本页面介绍了如何配置构建变体,以便从单个项目创建应用的不同版本,以及如何正确管理依赖项和签名配置。
每个构建变体代表您可以构建的应用的不同版本。例如,您可能希望构建一个具有有限内容的免费应用版本,以及另一个包含更多内容的付费版本。您还可以根据 API 级别或其他设备差异,构建针对不同设备的应用版本。
构建变体是 Gradle 使用一套特定规则来组合在您的构建类型和产品变体中配置的设置、代码和资源的结果。虽然您不直接配置构建变体,但您需要配置构成它们的构建类型和产品变体。
例如,一个“demo”产品变体可能指定某些功能和设备要求,例如自定义源代码、资源和最低 API 级别,而“debug”构建类型应用不同的构建和打包设置,例如调试选项和签名密钥。结合这两者的构建变体是应用的“demoDebug”版本,它包括“demo”产品变体、“debug”构建类型和 main/ 源集中包含的配置和资源的组合。
配置构建类型
您可以在模块级 build.gradle.kts 文件的 android 块中创建和配置构建类型。当您创建一个新模块时,Android Studio 会自动创建 debug 和 release 构建类型。虽然 debug 构建类型不会出现在构建配置文件中,但 Android Studio 会将其配置为 debuggable true。这使您可以在安全的 Android 设备上调试应用,并使用通用调试密钥库配置应用签名。
如果您想添加或更改某些设置,可以将 debug 构建类型添加到您的配置中。以下示例为 debug 构建类型指定了 applicationIdSuffix,并配置了一个“staging”构建类型,该类型使用 debug 构建类型中的设置进行初始化
Kotlin
android { defaultConfig { manifestPlaceholders["hostName"] = "www.example.com" ... } buildTypes { getByName("release") { isMinifyEnabled = true proguardFiles(getDefaultProguardFile("proguard-android.txt"), "proguard-rules.pro") } getByName("debug") { applicationIdSuffix = ".debug" isDebuggable = true } /** * The `initWith` property lets you copy configurations from other build types, * then configure only the settings you want to change. This one copies the debug build * type, and then changes the manifest placeholder and application ID. */ create("staging") { initWith(getByName("debug")) manifestPlaceholders["hostName"] = "internal.example.com" applicationIdSuffix = ".debugStaging" } } }
Groovy
android { defaultConfig { manifestPlaceholders = [hostName:"www.example.com"] ... } buildTypes { release { minifyEnabled true proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro' } debug { applicationIdSuffix ".debug" debuggable true } /** * The `initWith` property lets you copy configurations from other build types, * then configure only the settings you want to change. This one copies the debug build * type, and then changes the manifest placeholder and application ID. */ staging { initWith debug manifestPlaceholders = [hostName:"internal.example.com"] applicationIdSuffix ".debugStaging" } } }
注意:当您更改构建配置文件时,Android Studio 要求您将项目与新配置同步。要同步您的项目,请在出现通知栏时点击立即同步,或从工具栏点击同步项目  。如果 Android Studio 发现您的配置有任何错误,消息窗口将显示以描述问题。
。如果 Android Studio 发现您的配置有任何错误,消息窗口将显示以描述问题。
要了解有关您可以使用构建类型配置的所有属性的更多信息,请阅读 BuildType 参考。
配置产品变体
创建产品变体类似于创建构建类型。将产品变体添加到您的构建配置中的 productFlavors 块,并包含您想要的设置。产品变体支持与 defaultConfig 相同的属性,因为 defaultConfig 实际上属于 ProductFlavor 类。这意味着您可以在 defaultConfig 块中为所有变体提供基本配置,并且每个变体都可以更改这些默认值中的任何一个,例如 applicationId。要了解有关应用 ID 的更多信息,请阅读 设置应用 ID。
注意:您仍然需要使用 main/ 清单文件中的 package 属性指定软件包名称。您还必须在源代码中使用该软件包名称来引用 R 类或解析任何相对活动或服务注册。这使您可以使用 applicationId 为每个产品变体提供唯一的打包和分发 ID,而无需更改源代码。
所有变体都必须属于一个命名变体维度,这是一个产品变体组。您必须将所有变体分配给一个变体维度;否则,您将收到以下构建错误。
Error: All flavors must now belong to a named flavor dimension. The flavor 'flavor_name' is not assigned to a flavor dimension.
