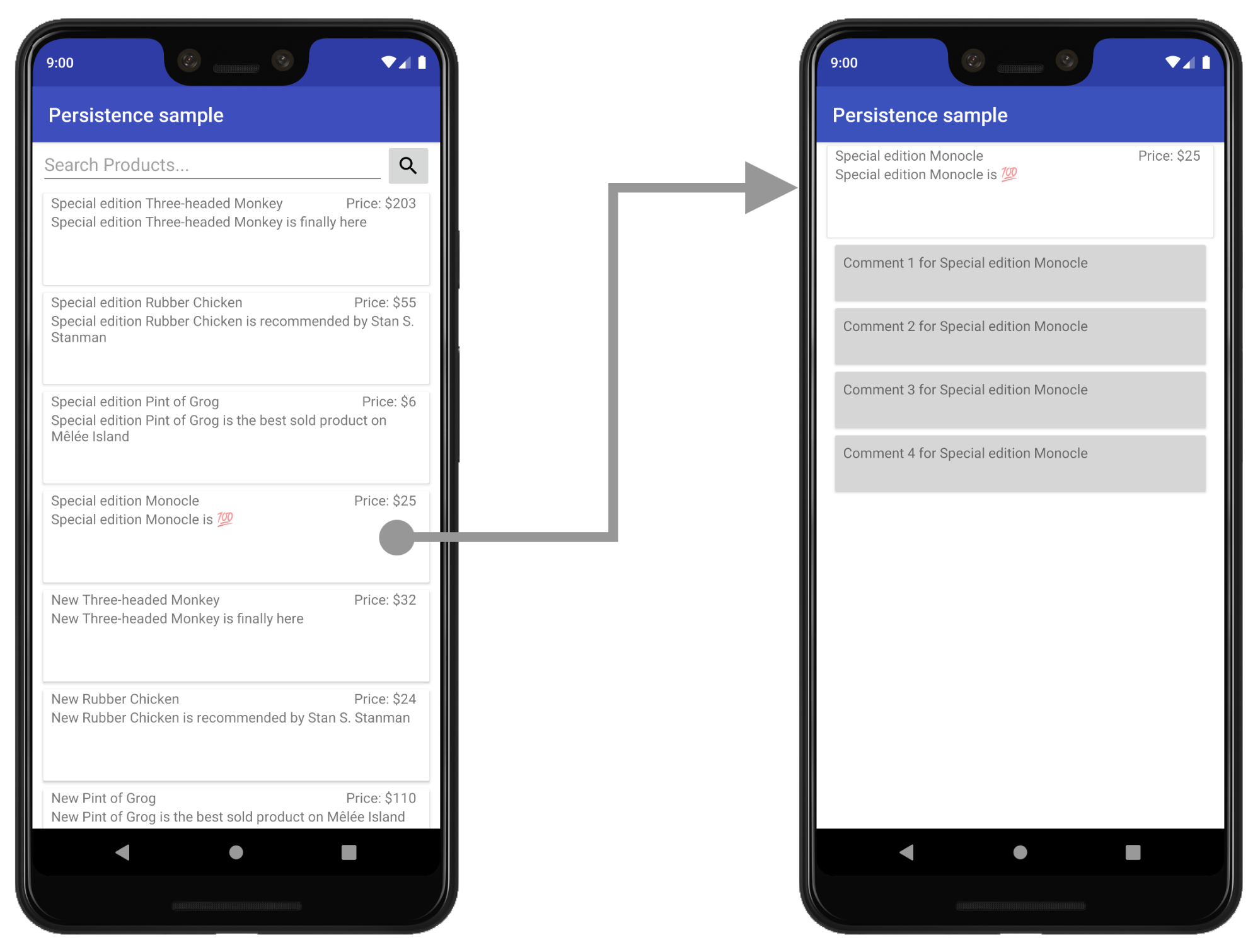
在此示例中,列表和详情屏幕目前是单独的 Activity。
创建新布局以托管界面
要引入 Fragment,首先为 Activity 创建一个新的布局文件来托管 Fragment。这将替换 Activity 当前的内容视图布局。
对于简单视图,您可以使用 FrameLayout,如以下示例 product_list_host 所示
<FrameLayout
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/main_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent" />
id 属性引用了我们稍后添加 Fragment 的内容部分。
接下来,在您 Activity 的 onCreate() 函数中,修改 Activity 的 onCreate 函数中的布局文件引用,使其指向这个新的布局文件
Kotlin
class ProductListActivity : AppCompatActivity() { ... override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { ... // Replace setContentView(R.layout.product_list) with the line below setContentView(R.layout.product_list_host) ... } }
Java
public class ProductListActivity extends AppCompatActivity { ... @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { ... // Replace setContentView(R.layout.product_list); with the line below setContentView(R.layout.product_list_host); ... } }
现有布局(在此示例中为 product_list)将用作您即将创建的 Fragment 的根视图。
创建 Fragment
创建一个新的 Fragment 来管理屏幕的界面。与您的 Activity 宿主名称保持一致是一个好习惯。例如,以下代码段使用 ProductListFragment
Kotlin
class ProductListFragment : Fragment() { // Leave empty for now. }
Java
public class ProductListFragment extends Fragment { // Leave empty for now. }
将 Activity 逻辑移到 Fragment 中
Fragment 定义就位后,下一步是将此屏幕的界面逻辑从 Activity 移到这个新的 Fragment 中。如果您是从基于 Activity 的架构迁移而来,那么您的 Activity 的 onCreate() 函数中可能有很多视图创建逻辑。
以下是一个基于 Activity 的屏幕示例,其中包含我们需要移动的界面逻辑
Kotlin
class ProductListActivity : AppCompatActivity() { // Views and/or ViewDataBinding references, Adapters... private lateinit var productAdapter: ProductAdapter private lateinit var binding: ProductListActivityBinding ... // ViewModels, System Services, other Dependencies... private val viewModel: ProductListViewModel by viewModels() ... override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) // View initialization logic DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.product_list_activity) // Post view initialization logic // Connect adapters productAdapter = ProductAdapter(productClickCallback) binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter) // Initialize view properties, set click listeners, etc. binding.productsSearchBtn.setOnClickListener {...} // Subscribe to state viewModel.products.observe(this, Observer { myProducts -> ... }) // ...and so on } ... }
Java
public class ProductListActivity extends AppCompatActivity { // Views and/or ViewDataBinding references, adapters... private ProductAdapter productAdapter; private ProductListActivityBinding binding; ... // ViewModels, system services, other dependencies... private ProductListViewModel viewModel; ... @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // View initialization logic DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.product_list_activity); // Post view initialization logic // Connect adapters productAdapter = new ProductAdapter(productClickCallback); binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter); // Initialize ViewModels and other dependencies ProductListViewModel viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this).get(ProductListViewModel.java); // Initialize view properties, set click listeners, etc. binding.productsSearchBtn.setOnClickListener(v -> { ... }); // Subscribe to state viewModel.getProducts().observe(this, myProducts -> ... ); // ...and so on }
您的 Activity 还可能控制用户何时以及如何导航到下一个屏幕,如以下示例所示
Kotlin
// Provided to ProductAdapter in ProductListActivity snippet. private val productClickCallback = ProductClickCallback { product -> show(product) } fun show(product: Product) { val intent = Intent(this, ProductActivity::class.java) intent.putExtra(ProductActivity.KEY_PRODUCT_ID, product.id) startActivity(intent) }
Java
// Provided to ProductAdapter in ProductListActivity snippet. private ProductClickCallback productClickCallback = this::show; private void show(Product product) { Intent intent = new Intent(this, ProductActivity.class); intent.putExtra(ProductActivity.KEY_PRODUCT_ID, product.getId()); startActivity(intent); }
在您的 Fragment 中,您将这项工作分配到 onCreateView() 和 onViewCreated() 之间,只有导航逻辑保留在 Activity 中
Kotlin
