注意:自 2021 年 8 月起,所有新应用都必须作为 App Bundle 发布。如果您将应用发布到 Google Play,请构建并上传 Android App Bundle。这样,Google Play 会自动为每个用户的设备配置生成并提供优化的 APK,因此他们只需下载运行应用所需的代码和资源。如果您要发布到不支持 AAB 格式的商店,则发布多个 APK 会很有用。在这种情况下,您必须自行构建、签名和管理每个 APK。
虽然在可能的情况下最好构建单个 APK 以支持所有目标设备,但这可能会导致 APK 文件非常大,因为其中包含支持多种屏幕密度或应用二进制接口 (ABI) 的文件。减小 APK 大小的一种方法是创建包含特定屏幕密度或 ABI 文件的多个 APK。
Gradle 可以创建单独的 APK,其中只包含特定于每种密度或 ABI 的代码和资源。本页面介绍了如何配置您的构建以生成多个 APK。如果您需要创建不基于屏幕密度或 ABI 的应用的不同版本,请改用构建变体。
配置多个 APK 的构建
要为多个 APK 配置您的构建,请将一个 splits 块添加到您的模块级 build.gradle 文件中。在 splits 块中,提供一个 density 块,用于指定您希望 Gradle 如何生成按密度划分的 APK,或一个 abi 块,用于指定您希望 Gradle 如何生成按 ABI 划分的 APK。您可以同时提供密度和 ABI 块,构建系统会为每种密度和 ABI 组合创建一个 APK。
为屏幕密度配置多个 APK
要为不同的屏幕密度创建单独的 APK,请在 splits 块中添加一个 density 块。在您的 density 块中,提供所需屏幕密度和兼容屏幕尺寸的列表。仅当您在每个 APK 的清单中需要特定的 <compatible-screens> 元素时,才使用兼容屏幕尺寸列表。
以下 Gradle DSL 选项用于为屏幕密度配置多个 APK
-
Groovy 的
enable,Kotlin 脚本的isEnable - 如果您将此元素设置为
true,Gradle 会根据您定义的屏幕密度生成多个 APK。默认值为false。 -
exclude - 指定一个逗号分隔的密度列表,您不希望 Gradle 为这些密度生成单独的 APK。如果您希望为大多数密度生成 APK,但需要排除应用不支持的少数密度,请使用
exclude。 -
reset() -
清除屏幕密度的默认列表。仅与
include元素结合使用,以指定要添加的密度。以下代码段通过调用
reset()清除列表,然后使用include将密度列表设置为仅ldpi和xxhdpireset() // Clears the default list from all densities // to no densities. include "ldpi", "xxhdpi" // Specifies the two densities to generate APKs // for. -
include - 指定一个逗号分隔的密度列表,您希望 Gradle 为这些密度生成 APK。仅与
reset()结合使用以指定精确的密度列表。 -
compatibleScreens -
指定一个逗号分隔的兼容屏幕尺寸列表。这会在每个 APK 的清单中注入一个匹配的
<compatible-screens>节点。此设置提供了一种便捷的方式,可以在同一
build.gradle部分中管理屏幕密度和屏幕尺寸。但是,使用<compatible-screens>可能会限制您的应用可使用的设备类型。有关支持不同屏幕尺寸的其他方法,请参阅屏幕兼容性概览。
由于每个基于屏幕密度的 APK 都包含一个 <compatible-screens> 标签,该标签对 APK 支持的屏幕类型有特定限制——即使您发布了多个 APK——一些新设备也不符合您的多个 APK 过滤器。因此,Gradle 总是生成一个额外的通用 APK,其中包含所有屏幕密度的资源,并且不包含 <compatible-screens> 标签。将此通用 APK 与您的按密度划分的 APK 一起发布,以便为不符合带有 <compatible-screens> 标签的 APK 的设备提供备用方案。
以下示例为除了 ldpi、xxhdpi 和 xxxhdpi 之外的每个屏幕密度生成一个单独的 APK。这是通过使用 exclude 从所有密度的默认列表中删除这三个密度来实现的。
Groovy
android { ... splits { // Configures multiple APKs based on screen density. density { // Configures multiple APKs based on screen density. enable true // Specifies a list of screen densities you don't want Gradle to create multiple APKs for. exclude "ldpi", "xxhdpi", "xxxhdpi" // Specifies a list of compatible screen size settings for the manifest. compatibleScreens 'small', 'normal', 'large', 'xlarge' } } }
Kotlin
android { ... splits { // Configures multiple APKs based on screen density. density { // Configures multiple APKs based on screen density. isEnable = true // Specifies a list of screen densities you don't want Gradle to create multiple APKs for. exclude("ldpi", "xxhdpi", "xxxhdpi") // Specifies a list of compatible screen size settings for the manifest. compatibleScreens("small", "normal", "large", "xlarge") } } }
有关根据特定屏幕类型和设备自定义应用的不同构建变体的更多详细信息,请参阅声明受限屏幕支持。
为 ABI 配置多个 APK
要为不同的 ABI 创建单独的 APK,请在 splits 块中添加一个 abi 块。在您的 abi 块中,提供所需 ABI 的列表。
以下 Gradle DSL 选项用于为每个 ABI 配置多个 APK
-
Groovy 的
enable,或 Kotlin 脚本的isEnable - 如果您将此元素设置为
true,Gradle 会根据您定义的 ABI 生成多个 APK。默认值为false。 -
exclude - 指定一个逗号分隔的 ABI 列表,您不希望 Gradle 为这些 ABI 生成单独的 APK。如果您希望为大多数 ABI 生成 APK,但需要排除应用不支持的少数 ABI,请使用
exclude。 -
reset() -
清除 ABI 的默认列表。仅与
include元素结合使用,以指定要添加的 ABI。以下代码段通过调用
reset()清除列表,然后使用include将 ABI 列表设置为仅x86和x86_64reset() // Clears the default list from all ABIs to no ABIs. include "x86", "x86_64" // Specifies the two ABIs we want to generate APKs for.
