自动填充服务是一种应用,它通过将数据注入其他应用的视图中,使用户更轻松地填写表单。自动填充服务还可以从应用中的视图检索用户数据,并将其存储以供以后使用。自动填充服务通常由管理用户数据的应用(例如密码管理器)提供。
Android 通过在 Android 8.0(API 级别 26)及更高版本中提供的自动填充框架,使填写表单更容易。只有当设备上存在提供自动填充服务的应用时,用户才能利用自动填充功能。
此页面介绍如何在您的应用中实现自动填充服务。如果您正在寻找展示如何实现服务的代码示例,请参阅 Java 或 Kotlin 中的 AutofillFramework 示例。有关自动填充服务的更多详细信息,请参阅 AutofillService 和 AutofillManager 类的参考页面。
清单声明和权限
提供自动填充服务的应用必须包含一个声明,该声明描述了服务的实现。要指定声明,请在 应用清单 中包含一个 <service> 元素。<service> 元素必须包含以下属性和元素
android:name属性,指向应用中实现服务的AutofillService的子类。android:permission属性,声明BIND_AUTOFILL_SERVICE权限。<intent-filter>元素,其必需的<action>子元素指定android.service.autofill.AutofillService操作。- 可选的
<meta-data>元素,您可以使用它来为服务提供其他配置参数。
以下示例显示了一个自动填充服务的声明
<service
android:name=".MyAutofillService"
android:label="My Autofill Service"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_AUTOFILL_SERVICE">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.service.autofill.AutofillService" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.autofill"
android:resource="@xml/service_configuration" />
</service>
<meta-data> 元素包含一个 android:resource 属性,该属性指向包含服务详细信息的 XML 资源。前面示例中的 service_configuration 资源指定了一个活动,允许用户配置服务。以下示例显示了 service_configuration XML 资源
<autofill-service
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:settingsActivity="com.example.android.SettingsActivity" />
有关 XML 资源的更多信息,请参阅应用资源概述。
提示启用服务
应用在声明BIND_AUTOFILL_SERVICE权限并用户在设备设置中启用它后,将用作自动填充服务。应用可以通过调用hasEnabledAutofillServices()(AutofillManager类的)方法来验证它是否是当前启用的服务。
如果应用不是当前的自动填充服务,则它可以使用ACTION_REQUEST_SET_AUTOFILL_SERVICE意图请求用户更改自动填充设置。如果用户选择与调用者包匹配的自动填充服务,则意图返回RESULT_OK的值。
填充客户端视图
当用户与其他应用交互时,自动填充服务会接收填充客户端视图的请求。如果自动填充服务具有满足请求的用户数据,则它会在响应中发送数据。Android 系统会显示包含可用数据的自动填充 UI,如图 1 所示。
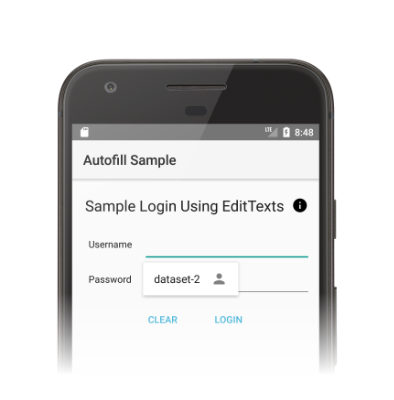
图 1. 显示数据集的自动填充 UI。
自动填充框架定义了一个用于填充视图的工作流程,该流程旨在最大限度地减少 Android 系统绑定到自动填充服务的时间。在每个请求中,Android 系统都会通过调用onFillRequest()方法,向服务发送一个AssistStructure对象。
自动填充服务会检查它是否可以使用之前存储的用户数据来满足请求。如果它可以满足请求,则服务会将数据打包在Dataset对象中。服务会调用onSuccess()方法,并传递包含Dataset对象的FillResponse对象。如果服务没有数据可以满足请求,则它会将null传递给onSuccess()方法。
如果处理请求时出错,服务会改用调用onFailure()方法。有关工作流程的详细说明,请参阅AutofillService参考页面上的说明。
以下代码显示了onFillRequest()方法的示例
Kotlin
override fun onFillRequest( request: FillRequest, cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal, callback: FillCallback ) { // Get the structure from the request val context: List<FillContext> = request.fillContexts val structure: AssistStructure = context[context.size - 1].structure // Traverse the structure looking for nodes to fill out val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure) // Fetch user data that matches the fields val (username: String, password: String) = fetchUserData(parsedStructure) // Build the presentation of the datasets val usernamePresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1) usernamePresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username") val passwordPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1) passwordPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username") // Add a dataset to the response val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(Dataset.Builder() .setValue( parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(username), usernamePresentation ) .setValue( parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(password), passwordPresentation ) .build()) .build() // If there are no errors, call onSuccess() and pass the response callback.onSuccess(fillResponse) } data class ParsedStructure(var usernameId: AutofillId, var passwordId: AutofillId) data class UserData(var username: String, var password: String)