class ProductListFragment : Fragment() { private lateinit var binding: ProductListFragmentBinding private val viewModel: ProductListViewModel by viewModels() // View initialization logic override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? { binding = DataBindingUtil.inflate( inflater, R.layout.product_list, container, false ) return binding.root } // Post view initialization logic override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { // Connect adapters productAdapter = ProductAdapter(productClickCallback) binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter) // Initialize view properties, set click listeners, etc. binding.productsSearchBtn.setOnClickListener {...} // Subscribe to state viewModel.products.observe(this, Observer { myProducts -> ... }) // ...and so on } // Provided to ProductAdapter private val productClickCallback = ProductClickCallback { product -> if (lifecycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.STARTED)) { (requireActivity() as ProductListActivity).show(product) } } ... }
Java
public class ProductListFragment extends Fragment { private ProductAdapter productAdapter; private ProductListFragmentBinding binding; // View initialization logic @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { binding = DataBindingUtil.inflate( inflater, R.layout.product_list_fragment, container, false); return binding.getRoot(); } // Post view initialization logic @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Connect adapters binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter); // Initialize ViewModels and other dependencies ProductListViewModel viewModel = new ViewModelProvider(this) .get(ProductListViewModel.class); // Initialize view properties, set click listeners, etc. binding.productsSearchBtn.setOnClickListener(...) // Subscribe to state viewModel.getProducts().observe(this, myProducts -> { ... }); // ...and so on // Provided to ProductAdapter private ProductClickCallback productClickCallback = new ProductClickCallback() { @Override public void onClick(Product product) { if (getLifecycle().getCurrentState().isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.STARTED)) { ((ProductListActivity) requireActivity()).show(product); } } }; ... }
在 ProductListFragment 中,请注意没有调用 setContentView() 来膨胀和连接布局。在 Fragment 中,onCreateView() 会初始化根视图。onCreateView() 接受一个 LayoutInflater 实例,该实例可用于根据布局资源文件膨胀根视图。此示例重新使用了 Activity 曾使用的现有 product_list 布局,因为布局本身不需要更改。
如果您的 Activity 的 onStart()、onResume()、onPause() 或 onStop() 函数中存在与导航无关的任何界面逻辑,您可以将这些逻辑移动到 Fragment 中同名的对应函数。
在宿主 Activity 中初始化 Fragment
将所有界面逻辑移动到 Fragment 后,Activity 中应只剩下导航逻辑。
Kotlin
class ProductListActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.product_list_host) } fun show(product: Product) { val intent = Intent(this, ProductActivity::class.java) intent.putExtra(ProductActivity.KEY_PRODUCT_ID, product.id) startActivity(intent) } }
Java
public class ProductListActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.product_list_host); } public void show(Product product) { Intent intent = new Intent(this, ProductActivity.class); intent.putExtra(ProductActivity.KEY_PRODUCT_ID, product.getId()); startActivity(intent); } }
最后一步是在 onCreate() 中创建 Fragment 实例,紧接在设置内容视图之后
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.product_list_host) if (savedInstanceState == null) { val fragment = ProductListFragment() supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.main_content, fragment) .commit() } }
Java
@Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.product_list_host); if (savedInstanceState == null) { ProductListFragment fragment = new ProductListFragment(); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.main_content, fragment) .commit(); } }
如本例所示,FragmentManager 会在配置更改时自动保存和恢复 Fragment,因此只有当 savedInstanceState 为 null 时才需要添加 Fragment。
将 Intent extra 传递给 Fragment
如果您的 Activity 通过 intent 接收 Extras,您可以将这些数据直接作为参数传递给 Fragment。
在此示例中,ProductDetailsFragment 直接从 Activity 的 intent extra 接收其参数
Kotlin
... if (savedInstanceState == null) { val fragment = ProductDetailsFragment() // Intent extras and Fragment Args are both of type android.os.Bundle. fragment.arguments = intent.extras supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.main_content, fragment) .commit() } ...