-
include - 指定一个逗号分隔的 ABI 列表,您希望 Gradle 为这些 ABI 生成 APK。仅与
reset()结合使用以指定精确的 ABI 列表。 -
Groovy 的
universalApk,或 Kotlin 脚本的isUniversalApk -
如果为
true,Gradle 除了按 ABI 划分的 APK 之外,还会生成一个通用 APK。通用 APK 在单个 APK 中包含所有 ABI 的代码和资源。默认值为false。请注意,此选项仅在
splits.abi块中可用。构建基于屏幕密度的多个 APK 时,Gradle 总是会生成一个通用 APK,其中包含所有屏幕密度的代码和资源。
以下示例为每个 ABI:x86 和 x86_64 生成一个单独的 APK。这是通过使用 reset() 开始一个空的 ABI 列表,然后使用 include 和一个 ABI 列表来完成的,每个 ABI 都会得到一个 APK。
Groovy
android { ... splits { // Configures multiple APKs based on ABI. abi { // Enables building multiple APKs per ABI. enable true // By default all ABIs are included, so use reset() and include to specify that you only // want APKs for x86 and x86_64. // Resets the list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for to none. reset() // Specifies a list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for. include "x86", "x86_64" // Specifies that you don't want to also generate a universal APK that includes all ABIs. universalApk false } } }
Kotlin
android { ... splits { // Configures multiple APKs based on ABI. abi { // Enables building multiple APKs per ABI. isEnable = true // By default all ABIs are included, so use reset() and include to specify that you only // want APKs for x86 and x86_64. // Resets the list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for to none. reset() // Specifies a list of ABIs for Gradle to create APKs for. include("x86", "x86_64") // Specifies that you don't want to also generate a universal APK that includes all ABIs. isUniversalApk = false } } }
有关支持的 ABI 列表,请参阅支持的 ABI。
不带原生/C++ 代码的项目
对于不带原生/C++ 代码的项目,**构建变体**面板有两列:**模块**和**活动构建变体**,如图 1 所示。
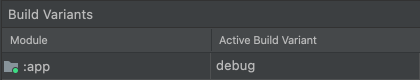
图 1. 不带原生/C++ 代码的项目的**构建变体**面板有两列。
模块的**活动构建变体**值决定了部署和在编辑器中可见的构建变体。要在变体之间切换,请点击模块的**活动构建变体**单元格,然后从列表字段中选择所需的变体。
带原生/C++ 代码的项目
对于带原生/C++ 代码的项目,**构建变体**面板有三列:**模块**、**活动构建变体**和**活动 ABI**,如图 2 所示。
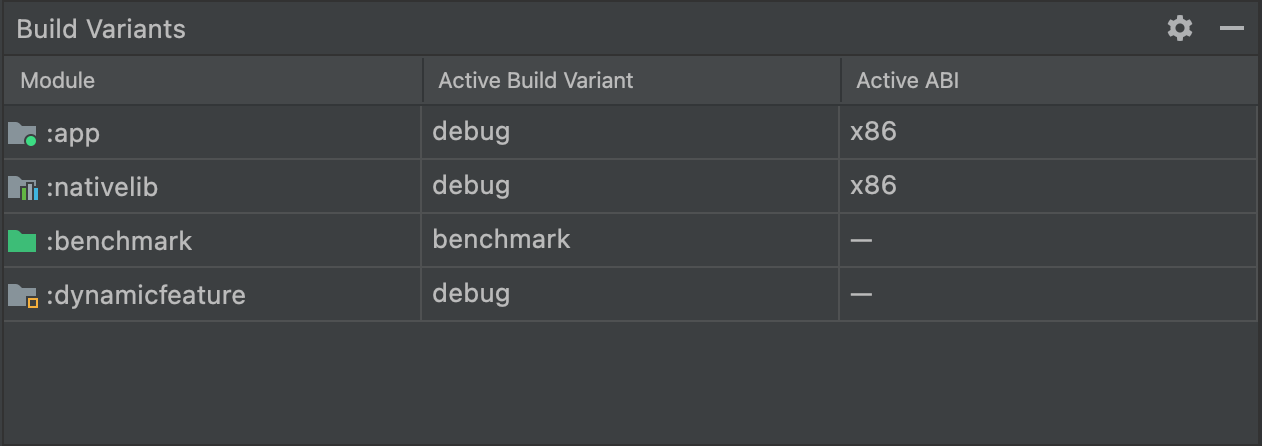 图 2. 带原生/C++ 代码的项目,“构建变体”面板会增加“活动 ABI”列。
图 2. 带原生/C++ 代码的项目,“构建变体”面板会增加“活动 ABI”列。
模块的**活动构建变体**值决定了部署和在编辑器中可见的构建变体。对于原生模块,**活动 ABI** 值决定了编辑器使用的 ABI,但不影响部署。
更改构建类型或 ABI
- 点击**活动构建变体**或**活动 ABI** 列的单元格。
- 从列表字段中选择所需的变体或 ABI。会自动运行新的同步。
更改应用或库模块的任一列都会将更改应用于所有依赖行。
配置版本控制
默认情况下,当 Gradle 生成多个 APK 时,每个 APK 都具有相同的版本信息,如模块级 build.gradle 或 build.gradle.kts 文件中所指定。由于 Google Play 商店不允许同一个应用有多个 APK 都具有相同的版本信息,因此您需要确保每个 APK 在上传到 Play 商店之前都具有唯一的 versionCode。
您可以配置模块级 build.gradle 文件以覆盖每个 APK 的 versionCode。通过创建一个映射,为配置了多个 APK 的每个 ABI 和密度分配一个唯一的数值,您可以将输出版本代码覆盖为一个值,该值结合了在 defaultConfig 或 productFlavors 块中定义的版本代码与分配给密度或 ABI 的数值。
在以下示例中,x86 ABI 的 APK 获得 versionCode 2004,x86_64 ABI 获得 versionCode 3004。