Java
@Override public void onFillRequest(FillRequest request, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal, FillCallback callback) { // Get the structure from the request List<FillContext> context = request.getFillContexts(); AssistStructure structure = context.get(context.size() - 1).getStructure(); // Traverse the structure looking for nodes to fill out ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure); // Fetch user data that matches the fields UserData userData = fetchUserData(parsedStructure); // Build the presentation of the datasets RemoteViews usernamePresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); usernamePresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username"); RemoteViews passwordPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); passwordPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username"); // Add a dataset to the response FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(new Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(userData.username), usernamePresentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(userData.password), passwordPresentation) .build()) .build(); // If there are no errors, call onSuccess() and pass the response callback.onSuccess(fillResponse); } class ParsedStructure { AutofillId usernameId; AutofillId passwordId; } class UserData { String username; String password; }
服务可以拥有多个满足请求的数据集。在这种情况下,Android 系统会在自动填充 UI 中显示多个选项——每个数据集一个。以下代码示例显示了如何在响应中提供多个数据集。
Kotlin
// Add multiple datasets to the response val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.username), username1Presentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.password), password1Presentation) .build()) .addDataset(Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.username), username2Presentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.password), password2Presentation) .build()) .build()
Java
// Add multiple datasets to the response FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(new Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.username), username1Presentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(user1Data.password), password1Presentation) .build()) .addDataset(new Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.username), username2Presentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(user2Data.password), password2Presentation) .build()) .build();
自动填充服务可以导航AssistStructure中的ViewNode对象以检索完成请求所需的自动填充数据。服务可以使用ViewNode类的方法(例如getAutofillId())检索自动填充数据。
服务必须能够描述视图的内容,以检查它是否可以满足请求。使用autofillHints属性是服务必须用来描述视图内容的第一种方法。但是,客户端应用必须在其视图中显式提供该属性,然后服务才能使用它。
如果客户端应用不提供autofillHints属性,则服务必须使用其自身的启发式方法来描述内容。服务可以使用其他类的方法(例如getText()或getHint())来获取有关视图内容的信息。有关更多信息,请参阅为自动填充提供提示。
以下示例显示了如何遍历AssistStructure并从ViewNode对象检索自动填充数据。
Kotlin
fun traverseStructure(structure: AssistStructure) { val windowNodes: List<AssistStructure.WindowNode> = structure.run { (0 until windowNodeCount).map { getWindowNodeAt(it) } } windowNodes.forEach { windowNode: AssistStructure.WindowNode -> val viewNode: ViewNode? = windowNode.rootViewNode traverseNode(viewNode) } } fun traverseNode(viewNode: ViewNode?) { if (viewNode?.autofillHints?.isNotEmpty() == true) { // If the client app provides autofill hints, you can obtain them using // viewNode.getAutofillHints(); } else { // Or use your own heuristics to describe the contents of a view // using methods such as getText() or getHint() } val children: List<ViewNode>? = viewNode?.run { (0 until childCount).map { getChildAt(it) } } children?.forEach { childNode: ViewNode -> traverseNode(childNode) } }