Java
... if (savedInstanceState == null) { ProductDetailsFragment fragment = new ProductDetailsFragment(); // Intent extras and fragment Args are both of type android.os.Bundle. fragment.setArguments(getIntent().getExtras()); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.main_content, fragment) .commit(); } ...
至此,您应该能够测试运行您的应用,其中第一个屏幕已更新为使用 Fragment。继续迁移其余基于 Activity 的屏幕,并在每次迭代后花时间进行测试。
集成 Navigation 组件
一旦您使用基于 Fragment 的架构,您就可以开始集成 Navigation 组件了。
首先,按照Navigation 库发布说明中的说明,将最新的 Navigation 依赖项添加到您的项目中。
创建导航图
Navigation 组件以图形的形式在资源文件中表示您的应用导航配置,就像您的应用视图一样。这有助于将您的应用导航组织在代码库之外,并提供一种可视化编辑应用导航的方式。
要创建导航图,首先创建一个名为 navigation 的新资源文件夹。要添加图,右键点击此目录,然后选择 New > Navigation resource file。

Navigation 组件使用 Activity 作为导航宿主,并在用户浏览应用时将单个 Fragment 交换到该宿主中。在您开始可视化布局您的应用导航之前,您需要在此图的宿主 Activity 中配置一个 NavHost。由于我们使用的是 Fragment,因此我们可以使用 Navigation 组件的默认 NavHost 实现,即 NavHostFragment。
通过放置在宿主 Activity 中的 FragmentContainerView 配置 NavHostFragment,如以下示例所示
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
app:navGraph="@navigation/product_list_graph"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
android:id="@+id/main_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
app:NavGraph 属性指向与此导航宿主关联的导航图。设置此属性会膨胀导航图,并在 NavHostFragment 上设置图属性。app:defaultNavHost 属性确保您的 NavHostFragment 拦截系统返回按钮。
如果您使用顶级导航,例如 DrawerLayout 或 BottomNavigationView,此 FragmentContainerView 会替换您的主内容视图元素。有关示例,请参阅使用 NavigationUI 更新界面组件。
对于简单布局,您可以将此 FragmentContainerView 元素作为根 ViewGroup 的子元素包含在内
<FrameLayout
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/main_content"
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
app:navGraph="@navigation/product_list_graph"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</FrameLayout>
如果您点击底部的设计选项卡,您应该会看到一个类似于下面所示的图形。在图的左上方,在目标下,您可以看到以 layout_name (resource_id) 形式引用的 NavHost Activity。
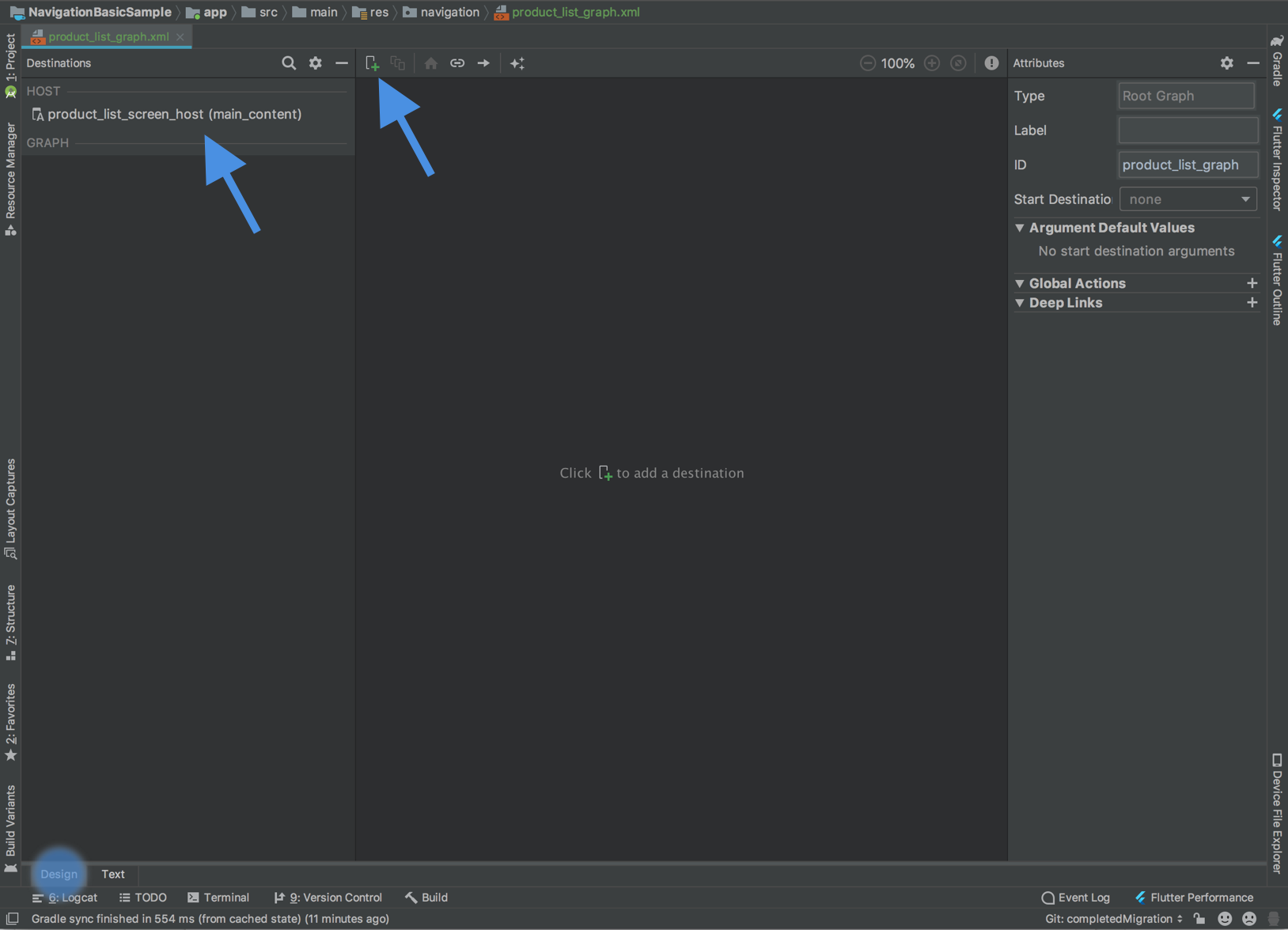
点击顶部的加号按钮 ![]() ,将您的 Fragment 添加到此图中。
,将您的 Fragment 添加到此图中。
Navigation 组件将单个屏幕称为目标。目标可以是 Fragment、Activity 或自定义目标。您可以将任何类型目标添加到您的图中,但请注意,Activity 目标被视为终端目标,因为一旦您导航到 Activity 目标,您就会在单独的导航宿主和图中操作。
Navigation 组件将用户从一个目标到达另一个目标的方式称为操作。操作还可以描述过渡动画和弹出行为。
移除 Fragment 事务
现在您正在使用 Navigation 组件,如果您在同一 Activity 下的基于 Fragment 的屏幕之间导航,则可以移除 FragmentManager 交互。
如果您的应用在同一 Activity 下使用多个 Fragment,或使用抽屉式布局或底部导航等顶级导航,那么您可能正在使用 FragmentManager 和 FragmentTransactions 来在界面的主要内容部分添加或替换 Fragment。现在可以使用 Navigation 组件通过提供操作来链接图中的目标,然后使用 NavController 进行导航,从而替换和简化此操作。
以下是您可能会遇到的几种场景以及每种场景的迁移方法。
单个 Activity 管理多个 Fragment
如果您有一个 Activity 管理多个 Fragment,则您的 Activity 代码可能如下所示
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) // Logic to load the starting destination // when the Activity is first created if (savedInstanceState == null) { val fragment = ProductListFragment() supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment, ProductListFragment.TAG) .commit() } } // Logic to navigate the user to another destination. // This may include logic to initialize and set arguments on the destination // fragment or even transition animations between the fragments (not shown here). fun navigateToProductDetail(productId: String) { val fragment = new ProductDetailsFragment() val args = Bundle().apply { putInt(KEY_PRODUCT_ID, productId) } fragment.arguments = args supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction() .addToBackStack(ProductDetailsFragment.TAG) .replace(R.id.fragment_container, fragment, ProductDetailsFragment.TAG) .commit() } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // Logic to load the starting destination when the activity is first created. if (savedInstanceState == null) { val fragment = ProductListFragment() supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction() .add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment, ProductListFragment.TAG) .commit(); } } // Logic to navigate the user to