如果给定模块只指定一个变体维度,Android Gradle 插件会自动将模块的所有变体分配给该维度。
以下代码示例创建了一个名为“version”的变体维度,并添加了“demo”和“full”产品变体。这些变体提供了自己的 applicationIdSuffix 和 versionNameSuffix
Kotlin
android { ... defaultConfig {...} buildTypes { getByName("debug"){...} getByName("release"){...} } // Specifies one flavor dimension. flavorDimensions += "version" productFlavors { create("demo") { // Assigns this product flavor to the "version" flavor dimension. // If you are using only one dimension, this property is optional, // and the plugin automatically assigns all the module's flavors to // that dimension. dimension = "version" applicationIdSuffix = ".demo" versionNameSuffix = "-demo" } create("full") { dimension = "version" applicationIdSuffix = ".full" versionNameSuffix = "-full" } } }
Groovy
android { ... defaultConfig {...} buildTypes { debug{...} release{...} } // Specifies one flavor dimension. flavorDimensions "version" productFlavors { demo { // Assigns this product flavor to the "version" flavor dimension. // If you are using only one dimension, this property is optional, // and the plugin automatically assigns all the module's flavors to // that dimension. dimension "version" applicationIdSuffix ".demo" versionNameSuffix "-demo" } full { dimension "version" applicationIdSuffix ".full" versionNameSuffix "-full" } } }
注意:如果您有一个传统应用(在 2021 年 8 月之前创建)并通过 Google Play 上的 APK 分发,那么要使用 Google Play 中的多 APK 支持分发您的应用,请将所有变体都分配相同的 applicationId 值,并为每个变体分配不同的 versionCode。要将应用的不同变体作为单独的应用在 Google Play 中分发,您需要为每个变体分配不同的 applicationId。
创建并配置产品变体后,点击通知栏中的立即同步。同步完成后,Gradle 会根据您的构建类型和产品变体自动创建构建变体,并根据 <product-flavor><Build-Type> 命名它们。例如,如果您创建了“demo”和“full”产品变体,并保留了默认的“debug”和“release”构建类型,Gradle 会创建以下构建变体
-
demoDebug -
demoRelease -
fullDebug -
fullRelease
要选择要构建和运行的构建变体,请依次选择 Build > Select Build Variant,然后从菜单中选择一个构建变体。要开始使用自己的功能和资源自定义每个构建变体,您需要创建和管理源集,如本页所述。
更改构建变体的应用 ID
当您为应用构建 APK 或 AAB 时,构建工具会使用 build.gradle.kts 文件中 defaultConfig 块中定义的应用 ID 为应用打上标签,如以下示例所示。但是,如果您想创建不同版本的应用,使其在 Google Play 商店中显示为单独的列表(例如“免费”和“专业”版本),则需要创建单独的构建变体,每个变体都有不同的应用 ID。
在这种情况下,将每个构建变体定义为单独的产品变体。对于 productFlavors 块中的每个变体,您可以重新定义 applicationId 属性,或者使用 applicationIdSuffix 将一个片段附加到默认应用 ID,如下所示
Kotlin
android { defaultConfig { applicationId = "com.example.myapp" } productFlavors { create("free") { applicationIdSuffix = ".free" } create("pro") { applicationIdSuffix = ".pro" } } }
Groovy
android { defaultConfig { applicationId "com.example.myapp" } productFlavors { free { applicationIdSuffix ".free" } pro { applicationIdSuffix ".pro" } } }
这样,"free" 产品变体的应用 ID 就是 "com.example.myapp.free"。
您还可以使用 applicationIdSuffix 根据您的构建类型附加一个片段,如下所示
Kotlin
android { ... buildTypes { getByName("debug") { applicationIdSuffix = ".debug" } } }
Groovy
android { ... buildTypes { debug { applicationIdSuffix ".debug" } } }
由于 Gradle 在产品变体之后应用构建类型配置,因此“free debug”构建变体的应用 ID 为“com.example.myapp.free.debug”。当您希望在同一设备上同时拥有调试版本和发布版本时,这非常有用,因为没有两个应用可以拥有相同的应用 ID。
如果您有一个遗留应用(在 2021 年 8 月之前创建)并通过 Google Play 上的 APK 分发,并且您想使用相同的应用列表来分发针对不同设备配置(例如 API 级别)的多个 APK,则必须为每个构建变体使用相同的应用 ID,但为每个 APK 提供不同的versionCode。有关更多信息,请阅读多 APK 支持。使用 AAB 发布不受影响,因为它默认使用单个工件,该工件使用单个版本代码和应用 ID。
提示:如果您需要在清单文件中引用应用 ID,则可以在任何清单属性中使用 ${applicationId} 占位符。在构建过程中,Gradle 会将此标记替换为实际的应用 ID。有关详细信息,请参阅将构建变量注入到清单中。
将多个产品变体与变体维度结合
在某些情况下,您可能希望将多个产品变体的配置结合起来。例如,您可能希望为“full”和“demo”产品变体创建基于 API 级别的不同配置。为此,Android Gradle 插件允许您创建多个产品变体组作为变体维度。
在构建应用时,Gradle 会将您定义的每个变体维度中的产品变体配置,以及构建类型配置,组合起来以创建最终的构建变体。Gradle 不会组合属于相同变体维度的产品变体。
以下代码示例使用 flavorDimensions 属性创建了一个“mode”变体维度,用于对“full”和“demo”产品变体进行分组,以及一个“api”变体维度,用于对基于 API 级别的产品变体配置进行分组
Kotlin