Java
public void traverseStructure(AssistStructure structure) { int nodes = structure.getWindowNodeCount(); for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++) { WindowNode windowNode = structure.getWindowNodeAt(i); ViewNode viewNode = windowNode.getRootViewNode(); traverseNode(viewNode); } } public void traverseNode(ViewNode viewNode) { if(viewNode.getAutofillHints() != null && viewNode.getAutofillHints().length > 0) { // If the client app provides autofill hints, you can obtain them using // viewNode.getAutofillHints(); } else { // Or use your own heuristics to describe the contents of a view // using methods such as getText() or getHint() } for(int i = 0; i < viewNode.getChildCount(); i++) { ViewNode childNode = viewNode.getChildAt(i); traverseNode(childNode); } }
保存用户数据
自动填充服务需要用户数据来填充应用中的视图。当用户手动填充视图时,系统会提示他们将数据保存到当前的自动填充服务,如图 2 所示。
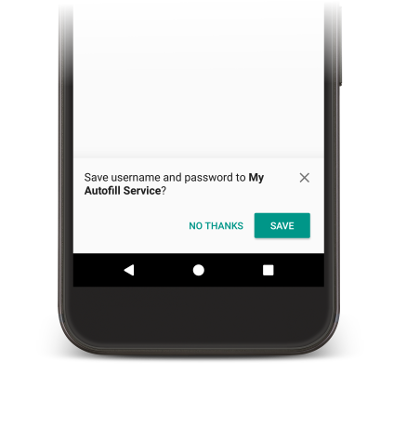
图 2. 自动填充保存 UI。
要保存数据,服务必须表明它有兴趣存储数据以备将来使用。在 Android 系统发送保存数据的请求之前,会发出填充请求,服务有机会填充视图。为了表明它有兴趣保存数据,服务会在填充请求的响应中包含一个SaveInfo对象。SaveInfo对象至少包含以下数据:
- 要保存的用户数据的类型。有关可用
SAVE_DATA值的列表,请参阅SaveInfo。 - 需要更改以触发保存请求的最小视图集。例如,登录表单通常要求用户更新
username和password视图以触发保存请求。
一个SaveInfo对象与一个FillResponse对象相关联,如下面的代码示例所示。
Kotlin
override fun onFillRequest( request: FillRequest, cancellationSignal: CancellationSignal, callback: FillCallback ) { ... // Builder object requires a non-null presentation val notUsed = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1) val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset( Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, null, notUsed) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, null, notUsed) .build() ) .setSaveInfo( SaveInfo.Builder( SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_USERNAME or SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_PASSWORD, arrayOf(parsedStructure.usernameId, parsedStructure.passwordId) ).build() ) .build() ... }
Java
@Override public void onFillRequest(FillRequest request, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal, FillCallback callback) { ... // Builder object requires a non-null presentation RemoteViews notUsed = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(new Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, null, notUsed) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, null, notUsed) .build()) .setSaveInfo(new SaveInfo.Builder( SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_USERNAME | SaveInfo.SAVE_DATA_TYPE_PASSWORD, new AutofillId[] {parsedStructure.usernameId, parsedStructure.passwordId}) .build()) .build(); ... }
自动填充服务可以在onSaveRequest()方法中实现持久化用户数据的逻辑,该方法通常在客户端活动完成或客户端应用调用commit()后调用。以下代码显示了onSaveRequest()方法的示例。
Kotlin
override fun onSaveRequest(request: SaveRequest, callback: SaveCallback) { // Get the structure from the request val context: List<FillContext> = request.fillContexts val structure: AssistStructure = context[context.size - 1].structure // Traverse the structure looking for data to save traverseStructure(structure) // Persist the data - if there are no errors, call onSuccess() callback.onSuccess() }
Java