another destination. // This may include logic to initialize and set arguments on the destination // fragment or even transition animations between the fragments (not shown here). public void navigateToProductDetail(String productId) { Fragment fragment = new ProductDetailsFragment(); Bundle args = new Bundle(); args.putInt(KEY_PRODUCT_ID, productId); fragment.setArguments(args); getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction() .addToBackStack(ProductDetailsFragment.TAG) .replace(R.id.fragment_container, fragment, ProductDetailsFragment.TAG) .commit(); } }
在源目标内部,您可能会响应某个事件调用导航函数,如下所示
Kotlin
class ProductListFragment : Fragment() { ... override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { // In this example a callback is passed to respond to an item clicked // in a RecyclerView productAdapter = ProductAdapter(productClickCallback) binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter) } ... // The callback makes the call to the activity to make the transition. private val productClickCallback = ProductClickCallback { product -> (requireActivity() as MainActivity).navigateToProductDetail(product.id) } }
Java
public class ProductListFragment extends Fragment { ... @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { // In this example a callback is passed to respond to an item clicked in a RecyclerView productAdapter = new ProductAdapter(productClickCallback); binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter); } ... // The callback makes the call to the activity to make the transition. private ProductClickCallback productClickCallback = product -> ( ((MainActivity) requireActivity()).navigateToProductDetail(product.getId()) ); }
这可以通过更新导航图来替换,以设置起始目标和操作,从而链接您的目标并在需要时定义参数
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/product_list_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/product_list">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_list"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductListFragment"
android:label="Product List"
tools:layout="@layout/product_list">
<action
android:id="@+id/navigate_to_product_detail"
app:destination="@id/product_detail" />
</fragment>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_detail"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductDetailFragment"
android:label="Product Detail"
tools:layout="@layout/product_detail">
<argument
android:name="product_id"
app:argType="integer" />
</fragment>
</navigation>
然后,您可以更新您的 Activity
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { // No need to load the start destination, handled automatically by the Navigation component override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { // No need to load the start destination, handled automatically by the Navigation component @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } }
该 Activity 不再需要 navigateToProductDetail() 方法。在下一节中,我们将更新 ProductListFragment 以使用 NavController 导航到下一个产品详情屏幕。
安全地传递参数
Navigation 组件有一个名为 Safe Args 的 Gradle 插件,它为目标和操作指定的参数生成简单的对象和构建器类,以实现类型安全的访问。
应用该插件后,在导航图中为目标定义的任何参数都会导致 Navigation 组件框架生成一个 Arguments 类,该类为目标目标提供类型安全参数。定义操作会使插件生成一个 Directions 配置类,该类可用于告知 NavController 如何将用户导航到目标目标。当操作指向需要参数的目标时,生成的 Directions 类会包含需要这些参数的构造函数方法。
在 Fragment 内部,使用 NavController 和生成的 Directions 类为目标目标提供类型安全参数,如以下示例所示
Kotlin
class ProductListFragment : Fragment() { override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { // In this example a callback is passed to respond to an item clicked in a RecyclerView productAdapter = ProductAdapter(productClickCallback) binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter) } ... // The callback makes the call to the NavController to make the transition. private val productClickCallback = ProductClickCallback { product -> val directions = ProductListDirections.navigateToProductDetail(product.id) findNavController().navigate(directions) } }