android { ... buildTypes { getByName("debug") {...} getByName("release") {...} } // Specifies the flavor dimensions you want to use. The order in which you // list the dimensions determines their priority, from highest to lowest, // when Gradle merges variant sources and configurations. You must assign // each product flavor you configure to one of the flavor dimensions. flavorDimensions += listOf("api", "mode") productFlavors { create("demo") { // Assigns this product flavor to the "mode" flavor dimension. dimension = "mode" ... } create("full") { dimension = "mode" ... } // Configurations in the "api" product flavors override those in "mode" // flavors and the defaultConfig block. Gradle determines the priority // between flavor dimensions based on the order in which they appear next // to the flavorDimensions property, with the first dimension having a higher // priority than the second, and so on. create("minApi24") { dimension = "api" minSdk = 24 // To ensure the target device receives the version of the app with // the highest compatible API level, assign version codes in increasing // value with API level. versionCode = 30000 + (android.defaultConfig.versionCode ?: 0) versionNameSuffix = "-minApi24" ... } create("minApi23") { dimension = "api" minSdk = 23 versionCode = 20000 + (android.defaultConfig.versionCode ?: 0) versionNameSuffix = "-minApi23" ... } create("minApi21") { dimension = "api" minSdk = 21 versionCode = 10000 + (android.defaultConfig.versionCode ?: 0) versionNameSuffix = "-minApi21" ... } } } ...
Groovy
android { ... buildTypes { debug {...} release {...} } // Specifies the flavor dimensions you want to use. The order in which you // list the dimensions determines their priority, from highest to lowest, // when Gradle merges variant sources and configurations. You must assign // each product flavor you configure to one of the flavor dimensions. flavorDimensions "api", "mode" productFlavors { demo { // Assigns this product flavor to the "mode" flavor dimension. dimension "mode" ... } full { dimension "mode" ... } // Configurations in the "api" product flavors override those in "mode" // flavors and the defaultConfig block. Gradle determines the priority // between flavor dimensions based on the order in which they appear next // to the flavorDimensions property, with the first dimension having a higher // priority than the second, and so on. minApi24 { dimension "api" minSdkVersion 24 // To ensure the target device receives the version of the app with // the highest compatible API level, assign version codes in increasing // value with API level. versionCode 30000 + android.defaultConfig.versionCode versionNameSuffix "-minApi24" ... } minApi23 { dimension "api" minSdkVersion 23 versionCode 20000 + android.defaultConfig.versionCode versionNameSuffix "-minApi23" ... } minApi21 { dimension "api" minSdkVersion 21 versionCode 10000 + android.defaultConfig.versionCode versionNameSuffix "-minApi21" ... } } } ...
Gradle 创建的构建变体数量等于每个变体维度中变体数量与您配置的构建类型数量的乘积。当 Gradle 命名每个构建变体或相应的工件时,属于更高优先级变体维度的产品变体首先出现,其次是来自较低优先级维度的产品变体,最后是构建类型。
以前面的构建配置为例,Gradle 总共创建了 12 个构建变体,其命名方案如下
- 构建变体:
[minApi24, minApi23, minApi21][Demo, Full][Debug, Release] - 对应的 APK:
app-[minApi24, minApi23, minApi21]-[demo, full]-[debug, release].apk - 例如,
- 构建变体:
minApi24DemoDebug - 对应的 APK:
app-minApi24-demo-debug.apk
除了您可以为每个单独的产品变体和构建变体创建的源集目录之外,您还可以为每个产品变体的组合创建源集目录。例如,您可以创建 Java 源文件并将其添加到 src/demoMinApi24/java/ 目录,Gradle 仅在构建结合了这两个产品变体的变体时才使用这些源文件。
您为产品变体组合创建的源集比属于每个单独产品变体的源集具有更高的优先级。要了解有关源集以及 Gradle 如何合并资源的更多信息,请阅读有关如何创建源集的部分。
过滤变体
Gradle 为您配置的产品变体和构建类型的每个可能组合创建一个构建变体。但是,某些构建变体可能是不需要的,或者在您的项目上下文中没有意义。要删除某些构建变体配置,请在模块级 build.gradle.kts 文件中创建变体过滤器。
以前一节中的构建配置为例,假设您计划只支持应用演示版的 API 级别 23 及更高版本。您可以使用 variantFilter 块来过滤掉所有结合了“minApi21”和“demo”产品变体的构建变体配置
Kotlin
android { ... buildTypes {...} flavorDimensions += listOf("api", "mode") productFlavors { create("demo") {...} create("full") {...} create("minApi24") {...} create("minApi23") {...} create("minApi21") {...} } } androidComponents { beforeVariants { variantBuilder -> // To check for a certain build type, use variantBuilder.buildType == "<buildType>" if (variantBuilder.productFlavors.containsAll(listOf("api" to "minApi21", "mode" to "demo"))) { // Gradle ignores any variants that satisfy the conditions above. variantBuilder.enable = false } } } ...