@Override public void onSaveRequest(SaveRequest request, SaveCallback callback) { // Get the structure from the request List<FillContext> context = request.getFillContexts(); AssistStructure structure = context.get(context.size() - 1).getStructure(); // Traverse the structure looking for data to save traverseStructure(structure); // Persist the data - if there are no errors, call onSuccess() callback.onSuccess(); }
自动填充服务必须在持久化敏感数据之前对其进行加密。但是,用户数据可以包含非敏感的标签或数据。例如,用户帐户可以包含将数据标记为“工作”或“个人”帐户的标签。服务不得加密标签。通过不加密标签,如果用户未进行身份验证,服务可以在展示视图中使用标签。然后,在用户进行身份验证后,服务可以使用实际数据替换标签。
推迟自动填充保存 UI
从 Android 10 开始,如果您使用多个屏幕来实现自动填充工作流程(例如,一个屏幕用于用户名字段,另一个屏幕用于密码),则可以使用SaveInfo.FLAG_DELAY_SAVE标志来推迟自动填充保存 UI。
如果设置了此标志,则在与SaveInfo响应关联的自动填充上下文提交时,不会触发自动填充保存 UI。相反,您可以使用同一任务中的单独活动来传递未来的填充请求,然后通过保存请求显示 UI。有关更多信息,请参阅SaveInfo.FLAG_DELAY_SAVE。
要求用户身份验证
自动填充服务可以通过要求用户在填充视图之前进行身份验证来提供额外的安全级别。以下场景是实现用户身份验证的良好候选者:
- 需要使用主密码或指纹扫描来解锁应用中的用户数据。
- 需要解锁特定数据集,例如使用卡片验证码 (CVC) 解锁信用卡详细信息。
在服务需要在解锁数据之前进行用户身份验证的场景中,服务可以呈现样板数据或标签,并指定负责身份验证的Intent。如果您在身份验证流程完成后需要其他数据来处理请求,则可以将这些数据添加到意图中。然后,您的身份验证活动可以将数据返回到应用中的AutofillService类。
以下代码示例显示了如何指定请求需要身份验证。
Kotlin
val authPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply { setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "requires authentication") } val authIntent = Intent(this, AuthActivity::class.java).apply { // Send any additional data required to complete the request putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, "my_dataset") } val intentSender: IntentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity( this, 1001, authIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT ).intentSender // Build a FillResponse object that requires authentication val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder() .setAuthentication(autofillIds, intentSender, authPresentation) .build()
Java
RemoteViews authPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); authPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "requires authentication"); Intent authIntent = new Intent(this, AuthActivity.class); // Send any additional data required to complete the request authIntent.putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, "my_dataset"); IntentSender intentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity( this, 1001, authIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT ).getIntentSender(); // Build a FillResponse object that requires authentication FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder() .setAuthentication(autofillIds, intentSender, authPresentation) .build();
活动完成身份验证流程后,必须调用setResult()方法,传递RESULT_OK值,并将EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT额外数据设置为包含已填充数据集的FillResponse对象。以下代码显示了身份验证流程完成后如何返回结果的示例。
Kotlin
// The data sent by the service and the structure are included in the intent val datasetName: String? = intent.getStringExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME) val structure: AssistStructure = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_ASSIST_STRUCTURE) val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure) val (username, password) = fetchUserData(parsedStructure) // Build the presentation of the datasets val usernamePresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply { setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username") } val passwordPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply { setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username") } // Add the dataset