Java
public class ProductListFragment extends Fragment { ... @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { // In this example a callback is passed to respond to an item clicked in a RecyclerView productAdapter = new ProductAdapter(productClickCallback); binding.productsList.setAdapter(productAdapter); } ... // The callback makes the call to the activity to make the transition. private ProductClickCallback productClickCallback = product -> { ProductListDirections.ViewProductDetails directions = ProductListDirections.navigateToProductDetail(product.getId()); NavHostFragment.findNavController(this).navigate(directions); }; }
顶级导航
如果您的应用使用 DrawerLayout,您的 Activity 中可能有很多配置逻辑,用于管理抽屉的打开和关闭以及导航到其他目标。
您的结果 Activity 可能如下所示
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), NavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) val toolbar: Toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar) setSupportActionBar(toolbar) val drawerLayout: DrawerLayout = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout) val navView: NavigationView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view) val toggle = ActionBarDrawerToggle( this, drawerLayout, toolbar, R.string.navigation_drawer_open, R.string.navigation_drawer_close ) drawerLayout.addDrawerListener(toggle) toggle.syncState() navView.setNavigationItemSelectedListener(this) } override fun onBackPressed() { val drawerLayout: DrawerLayout = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout) if (drawerLayout.isDrawerOpen(GravityCompat.START)) { drawerLayout.closeDrawer(GravityCompat.START) } else { super.onBackPressed() } } override fun onNavigationItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean { // Handle navigation view item clicks here. when (item.itemId) { R.id.home -> { val homeFragment = HomeFragment() show(homeFragment) } R.id.gallery -> { val galleryFragment = GalleryFragment() show(galleryFragment) } R.id.slide_show -> { val slideShowFragment = SlideShowFragment() show(slideShowFragment) } R.id.tools -> { val toolsFragment = ToolsFragment() show(toolsFragment) } } val drawerLayout: DrawerLayout = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout) drawerLayout.closeDrawer(GravityCompat.START) return true } } private fun show(fragment: Fragment) { val drawerLayout = drawer_layout as DrawerLayout val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager fragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(R.id.main_content, fragment) .commit() drawerLayout.closeDrawer(GravityCompat.START) }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements NavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); setSupportActionBar(toolbar); DrawerLayout drawer = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout); NavigationView navigationView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view); ActionBarDrawerToggle toggle = new ActionBarDrawerToggle( this, drawer, toolbar, R.string.navigation_drawer_open, R.string.navigation_drawer_close); drawer.addDrawerListener(toggle); toggle.syncState(); navigationView.setNavigationItemSelectedListener(this); } @Override public void onBackPressed() { DrawerLayout drawer = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout); if (drawer.isDrawerOpen(GravityCompat.START)) { drawer.closeDrawer(GravityCompat.START); } else { super.onBackPressed(); } } @Override public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(MenuItem item) { // Handle navigation view item clicks here. int id = item.getItemId(); if (id == R.id.home) { Fragment homeFragment = new HomeFragment(); show(homeFragment); } else if (id == R.id.gallery) { Fragment galleryFragment = new GalleryFragment(); show(galleryFragment); } else if (id == R.id.slide_show) { Fragment