Groovy
android { ... buildTypes {...} flavorDimensions "api", "mode" productFlavors { demo {...} full {...} minApi24 {...} minApi23 {...} minApi21 {...} } variantFilter { variant -> def names = variant.flavors*.name // To check for a certain build type, use variant.buildType.name == "<buildType>" if (names.contains("minApi21") && names.contains("demo")) { // Gradle ignores any variants that satisfy the conditions above. setIgnore(true) } } } ...
将变体过滤器添加到构建配置中,并点击通知栏中的立即同步后,Gradle 将忽略任何符合您指定条件的构建变体。当您从菜单栏中点击Build > Select Build Variant或从工具窗口栏中点击Build Variants  时,构建变体将不再显示在菜单中。
时,构建变体将不再显示在菜单中。
创建源集
默认情况下,Android Studio 会创建 main/ 源集和目录,用于共享所有构建变体之间的所有内容。但是,您可以创建新的源集,以精确控制 Gradle 为特定构建类型、产品变体、产品变体组合(在使用变体维度时)和构建变体编译和打包哪些文件。
例如,您可以在 main/ 源集中定义基本功能,并使用产品变体源集更改应用针对不同客户端的品牌,或仅为使用调试构建类型的构建变体包含特殊权限和日志记录功能。
Gradle 期望源集文件和目录以特定方式组织,类似于 main/ 源集。例如,Gradle 期望特定于“debug”构建类型的 Kotlin 或 Java 类文件位于 src/debug/kotlin/ 或 src/debug/java/ 目录中。
Android Gradle 插件提供了一个有用的 Gradle 任务,它向您展示了如何为每个构建类型、产品变体和构建变体组织文件。例如,以下任务输出示例描述了 Gradle 期望在何处找到“debug”构建类型的某些文件
------------------------------------------------------------ Project :app ------------------------------------------------------------ ... debug ---- Compile configuration: debugCompile build.gradle name: android.sourceSets.debug Java sources: [app/src/debug/java] Kotlin sources: [app/src/debug/kotlin, app/src/debug/java] Manifest file: app/src/debug/AndroidManifest.xml Android resources: [app/src/debug/res] Assets: [app/src/debug/assets] AIDL sources: [app/src/debug/aidl] RenderScript sources: [app/src/debug/rs] JNI sources: [app/src/debug/jni] JNI libraries: [app/src/debug/jniLibs] Java-style resources: [app/src/debug/resources]
要查看此输出,请执行以下操作
- 点击工具窗口栏中的 Gradle。
导航到 MyApplication > Tasks > android,然后双击 sourceSets。
要查看 Tasks 文件夹,您必须在同步期间让 Gradle 构建任务列表。为此,请按照以下步骤操作
- 点击 File > Settings > Experimental(在 macOS 上为 Android Studio > Settings > Experimental)。
- 取消选择 Do not build Gradle task list during Gradle sync。
- Gradle 执行任务后,Run 窗口将打开以显示输出。
注意:任务输出还向您展示了如何组织用于运行应用测试的文件源集,例如 test/ 和 androidTest/ 测试源集。
当您创建新的构建变体时,Android Studio 不会为您创建源集目录,但它会提供一些选项来帮助您。例如,只为“debug”构建类型创建 java/ 目录
- 打开 Project 窗格,然后从窗格顶部的菜单中选择 Project 视图。
- 导航到
MyProject/app/src/。 - 右键点击
src目录,然后选择 New > Directory。 - 从 Gradle Source Sets 下的菜单中,选择 full/java。
- 按 Enter 键。
Android Studio 为您的调试构建类型创建了一个源集目录,然后在其中创建了 java/ 目录。或者,当您为特定构建变体向项目添加新文件时,Android Studio 可以为您创建目录。
例如,为您的“debug”构建类型创建 values XML 文件
- 在 Project 窗格中,右键点击