to the response val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(Dataset.Builder() .setValue( parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(username), usernamePresentation ) .setValue( parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(password), passwordPresentation ) .build() ).build() val replyIntent = Intent().apply { // Send the data back to the service putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, datasetName) putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, fillResponse) } setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, replyIntent)
Java
Intent intent = getIntent(); // The data sent by the service and the structure are included in the intent String datasetName = intent.getStringExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME); AssistStructure structure = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_ASSIST_STRUCTURE); ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure); UserData userData = fetchUserData(parsedStructure); // Build the presentation of the datasets RemoteViews usernamePresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); usernamePresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "my_username"); RemoteViews passwordPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); passwordPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, "Password for my_username"); // Add the dataset to the response FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(new Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.usernameId, AutofillValue.forText(userData.username), usernamePresentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.passwordId, AutofillValue.forText(userData.password), passwordPresentation) .build()) .build(); Intent replyIntent = new Intent(); // Send the data back to the service replyIntent.putExtra(MY_EXTRA_DATASET_NAME, datasetName); replyIntent.putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, fillResponse); setResult(RESULT_OK, replyIntent);
在需要解锁信用卡数据集的场景中,服务可以显示一个 UI 来要求输入 CVC。您可以通过显示样板数据(例如银行名称和信用卡后四位数)来隐藏数据,直到数据集解锁。以下示例显示了如何要求数据集进行身份验证并在用户提供 CVC 之前隐藏数据。
Kotlin
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure) val paymentData: Payment = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure) // Build the presentation that shows the bank and the last four digits of the // credit card number, such as 'Bank-1234' val maskedPresentation: String = "${paymentData.bank}-" + paymentData.creditCardNumber.substring(paymentData.creditCardNumber.length - 4) val authPresentation = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1).apply { setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, maskedPresentation) } // Prepare an intent that displays the UI that asks for the CVC val cvcIntent = Intent(this, CvcActivity::class.java) val cvcIntentSender: IntentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity( this, 1001, cvcIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT ).intentSender // Build a FillResponse object that includes a Dataset that requires authentication val fillResponse: FillResponse = FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset( Dataset.Builder() // The values in the dataset are replaced by the actual // data once the user provides the CVC .setValue(parsedStructure.creditCardId, null, authPresentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.expDateId, null, authPresentation) .setAuthentication(cvcIntentSender) .build() ).build()
