有时,你可能需要查询三个或更多相互关联的表。在这种情况下,你需要定义表之间的嵌套关系。
假设在音乐流媒体应用示例中,你想要查询所有用户、每个用户的所有播放列表以及每个用户每个播放列表中的所有歌曲。用户与播放列表之间存在一对多关系,播放列表与歌曲之间存在多对多关系。以下代码示例展示了代表这些实体的类,以及播放列表与歌曲之间的多对多关系的交叉引用表。
Kotlin
@Entity
data class User(
@PrimaryKey val userId: Long,
val name: String,
val age: Int
)
@Entity
data class Playlist(
@PrimaryKey val playlistId: Long,
val userCreatorId: Long,
val playlistName: String
)
@Entity
data class Song(
@PrimaryKey val songId: Long,
val songName: String,
val artist: String
)
@Entity(primaryKeys = ["playlistId", "songId"])
data class PlaylistSongCrossRef(
val playlistId: Long,
val songId: Long
)
Java
@Entity
public class User {
@PrimaryKey public long userId;
public String name;
public int age;
}
@Entity
public class Playlist {
@PrimaryKey public long playlistId;
public long userCreatorId;
public String playlistName;
}
@Entity
public class Song {
@PrimaryKey public long songId;
public String songName;
public String artist;
}
@Entity(primaryKeys = {"playlistId", "songId"})
public class PlaylistSongCrossRef {
public long playlistId;
public long songId;
}
首先,像往常一样,使用数据类和 @Relation 注解来建模集合中两个表之间的关系。以下示例展示了一个 PlaylistWithSongs 类,它建模了 Playlist 实体类和 Song 实体类之间的多对多关系。
Kotlin
data class PlaylistWithSongs(
@Embedded val playlist: Playlist,
@Relation(
parentColumn = "playlistId",
entityColumn = "songId",
associateBy = Junction(PlaylistSongCrossRef::class)
)
val songs: List<Song>
)
Java
public class PlaylistWithSongs {
@Embedded public Playlist playlist;
@Relation(
parentColumn = "playlistId",
entityColumn = "songId",
associateBy = Junction(PlaylistSongCrossRef.class)
)
public List<Song> songs;
}
定义了表示此关系的数据类后,创建另一个数据类来建模集合中的另一个表与第一个关系类之间的关系,将现有关系“嵌套”在新关系中。以下示例展示了一个 UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs 类,它建模了 User 实体类和 PlaylistWithSongs 关系类之间的一对多关系。
Kotlin
data class UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs(
@Embedded val user: User
@Relation(
entity = Playlist::class,
parentColumn = "userId",
entityColumn = "userCreatorId"
)
val playlists: List<PlaylistWithSongs>
)
Java
public class UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs {
@Embedded public User user;
@Relation(
entity = Playlist.class,
parentColumn = "userId",
entityColumn = "userCreatorId"
)
public List<PlaylistWithSongs> playlists;
}
UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs 类间接建模了所有三个实体类之间的关系:User、Playlist 和 Song。图 1 对此进行了说明。
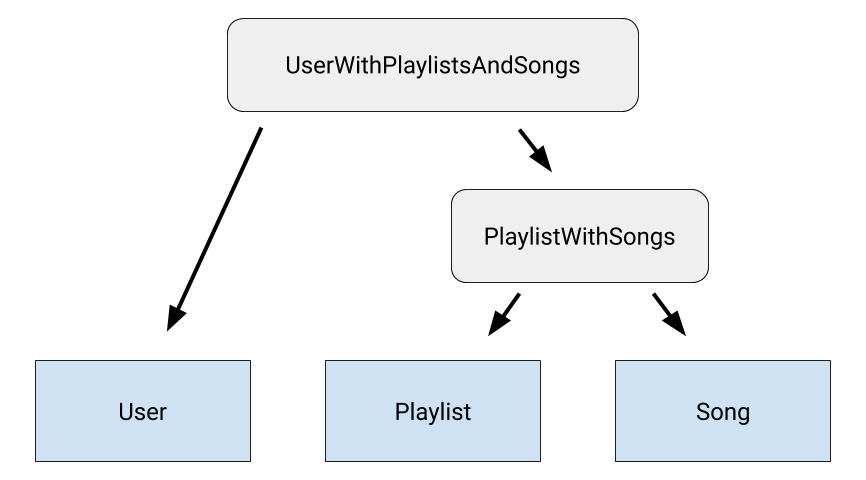
如果集合中还有更多表,请创建一个类来建模每个剩余表与建模所有先前表之间关系的关系类之间的关系。这将在所有要查询的表之间创建一个嵌套关系链。
最后,在 DAO 类中添加一个方法,以暴露应用所需的查询函数。此方法需要 Room 运行多个查询,因此添加 @Transaction 注解,以确保整个操作以原子方式执行。
Kotlin
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
fun getUsersWithPlaylistsAndSongs(): List<UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs>
Java
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM User")
public List<UserWithPlaylistsAndSongs> getUsersWithPlaylistsAndSongs();