src目录,然后选择 New > XML > Values XML File。 - 输入 XML 文件的名称或保留默认名称。
- 从 Target Source Set 旁边的菜单中,选择 debug。
- 点击 Finish。
由于“debug”构建类型被指定为目标源集,因此 Android Studio 在创建 XML 文件时会自动创建必要的目录。最终的目录结构如图 1 所示。
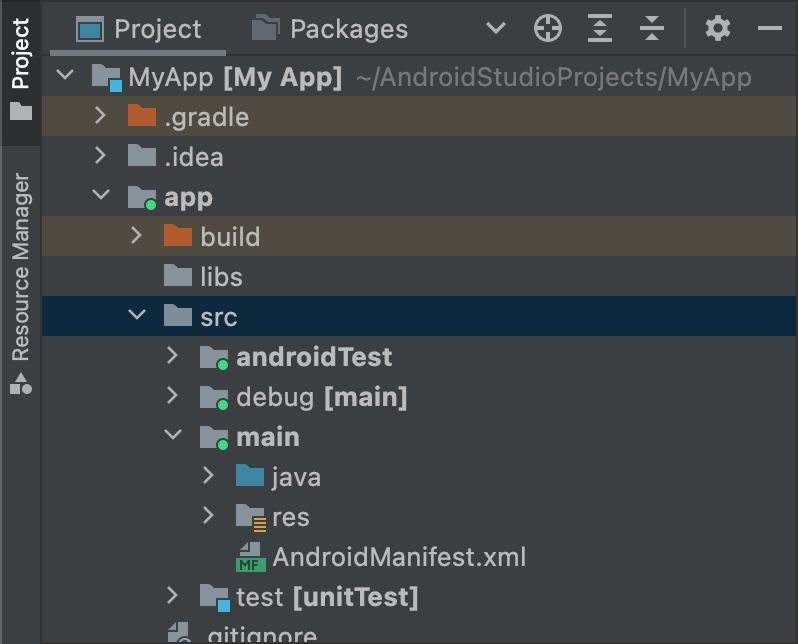
图 1. “debug”构建类型的新源集目录。
活动的源集在其图标中有一个绿色指示器,表示它们是活动的。debug 源集后缀为 [main],表示它将合并到 main 源集中。
使用相同的步骤,您还可以为产品变体(例如 src/demo/)和构建变体(例如 src/demoDebug/)创建源集目录。此外,您可以创建针对特定构建变体的测试源集,例如 src/androidTestDemoDebug/。要了解更多信息,请阅读有关测试源集的内容。
更改默认源集配置
如果您有未按 Gradle 期望的默认源集文件结构组织(如前文创建源集中所述)的源文件,则可以使用 sourceSets 块来更改 Gradle 在何处查找每个源集组件的文件。
sourceSets 块必须在 android 块中。您不需要重新定位源文件;您只需要向 Gradle 提供相对于模块级 build.gradle.kts 文件的路径,以便 Gradle 可以找到每个源集组件的文件。要了解您可以配置哪些组件以及是否可以将它们映射到多个文件或目录,请参阅 Android Gradle 插件 API 参考。
以下代码示例将 app/other/ 目录中的源文件映射到 main 源集的某些组件,并更改 androidTest 源集的根目录
Kotlin
android { ... // Encapsulates configurations for the main source set. sourceSets.getByName("main") { // Changes the directory for Java sources. The default directory is // 'src/main/java'. java.setSrcDirs(listOf("other/java")) // If you list multiple directories, Gradle uses all of them to collect // sources. Because Gradle gives these directories equal priority, if // you define the same resource in more than one directory, you receive an // error when merging resources. The default directory is 'src/main/res'. res.setSrcDirs(listOf("other/res1", "other/res2")) // Note: Avoid specifying a directory that is a parent to one // or more other directories you specify. For example, avoid the following: // res.srcDirs = ['other/res1', 'other/res1/layouts', 'other/res1/strings'] // Specify either only the root 'other/res1' directory or only the // nested 'other/res1/layouts' and 'other/res1/strings' directories. // For each source set, you can specify only one Android manifest. // By default, Android Studio creates a manifest for your main source // set in the src/main/ directory. manifest.srcFile("other/AndroidManifest.xml") ... } // Create additional blocks to configure other source sets. sourceSets.getByName("androidTest") { // If all the files for a source set are located under a single root // directory, you can specify that directory using the setRoot property. // When gathering sources for the source set, Gradle looks only in locations // relative to the root directory you specify. For example, after applying the // configuration below for the androidTest source set, Gradle looks for Java // sources only in the src/tests/java/ directory. setRoot("src/tests") ... } } ...