Java
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure); Payment paymentData = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure); // Build the presentation that shows the bank and the last four digits of the // credit card number, such as 'Bank-1234' String maskedPresentation = paymentData.bank + "-" + paymentData.creditCardNumber.subString(paymentData.creditCardNumber.length - 4); RemoteViews authPresentation = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); authPresentation.setTextViewText(android.R.id.text1, maskedPresentation); // Prepare an intent that displays the UI that asks for the CVC Intent cvcIntent = new Intent(this, CvcActivity.class); IntentSender cvcIntentSender = PendingIntent.getActivity( this, 1001, cvcIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT ).getIntentSender(); // Build a FillResponse object that includes a Dataset that requires authentication FillResponse fillResponse = new FillResponse.Builder() .addDataset(new Dataset.Builder() // The values in the dataset are replaced by the actual // data once the user provides the CVC .setValue(parsedStructure.creditCardId, null, authPresentation) .setValue(parsedStructure.expDateId, null, authPresentation) .setAuthentication(cvcIntentSender) .build()) .build();
活动验证 CVC 后,应调用setResult()方法,传递RESULT_OK值,并将EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT额外数据设置为包含信用卡号码和有效期的Dataset对象。新的数据集将替换需要身份验证的数据集,并且视图会立即填充。以下代码显示了用户提供 CVC 后如何返回数据集的示例。
Kotlin
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data. val parsedStructure: ParsedStructure = parseStructure(structure) val paymentData: Payment = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure) // Build a non-null RemoteViews object to use as the presentation when // creating the Dataset object. This presentation isn't actually used, but the // Builder object requires a non-null presentation. val notUsed = RemoteViews(packageName, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1) // Create a dataset with the credit card number and expiration date. val responseDataset: Dataset = Dataset.Builder() .setValue( parsedStructure.creditCardId, AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.creditCardNumber), notUsed ) .setValue( parsedStructure.expDateId, AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.expirationDate), notUsed ) .build() val replyIntent = Intent().apply { putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, responseDataset) }
Java
// Parse the structure and fetch payment data. ParsedStructure parsedStructure = parseStructure(structure); Payment paymentData = fetchPaymentData(parsedStructure); // Build a non-null RemoteViews object to use as the presentation when // creating the Dataset object. This presentation isn't actually used, but the // Builder object requires a non-null presentation. RemoteViews notUsed = new RemoteViews(getPackageName(), android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1); // Create a dataset with the credit card number and expiration date. Dataset responseDataset = new Dataset.Builder() .setValue(parsedStructure.creditCardId, AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.creditCardNumber), notUsed) .setValue(parsedStructure.expDateId, AutofillValue.forText(paymentData.expirationDate), notUsed) .build(); Intent replyIntent = new Intent(); replyIntent.putExtra(EXTRA_AUTHENTICATION_RESULT, responseDataset);