slideShowFragment = new SlideShowFragment(); show(slideShowFragment); } else if (id == R.id.tools) { Fragment toolsFragment = new ToolsFragment(); show(toolsFragment); } DrawerLayout drawer = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout); drawer.closeDrawer(GravityCompat.START); return true; } private void show(Fragment fragment) { DrawerLayout drawerLayout = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout); FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager(); fragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(R.id.main_content, fragment) .commit(); drawerLayout.closeDrawer(GravityCompat.START); } }
将 Navigation 组件添加到项目并创建导航图后,添加图中每个内容目标(例如,上面示例中的主页、图库、幻灯片放映和工具)。请确保您的菜单项 id 值与其关联的目标 id 值匹配,如下所示
<!-- activity_main_drawer.xml -->
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:showIn="navigation_view">
<group android:checkableBehavior="single">
<item
android:id="@+id/home"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_menu_camera"
android:title="@string/menu_home" />
<item
android:id="@+id/gallery"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_menu_gallery"
android:title="@string/menu_gallery" />
<item
android:id="@+id/slide_show"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_menu_slideshow"
android:title="@string/menu_slideshow" />
<item
android:id="@+id/tools"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_menu_manage"
android:title="@string/menu_tools" />
</group>
</menu>
<!-- activity_main_graph.xml -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/home">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/home"
android:name="com.example.HomeFragment"
android:label="Home"
tools:layout="@layout/home" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/gallery"
android:name="com.example.GalleryFragment"
android:label="Gallery"
tools:layout="@layout/gallery" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/slide_show"
android:name="com.example.SlideShowFragment"
android:label="Slide Show"
tools:layout="@layout/slide_show" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/tools"
android:name="com.example.ToolsFragment"
android:label="Tools"
tools:layout="@layout/tools" />
</navigation>
如果您将菜单和图中的 id 值匹配起来,那么您可以将此 Activity 的 NavController 连接起来,以根据菜单项自动处理导航。NavController 还会处理 DrawerLayout 的打开和关闭,并适当处理向上和返回按钮的行为。
然后可以更新您的 MainActivity,将 NavController 连接到 Toolbar 和 NavigationView。
有关示例,请参见以下代码段
Kotlin
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { val drawerLayout by lazy { findViewById<DrawerLayout>(R.id.drawer_layout) } val navController by lazy { (supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.main_content) as NavHostFragment).navController } val navigationView by lazy { findViewById<NavigationView>(R.id.nav_view) } override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) val toolbar = findViewById<Toolbar>(R.id.toolbar) setSupportActionBar(toolbar) // Show and Manage the Drawer and Back Icon setupActionBarWithNavController(navController, drawerLayout) // Handle Navigation item clicks // This works with no further action on your part if the menu and destination id’s match. navigationView.setupWithNavController(navController) } override fun onSupportNavigateUp(): Boolean { // Allows NavigationUI to support proper up navigation or the drawer layout // drawer menu, depending on the situation return navController.navigateUp(drawerLayout) } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private DrawerLayout drawerLayout; private NavController navController; private NavigationView navigationView; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); drawerLayout = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout); NavHostFragment navHostFragment = (NavHostFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.main_content); navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); navigationView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view); Toolbar toolbar = findViewById(R.id.toolbar); setSupportActionBar(toolbar); // Show and Manage the Drawer and Back Icon NavigationUI.setupActionBarWithNavController(this, navController, drawerLayout); // Handle Navigation item clicks // This works with no further action on your part if the menu and destination id’s match. NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(navigationView, navController); } @Override public boolean onSupportNavigateUp() { // Allows NavigationUI to support proper up navigation or the drawer layout // drawer menu, depending on the situation. return NavigationUI.navigateUp(navController, drawerLayout); } }
您可以将相同的技术用于基于 BottomNavigationView 的导航和基于菜单的导航。有关更多示例,请参阅使用 NavigationUI 更新界面组件。
添加 Activity 目标
一旦您的应用中的每个屏幕都已连接以使用 Navigation 组件,并且您不再使用 FragmentTransactions 在基于 Fragment 的目标之间进行过渡,下一步就是消除 startActivity 调用。
首先,确定您应用中存在两个独立导航图且使用 startActivity 在它们之间进行过渡的地方。
此示例包含两个图(A 和 B)以及一个用于从 A 过渡到 B 的 startActivity() 调用。
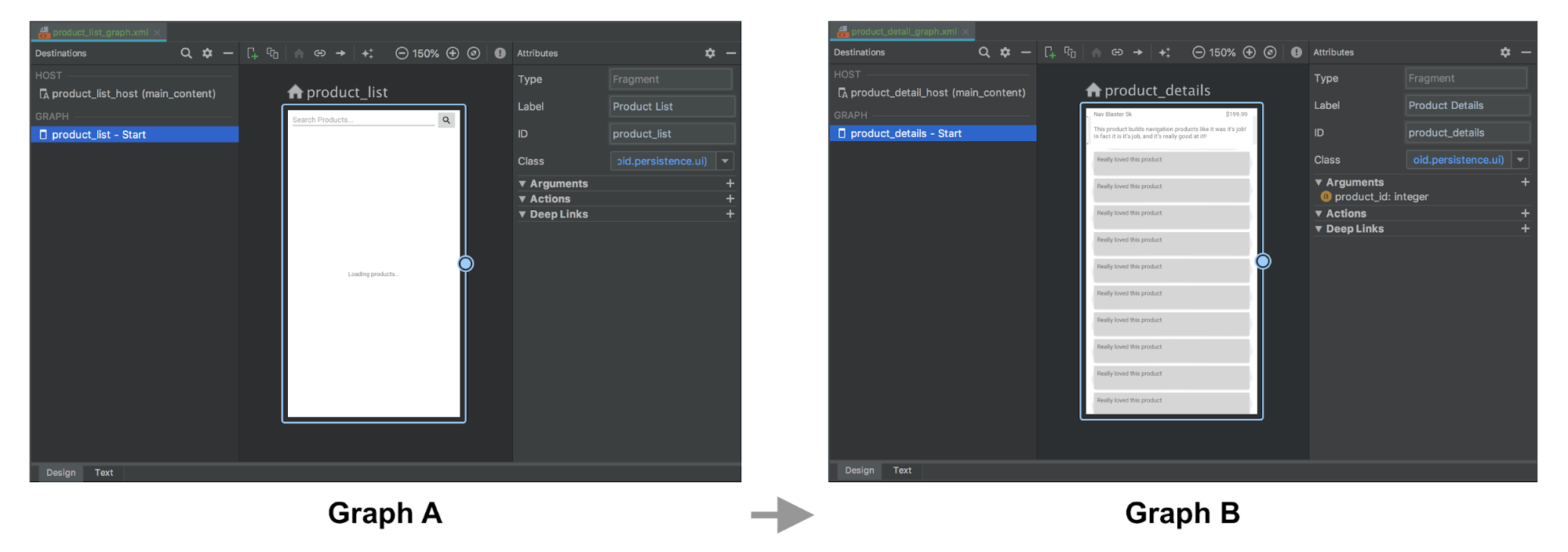
Kotlin
fun navigateToProductDetails(productId: String) { val intent = Intent(this, ProductDetailsActivity::class.java) intent.putExtra(KEY_PRODUCT_ID, productId) startActivity(intent) }
Java
private void navigateToProductDetails(String productId) { Intent intent = new Intent(this, ProductDetailsActivity.class); intent.putExtra(KEY_PRODUCT_ID, productId); startActivity(intent);
接下来,用图 A 中的 Activity 目标替换这些,该目标表示导航到图 B 的宿主 Activity。如果您有要传递给图 B 的起始目标的参数,则可以在 Activity 目标定义中指定它们。
在以下示例中,图 A 定义了一个 Activity 目标,该目标接受 product_id 参数以及一个操作。图 B 没有更改。
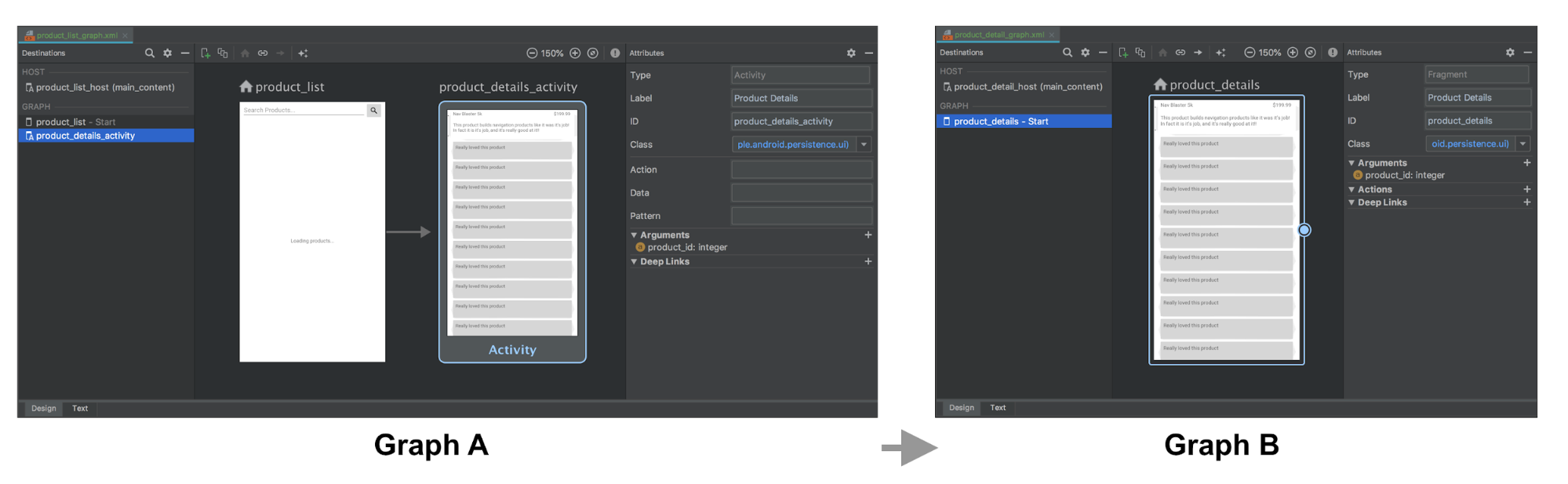
图 A 和图 B 的 XML 表示可能如下所示
<!-- Graph A -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/product_list_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/product_list">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_list"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductListFragment"
android:label="Product List"
tools:layout="@layout/product_list_fragment">
<action
android:id="@+id/navigate_to_product_detail"
app:destination="@id/product_details_activity" />
</fragment>
<activity
android:id="@+id/product_details_activity"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductDetailsActivity"
android:label="Product Details"
tools:layout="@layout/product_details_host">
<argument
android:name="product_id"
app:argType="integer" />
</activity>
</navigation>
<!-- Graph B -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
app:startDestination="@id/product_details">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_details"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductDetailsFragment"
android:label="Product Details"
tools:layout="@layout/product_details_fragment">
<argument
android:name="product_id"
app:argType="integer" />
</fragment>
</navigation>
您可以使用与导航到 Fragment 目标相同的机制导航到图 B 的宿主 Activity
Kotlin
fun navigateToProductDetails(productId: String) { val directions = ProductListDirections.navigateToProductDetail(productId) findNavController().navigate(directions) }
Java
private void navigateToProductDetails(String productId) { ProductListDirections.NavigateToProductDetail directions = ProductListDirections.navigateToProductDetail(productId); Navigation.findNavController(getView()).navigate(directions);
将 Activity 目标参数传递给起始目标 Fragment
如果目标 Activity 接收 extra,如上一个示例所示,您可以将这些数据直接作为参数传递给起始目标,但您需要手动在宿主 Activity 的 onCreate() 方法中设置宿主的导航图,以便将 intent extra 作为参数传递给 Fragment,如下所示
Kotlin
class ProductDetailsActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.product_details_host) val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.main_content) as NavHostFragment val navController = navHostFragment.navController navController .setGraph(R.navigation.product_detail_graph, intent.extras) } }