Groovy
android { ... sourceSets { // Encapsulates configurations for the main source set. main { // Changes the directory for Java sources. The default directory is // 'src/main/java'. java.srcDirs = ['other/java'] // If you list multiple directories, Gradle uses all of them to collect // sources. Because Gradle gives these directories equal priority, if // you define the same resource in more than one directory, you receive an // error when merging resources. The default directory is 'src/main/res'. res.srcDirs = ['other/res1', 'other/res2'] // Note: Avoid specifying a directory that is a parent to one // or more other directories you specify. For example, avoid the following: // res.srcDirs = ['other/res1', 'other/res1/layouts', 'other/res1/strings'] // Specify either only the root 'other/res1' directory or only the // nested 'other/res1/layouts' and 'other/res1/strings' directories. // For each source set, you can specify only one Android manifest. // By default, Android Studio creates a manifest for your main source // set in the src/main/ directory. manifest.srcFile 'other/AndroidManifest.xml' ... } // Create additional blocks to configure other source sets. androidTest { // If all the files for a source set are located under a single root // directory, you can specify that directory using the setRoot property. // When gathering sources for the source set, Gradle looks only in locations // relative to the root directory you specify. For example, after applying the // configuration below for the androidTest source set, Gradle looks for Java // sources only in the src/tests/java/ directory. setRoot 'src/tests' ... } } } ...
请注意,一个源目录只能属于一个源集。例如,您不能与 test 和 androidTest 源集共享相同的测试源。这是因为 Android Studio 为每个源集创建单独的 IntelliJ 模块,并且不支持跨源集的重复内容根。
使用源集构建
您可以使用源集目录来包含您只想与特定配置打包在一起的代码和资源。例如,如果您正在构建“demoDebug”构建变体(它是“demo”产品变体和“debug”构建类型的交叉产品),Gradle 会查看这些目录并赋予它们以下优先级
-
src/demoDebug/(构建变体源集) -
src/debug/(构建类型源集) -
src/demo/(产品变体源集) -
src/main/(主源集)
为产品变体组合创建的源集必须包含所有变体维度。例如,构建变体源集必须是构建类型和所有变体维度的组合。不支持合并包含多个(但不是所有)变体维度的文件夹的代码和资源。
如果您组合多个产品变体,产品变体之间的优先级由它们所属的变体维度决定。当使用 android.flavorDimensions 属性列出变体维度时,属于您列出的第一个变体维度的产品变体具有比属于第二个变体维度的产品变体更高的优先级,依此类推。此外,您为产品变体组合创建的源集比属于单个产品变体的源集具有更高的优先级。
优先级顺序决定了 Gradle 组合代码和资源时哪个源集具有更高的优先级。因为 demoDebug/ 源集目录可能包含特定于该构建变体的文件,如果 demoDebug/ 包含一个在 debug/ 中也定义的文件,Gradle 会使用 demoDebug/ 源集中的文件。同样,Gradle 会赋予构建类型和产品变体源集中的文件比 main/ 中相同的文件更高的优先级。Gradle 在应用以下构建规则时会考虑此优先级顺序
kotlin/或java/目录中的所有源代码都会一起编译,以生成单个输出。注意:对于给定的构建变体,如果 Gradle 遇到两个或多个已定义相同 Kotlin 或 Java 类的源集目录,它会抛出构建错误。例如,在构建调试应用时,您不能同时定义
src/debug/Utility.kt和src/main/Utility.kt,因为 Gradle 在构建过程中会同时查看这两个目录并抛出“重复类”错误。如果您希望针对不同的构建类型使用不同版本的Utility.kt,则每个构建类型都必须定义自己的文件版本,并且不将其包含在main/源集中。- 清单会合并成一个清单。优先级与上一个示例中的列表顺序相同。也就是说,构建类型的清单设置会覆盖产品变体的清单设置,依此类推。要了解更多信息,请阅读有关清单合并的内容。
values/目录中的文件会合并在一起。如果两个文件具有相同的名称,例如两个strings.xml文件,则优先级与上一个示例中的列表顺序相同。也就是说,构建类型源集中文件中定义的值会覆盖产品变体中相同文件中定义的值,依此类推。res/和asset/目录中的资源会打包在一起。如果两个或更多源集中定义了同名资源,则优先级与上一个示例中的列表顺序相同。- 在构建应用时,Gradle 会赋予库模块依赖项所包含的资源和清单最低优先级。
声明依赖项
要为特定的构建变体或测试源集配置依赖项,请在 Implementation 关键字前加上构建变体或测试源集的名称,如以下示例所示
Kotlin
dependencies { // Adds the local "mylibrary" module as a dependency to the "free" flavor. "freeImplementation"(project(":mylibrary")) // Adds a remote binary dependency only for local tests. testImplementation("junit:junit:4.12") // Adds a remote binary dependency only for the instrumented test APK. androidTestImplementation("com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.6.1") }
Groovy
dependencies { // Adds the local "mylibrary" module as a dependency to the "free" flavor. freeImplementation project(":mylibrary") // Adds a remote binary dependency only for local tests. testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12' // Adds a remote binary dependency only for the instrumented test APK. androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.6.1' }
有关配置依赖项的更多信息,请参阅添加构建依赖项。
使用变体感知依赖项管理
Android Gradle 插件 3.0.0 及更高版本包含一种新的依赖项机制,可在使用库时自动匹配变体。这意味着应用的 debug 变体会自动使用库的 debug 变体,依此类推。它也适用于使用产品变体的情况:应用的 freeDebug 变体将使用库的 freeDebug 变体。
为了让插件准确匹配变体,在无法直接匹配的情况下,您需要提供匹配回退,如下一节所述。
例如,假设您的应用配置了一个名为“staging”的构建类型,但其库依赖项中没有。当插件尝试构建应用的“staging”版本时,它将不知道要使用哪个版本的库,并且您会看到类似于以下内容的错误消息
Error:Failed to resolve: Could not resolve project :mylibrary.