以较大增量(例如 1000)分配版本代码,可以在以后更新应用时分配唯一的版本代码。例如,如果在后续更新中 defaultConfig.versionCode 迭代到 5,Gradle 会为 x86 APK 分配 versionCode 2005,为 x86_64 APK 分配 3005。
提示:如果您的构建包含通用 APK,请为其分配一个比其他任何 APK 都低的 versionCode。由于 Google Play 商店会安装与目标设备兼容且 versionCode 最高的应用版本,因此为通用 APK 分配较低的 versionCode 可确保 Google Play 商店在回退到通用 APK 之前尝试安装您的某个 APK。以下示例代码通过不覆盖通用 APK 的默认 versionCode 来处理此问题。
Groovy
android { ... defaultConfig { ... versionCode 4 } splits { ... } } // Map for the version code that gives each ABI a value. ext.abiCodes = ['armeabi-v7a':1, x86:2, x86_64:3] // For per-density APKs, create a similar map: // ext.densityCodes = ['mdpi': 1, 'hdpi': 2, 'xhdpi': 3] import com.android.build.OutputFile // For each APK output variant, override versionCode with a combination of // ext.abiCodes * 1000 + variant.versionCode. In this example, variant.versionCode // is equal to defaultConfig.versionCode. If you configure product flavors that // define their own versionCode, variant.versionCode uses that value instead. android.applicationVariants.all { variant -> // Assigns a different version code for each output APK // other than the universal APK. variant.outputs.each { output -> // Stores the value of ext.abiCodes that is associated with the ABI for this variant. def baseAbiVersionCode = // Determines the ABI for this variant and returns the mapped value. project.ext.abiCodes.get(output.getFilter(OutputFile.ABI)) // Because abiCodes.get() returns null for ABIs that are not mapped by ext.abiCodes, // the following code doesn't override the version code for universal APKs. // However, because you want universal APKs to have the lowest version code, // this outcome is desirable. if (baseAbiVersionCode != null) { // Assigns the new version code to versionCodeOverride, which changes the // version code for only the output APK, not for the variant itself. Skipping // this step causes Gradle to use the value of variant.versionCode for the APK. output.versionCodeOverride = baseAbiVersionCode * 1000 + variant.versionCode } } }
Kotlin
android { ... defaultConfig { ... versionCode = 4 } splits { ... } } // Map for the version code that gives each ABI a value. val abiCodes = mapOf("armeabi-v7a" to 1, "x86" to 2, "x86_64" to 3) // For per-density APKs, create a similar map: // val densityCodes = mapOf("mdpi" to 1, "hdpi" to 2, "xhdpi" to 3) import com.android.build.api.variant.FilterConfiguration.FilterType.