Java
public class ProductDetailsActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.product_details_host); NavHostFragment navHostFragment = (NavHostFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.main_content); NavController navController = navHostFragment.getNavController(); navController .setGraph(R.navigation.product_detail_graph, getIntent().getExtras()); } }
可以使用生成的 args 类从 Fragment 参数 Bundle 中提取数据,如以下示例所示
Kotlin
class ProductDetailsFragment : Fragment() { val args by navArgs<ProductDetailsArgs>() override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { val productId = args.productId ... } ...
Java
public class ProductDetailsFragment extends Fragment { ProductDetailsArgs args; @Override public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); args = ProductDetailsArgs.fromBundle(requireArguments()); } @Override public void onViewCreated(@NonNull View view, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { int productId = args.getProductId(); ... } ...
合并 Activity
您可以在多个 Activity 共享同一布局(例如包含单个 Fragment 的简单 FrameLayout)的情况下合并导航图。在大多数这些情况下,您只需合并每个导航图中的所有元素,并将任何 Activity 目标元素更新为 Fragment 目标即可。
以下示例结合了上一节中的图 A 和图 B
合并前
<!-- Graph A -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/product_list_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/product_list">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_list"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductListFragment"
android:label="Product List Fragment"
tools:layout="@layout/product_list">
<action
android:id="@+id/navigate_to_product_detail"
app:destination="@id/product_details_activity" />
</fragment>
<activity
android:id="@+id/product_details_activity"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductDetailsActivity"
android:label="Product Details Host"
tools:layout="@layout/product_details_host">
<argument android:name="product_id"
app:argType="integer" />
</activity>
</navigation>
<!-- Graph B -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/product_detail_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/product_details">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_details"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductDetailsFragment"
android:label="Product Details"
tools:layout="@layout/product_details">
<argument
android:name="product_id"
app:argType="integer" />
</fragment>
</navigation>
合并后
<!-- Combined Graph A and B -->
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/product_list_graph"
app:startDestination="@id/product_list">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_list"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductListFragment"
android:label="Product List Fragment"
tools:layout="@layout/product_list">
<action
android:id="@+id/navigate_to_product_detail"
app:destination="@id/product_details" />
</fragment>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/product_details"
android:name="com.example.android.persistence.ui.ProductDetailsFragment"
android:label="Product Details"
tools:layout="@layout/product_details">
<argument
android:name="product_id"
app:argType="integer" />
</fragment>
</navigation>
在合并时保持操作名称不变可以使这个过程无缝进行,无需对现有代码库进行任何更改。例如,这里的 navigateToProductDetail 保持不变。唯一的区别是,此操作现在表示导航到同一 NavHost 中的 Fragment 目标,而不是 Activity 目标
Kotlin
fun navigateToProductDetails(productId: String) { val directions = ProductListDirections.navigateToProductDetail(productId) findNavController().navigate(directions) }
Java
private void navigateToProductDetails(String productId) { ProductListDirections.NavigateToProductDetail directions = ProductListDirections.navigateToProductDetail(productId); Navigation.findNavController(getView()).navigate(directions);
其他资源
有关导航的更多信息,请参阅以下主题
- 使用 NavigationUI 更新界面组件 - 了解如何使用顶部应用栏、抽屉式导航栏和底部导航管理导航
- 测试导航 - 了解如何测试您的应用导航工作流程