Required by:
project :app
解决与变体匹配相关的构建错误
该插件包含 DSL 元素,可帮助您控制 Gradle 如何解决应用与依赖项之间无法直接进行变体匹配的情况。
以下是与变体感知依赖项匹配相关的问题列表,以及如何使用 DSL 属性解决它们您的应用包含库依赖项中不存在的构建类型。
例如,您的应用包含“staging”构建类型,但依赖项只包含“debug”和“release”构建类型。
请注意,当库依赖项包含您的应用不包含的构建类型时,没有问题。这是因为插件从不请求依赖项的该构建类型。
使用
matchingFallbacks为给定构建类型指定备用匹配项,如下所示Kotlin
// In the app's build.gradle.kts file. android { buildTypes { getByName("debug") {} getByName("release") {} create("staging") { // Specifies a sorted list of fallback build types that the // plugin can try to use when a dependency does not include a // "staging" build type. You may specify as many fallbacks as you // like, and the plugin selects the first build type that's // available in the dependency. matchingFallbacks += listOf("debug", "qa", "release") } } }
Groovy
// In the app's build.gradle file. android { buildTypes { debug {} release {} staging { // Specifies a sorted list of fallback build types that the // plugin can try to use when a dependency does not include a // "staging" build type. You may specify as many fallbacks as you // like, and the plugin selects the first build type that's // available in the dependency. matchingFallbacks = ['debug', 'qa', 'release'] } } }
对于应用及其库依赖项中都存在的给定变体维度,您的应用包含库中不存在的变体。
例如,您的应用及其库依赖项都包含“tier”变体维度。但是,应用中的“tier”维度包含“free”和“paid”变体,但依赖项在该维度中只包含“demo”和“paid”变体。
请注意,对于应用及其库依赖项中都存在的给定变体维度,当库包含您的应用不包含的产品变体时,没有问题。这是因为插件只匹配依赖项中存在的维度的产品变体。例如,如果依赖项不包含 ABI 的维度,则应用的“freeX86Debug”版本将使用依赖项的“freeDebug”版本。
在
defaultConfig块中使用missingDimensionStrategy指定插件从每个缺失维度中选择的默认变体,如以下示例所示。您还可以在productFlavors块中覆盖您的选择,这样每个变体都可以为缺失的维度指定不同的匹配策略。Kotlin
// In the app's build.gradle.kts file. android { defaultConfig{ // Don't configure matchingFallbacks in the defaultConfig block. // Instead, specify fallbacks for a given product flavor in the // productFlavors block, as shown below. } flavorDimensions += "tier" productFlavors { create("paid") { dimension = "tier" // Because the dependency already includes a "paid" flavor in its // "tier" dimension, you don't need to provide a list of fallbacks // for the "paid" flavor. } create("free") { dimension = "tier" // Specifies a sorted list of fallback flavors that the plugin // can try to use when a dependency's matching dimension does // not include a "free" flavor. Specify as many // fallbacks as you like; the plugin selects the first flavor // that's available in the dependency's "tier" dimension. matchingFallbacks += listOf("demo", "trial") } } }
Groovy
// In the app's build.gradle file. android { defaultConfig{ // Don't configure matchingFallbacks in the defaultConfig block. // Instead, specify fallbacks for a given product flavor in the // productFlavors block, as shown below. } flavorDimensions 'tier' productFlavors { paid { dimension 'tier' // Because the dependency already includes a "paid" flavor in its // "tier" dimension, you don't need to provide a list of fallbacks // for the "paid" flavor. } free { dimension 'tier' // Specifies a sorted list of fallback flavors that the plugin // can try to use when a dependency's matching dimension does // not include a "free" flavor. Specify as many // fallbacks as you like; the plugin selects the first flavor // that's available in the dependency's "tier" dimension. matchingFallbacks = ['demo', 'trial'] } } }
有关更多信息,请参阅 Android Gradle 插件 DSL 参考中的
matchingFallbacks和missingDimensionStrategy。库依赖项中包含应用不包含的变体维度。
例如,库依赖项包含“minApi”维度的变体,但您的应用只包含“tier”维度的变体。当您想要构建应用的“freeDebug”版本时,插件不知道是使用依赖项的“minApi23Debug”版本还是“minApi18Debug”版本。