将数据组织到逻辑组中
自动填充服务必须将数据组织到逻辑组中,以隔离来自不同域的概念。在此页面中,这些逻辑组被称为“分区”。以下列表显示了分区的典型示例和字段:
- 凭据,包括用户名和密码字段。
- 地址,包括街道、城市、州和邮政编码字段。
- 支付信息,包括信用卡号码、有效期和验证码字段。
正确划分数据的自动填充服务能够更好地保护其用户的数据,方法是不在一个数据集中公开多个分区的数据。例如,包含凭据的数据集不需要包含支付信息。将数据组织到分区中,可以让您的服务公开满足请求所需的最小相关信息量。
将数据组织到分区中,使服务能够填充具有多个分区视图的活动,同时向客户端应用发送最少的相关数据。例如,考虑一个包含用户名、密码、街道和城市视图的活动,以及具有以下数据的自动填充服务:
| 分区 | 字段 1 | 字段 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 凭据 | work_username | work_password |
| personal_username | 个人密码 | |
| 地址 | 工作地址街道 | 工作地址城市 |
| 个人地址街道 | 个人地址城市 |
该服务可以准备一个数据集,其中包含工作和个人帐户的凭据分区。当用户选择一个数据集时,后续的自动填充响应可以提供工作地址或个人地址,具体取决于用户的第一次选择。
服务可以通过遍历AssistStructure对象时调用isFocused()方法来识别发起请求的字段。这允许服务准备包含适当分区数据的FillResponse。
短信一次性验证码自动填充
您的自动填充服务可以使用短信检索 API 来帮助用户填充通过短信发送的一次性验证码。
要使用此功能,必须满足以下要求:
- 自动填充服务运行在 Android 9(API 级别 28)或更高版本上。
- 用户允许您的自动填充服务从短信中读取一次性验证码。
- 您正在为其提供自动填充服务的应用程序尚未使用短信检索 API 读取一次性验证码。
您的自动填充服务可以使用SmsCodeAutofillClient(通过从 Google Play 服务 19.0.56 或更高版本调用SmsCodeRetriever.getAutofillClient()获得)。
在自动填充服务中使用此 API 的主要步骤如下:
- 在自动填充服务中,使用
hasOngoingSmsRequest(来自SmsCodeAutofillClient)确定是否有任何针对您正在填充的应用程序的包名的活动请求。只有当此方法返回false时,您的自动填充服务才应显示建议提示。 - 在自动填充服务中,使用
checkPermissionState(来自SmsCodeAutofillClient)检查自动填充服务是否具有自动填充一次性验证码的权限。此权限状态可以是NONE、GRANTED或DENIED。对于NONE和GRANTED状态,自动填充服务必须显示建议提示。 - 在自动填充身份验证活动中,使用
SmsRetriever.SEND_PERMISSION权限注册一个侦听SmsCodeRetriever.SMS_CODE_RETRIEVED_ACTION的BroadcastReceiver,以便在可用时接收短信验证码结果。 在
SmsCodeAutofillClient上调用startSmsCodeRetriever以开始侦听通过短信发送的一次性验证码。如果用户允许您的自动填充服务从短信中检索一次性验证码,则此方法将查找从现在起一到五分钟内收到的短信。如果您的自动填充服务需要请求用户权限来读取一次性验证码,则
startSmsCodeRetriever返回的Task可能会失败,并返回ResolvableApiException。如果发生这种情况,您需要调用ResolvableApiException.startResolutionForResult()方法来显示权限请求的同意对话框。从 intent 中接收短信验证码结果,然后将短信验证码作为自动填充响应返回。
高级自动填充场景
- 与键盘集成
- 从 Android 11 开始,平台允许键盘和其他输入法编辑器 (IME) 内联显示自动填充建议,而不是使用下拉菜单。有关您的自动填充服务如何支持此功能的更多信息,请参阅将自动填充与键盘集成。
- 分页数据集
- 大型自动填充响应可能会超过表示处理请求所需的远程对象的可移除对象的
Binder对象的允许事务大小。为了防止 Android 系统在这些情况下抛出异常,您可以通过一次最多添加 20 个Dataset对象来保持FillResponse较小。如果您的响应需要更多数据集,您可以添加一个数据集,让用户知道还有更多信息,并在选择时检索下一组数据集。有关更多信息,请参阅addDataset(Dataset)。 - 保存拆分在多个屏幕中的数据
应用程序通常会将用户数据拆分到同一活动中的多个屏幕中,尤其是在用于创建新用户帐户的活动中。例如,第一个屏幕要求输入用户名,如果用户名可用,则第二个屏幕要求输入密码。在这些情况下,自动填充服务必须等到用户输入这两个字段后才能显示自动填充保存 UI。请按照以下步骤处理此类场景:
- 在第一个填充请求中,在响应中添加一个客户端状态包,其中包含屏幕中存在的局部字段的自动填充 ID。
- 在第二个填充请求中,检索客户端状态包,从客户端状态获取在上一个请求中设置的自动填充 ID,并将这些 ID 和
FLAG_SAVE_ON_ALL_VIEWS_INVISIBLE标志添加到第二个响应中使用的SaveInfo对象中。 - 在保存请求中,使用正确的
FillContext对象来获取每个字段的值。每个填充请求都有一个填充上下文。
有关更多信息,请参阅数据拆分在多个屏幕中的保存方式。
- 为每个请求提供初始化和拆卸逻辑
每次有自动填充请求时,Android 系统都会绑定到服务并调用其
onConnected()方法。服务处理完请求后,Android 系统会调用onDisconnected()方法并从服务中解除绑定。您可以实现onConnected()来提供在处理请求之前运行的代码,并实现onDisconnected()来提供在处理请求之后运行的代码。- 自定义自动填充保存 UI
自动填充服务可以自定义自动填充保存 UI,以帮助用户决定是否要让服务保存其数据。服务可以通过简单的文本或自定义视图提供有关保存内容的附加信息。服务还可以更改取消保存请求的按钮的外观,并在用户点击该按钮时收到通知。有关更多信息,请参阅
SaveInfo参考页面。- 兼容模式
兼容模式允许自动填充服务将辅助功能虚拟结构用于自动填充目的。这对于在没有明确实现自动填充 API 的浏览器中提供自动填充功能特别有用。
要使用兼容模式测试您的自动填充服务,请明确允许列出需要兼容模式的浏览器或应用程序。您可以运行以下命令来检查哪些包已被允许列出:
$ adb shell settings get global autofill_compat_mode_allowed_packages
如果要测试的包未列出,请运行以下命令添加它,其中
pkgX是应用程序的包:$ adb shell settings put global autofill_compat_mode_allowed_packages pkg1[resId1]:pkg2[resId1,resId2]
如果应用程序是浏览器,则使用
resIdx指定包含渲染页面 URL 的输入字段的资源 ID。
兼容模式具有以下限制:
- 当服务使用
FLAG_SAVE_ON_ALL_VIEWS_INVISIBLE标志或调用setTrigger()方法时,会触发保存请求。FLAG_SAVE_ON_ALL_VIEWS_INVISIBLE在使用兼容模式时默认设置。 - 节点的文本值可能在
onSaveRequest(SaveRequest, SaveCallback)方法中不可用。
有关兼容模式的更多信息(包括其相关的限制),请参阅AutofillService类参考。