* // For each APK output variant, override versionCode with a combination of // abiCodes * 1000 + variant.versionCode. In this example, variant.versionCode // is equal to defaultConfig.versionCode. If you configure product flavors that // define their own versionCode, variant.versionCode uses that value instead. androidComponents { onVariants { variant -> // Assigns a different version code for each output APK // other than the universal APK. variant.outputs.forEach { output -> val name = output.filters.find { it.filterType == ABI }?.identifier // Stores the value of abiCodes that is associated with the ABI for this variant. val baseAbiCode = abiCodes[name] // Because abiCodes.get() returns null for ABIs that are not mapped by ext.abiCodes, // the following code doesn't override the version code for universal APKs. // However, because you want universal APKs to have the lowest version code, // this outcome is desirable. if (baseAbiCode != null) { // Assigns the new version code to output.versionCode, which changes the version code // for only the output APK, not for the variant itself. output.versionCode.set(baseAbiCode * 1000 + (output.versionCode.get() ?: 0)) } } } }
有关其他版本代码方案的更多示例,请参阅分配版本代码。
构建多个 APK
配置好模块级 build.gradle 或 build.gradle.kts 文件以构建多个 APK 后,点击 **Build > Build APK**(构建 > 构建 APK)以构建**项目**窗格中当前选定模块的所有 APK。Gradle 会在项目的 build/outputs/apk/ 目录中为每个密度或 ABI 创建 APK。
Gradle 会为每个密度或 ABI 构建一个 APK,您可以为其配置多个 APK。如果您为密度和 ABI 都启用多个 APK,Gradle 会为每个密度和 ABI 组合创建一个 APK。
例如,以下 build.gradle 代码段启用了针对 mdpi 和 hdpi 密度以及 x86 和 x86_64 ABI 构建多个 APK
Groovy
... splits { density { enable true reset() include "mdpi", "hdpi" } abi { enable true reset() include "x86", "x86_64" } }
Kotlin
... splits { density { isEnable = true reset() include("mdpi", "hdpi") } abi { isEnable = true reset() include("x86", "x86_64") } }
示例配置的输出包括以下 4 个 APK
app-hdpiX86-release.apk:包含hdpi密度和x86ABI 的代码和资源。app-hdpiX86_64-release.apk:包含hdpi密度和x86_64ABI 的代码和资源。app-mdpiX86-release.apk:包含mdpi密度和x86ABI 的代码和资源。app-mdpiX86_64-release.apk:包含mdpi密度和x86_64ABI 的代码和资源。
当基于屏幕密度构建多个 APK 时,Gradle 除了按密度划分的 APK 之外,总是会生成一个通用 APK,其中包含所有密度的代码和资源。
当基于 ABI 构建多个 APK 时,只有当您在 build.gradle 文件(适用于 Groovy)中的 splits.abi 块中指定 universalApk true 或在 build.gradle.kts 文件(适用于 Kotlin 脚本)中的 splits.abi 块中指定 isUniversalApk = true 时,Gradle 才会生成一个包含所有 ABI 代码和资源的 APK。
APK 文件名格式
构建多个 APK 时,Gradle 使用以下方案生成 APK 文件名
modulename-screendensityABI-buildvariant.apk
方案组件为
-
modulename - 指定正在构建的模块名称。
-
screendensity - 如果启用了按屏幕密度划分的多个 APK,则指定 APK 的屏幕密度,例如
mdpi。 -
ABI -
如果启用了按 ABI 划分的多个 APK,则指定 APK 的 ABI,例如
x86。如果同时启用了按屏幕密度和按 ABI 划分的多个 APK,Gradle 会将密度名称与 ABI 名称连接起来,例如
mdpiX86。如果为按 ABI 划分的 APK 启用了universalApk,Gradle 会使用universal作为通用 APK 文件名的 ABI 部分。 -
buildvariant - 指定正在构建的构建变体,例如
debug。
例如,当为 myApp 的调试版本构建 mdpi 屏幕密度 APK 时,APK 文件名为 myApp-mdpi-debug.apk。配置为同时为 mdpi 屏幕密度和 x86 ABI 构建多个 APK 的 myApp 发布版本,其 APK 文件名为 myApp-mdpiX86-release.apk。