请注意,当您的应用包含库依赖项中不存在的变体维度时,没有问题。这是因为插件只匹配依赖项中存在的维度的变体。例如,如果依赖项不包含 ABI 的维度,则您的应用的“freeX86Debug”版本将使用依赖项的“freeDebug”版本。
Kotlin
// In the app's build.gradle.kts file. android { defaultConfig{ // Specifies a sorted list of flavors that the plugin can try to use from // a given dimension. This tells the plugin to select the "minApi18" flavor // when encountering a dependency that includes a "minApi" dimension. // You can include additional flavor names to provide a // sorted list of fallbacks for the dimension. missingDimensionStrategy("minApi", "minApi18", "minApi23") // Specify a missingDimensionStrategy property for each // dimension that exists in a local dependency but not in your app. missingDimensionStrategy("abi", "x86", "arm64") } flavorDimensions += "tier" productFlavors { create("free") { dimension = "tier" // You can override the default selection at the product flavor // level by configuring another missingDimensionStrategy property // for the "minApi" dimension. missingDimensionStrategy("minApi", "minApi23", "minApi18") } create("paid") {} } }
Groovy
// In the app's build.gradle file. android { defaultConfig{ // Specifies a sorted list of flavors that the plugin can try to use from // a given dimension. This tells the plugin to select the "minApi18" flavor // when encountering a dependency that includes a "minApi" dimension. // You can include additional flavor names to provide a // sorted list of fallbacks for the dimension. missingDimensionStrategy 'minApi', 'minApi18', 'minApi23' // Specify a missingDimensionStrategy property for each // dimension that exists in a local dependency but not in your app. missingDimensionStrategy 'abi', 'x86', 'arm64' } flavorDimensions 'tier' productFlavors { free { dimension 'tier' // You can override the default selection at the product flavor // level by configuring another missingDimensionStrategy property // for the 'minApi' dimension. missingDimensionStrategy 'minApi', 'minApi23', 'minApi18' } paid {} } }
在 defaultConfig 块中使用 missingDimensionStrategy 指定插件从每个缺失维度中选择的默认变体,如以下示例所示。您还可以在 productFlavors 块中覆盖您的选择,这样每个变体都可以为缺失的维度指定不同的匹配策略。
有关更多信息,请参阅 Android Gradle 插件 DSL 参考中的 matchingFallbacks 和 missingDimensionStrategy。
配置签名设置
Gradle 不会签署您发布版本的 APK 或 AAB,除非您明确为此构建定义了签名配置。如果您还没有签名密钥,请使用 Android Studio 生成上传密钥和密钥库。
- 要使用 Gradle 构建配置手动配置发布构建类型的签名配置
- 创建密钥库。密钥库是一个二进制文件,包含一组私钥。您必须将密钥库保存在安全的地方。
-
创建私钥。私钥用于签署您的应用以进行分发,绝不会随应用一起包含或泄露给未经授权的第三方。
Kotlin
... android { ... defaultConfig {...} signingConfigs { create("release") { storeFile = file("myreleasekey.keystore") storePassword = "password" keyAlias = "MyReleaseKey" keyPassword = "password" } } buildTypes { getByName("release") { ... signingConfig = signingConfigs.getByName("release") } } }
Groovy
... android { ... defaultConfig {...} signingConfigs { release { storeFile file("myreleasekey.keystore") storePassword "password" keyAlias "MyReleaseKey" keyPassword "password" } } buildTypes { release { ... signingConfig signingConfigs.release } } }
将签名配置添加到模块级 build.gradle.kts 文件
注意:在构建文件中包含发布密钥和密钥库的密码不是良好的安全实践。相反,请将构建文件配置为从环境变量中获取这些密码,或者让构建过程提示您输入这些密码。
Kotlin
storePassword = System.getenv("KSTOREPWD") keyPassword = System.getenv("KEYPWD")
Groovy
storePassword System.getenv("KSTOREPWD") keyPassword System.getenv("KEYPWD")
要从环境变量中获取这些密码
或者,您可以从本地属性文件中加载密钥库。出于安全原因,请勿将此文件添加到源代码管理中。相反,请为每个开发者在本地设置它。要了解更多信息,请阅读 从构建文件中移除签名信息。
完成此过程后,您就可以分发您的应用并将其发布到 Google Play 上了。
警告:将您的密钥库和私钥保存在安全的地方,并确保您有安全的备份。如果您使用 Play 应用签名并丢失了上传密钥,您可以使用 Play 管理中心请求重置。如果您在没有 Play 应用签名的情况下发布应用(对于 2021 年 8 月之前创建的应用),并且您丢失了应用签名密钥,您将无法发布应用的任何更新,因为您必须始终使用相同的密钥签署应用的所有版本。
签署 Wear OS 应用
