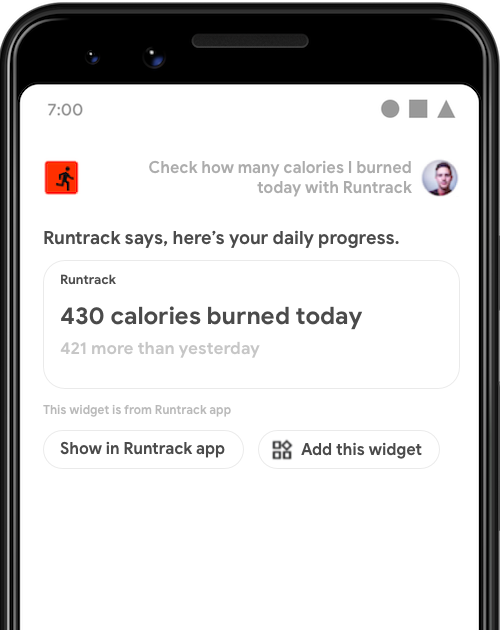
GET_EXERCISE_OBSERVATION 启动小部件。对于许多 intent,最佳响应是向用户提供简单的答案、简短的确认或快速的交互体验。您可以在 Google 助理中显示 Android 应用小部件,以实现这些类型的 intent。
本指南介绍如何使用小部件实现助理用户查询,以及如何通过应用操作 小部件扩展库 增强助理的小部件体验。
优势
小部件是可以嵌入到 Android 界面(例如启动器或锁定屏幕)中的微型应用视图。借助应用操作,您可以让小部件有资格在助理中显示,从而提高它们的影响力
- 发现: 积极响应用户的自然语言查询来显示小部件。
- 互动: 在免提场景中显示小部件,例如当助理在锁定屏幕上提供个人结果时,以及在 Android Auto 上。
- 留存: 允许用户将助理中显示的小部件固定到其启动器。固定功能需要 小部件扩展库。
助理如何显示小部件
用户可以通过两种方式在助理上调用小部件
- 通过名称明确请求小部件。
- 向助理说出查询,触发配置为小部件实现功能的内置 intent (BII) 或自定义 intent。
明确调用
要明确调用任何已安装应用的小部件,用户可以向助理询问以下内容
- “嘿 Google,显示 ExampleApp 小部件。”
- “来自 ExampleApp 的小部件。”
助理会显示这些小部件并附带通用介绍:“ExampleApp 表示,这是小部件。” 尽管助理会以这种方式原生返回所请求的小部件,无需应用开发者进行任何操作,但这种调用方法要求用户明确了解小部件才能请求它。为了简化小部件的发现,请使用下一节中详述的 intent 实现方法。
Intent 实现
通过使用小部件实现用户在助理上执行的自然语言查询,让您的小部件更易于查找。例如,每当用户通过询问 “嘿 Google,我这周在 ExampleApp 上跑了多少英里?” 在您的健身应用中触发 GET_EXERCISE_OBSERVATION BII 时,您都可以返回一个小部件。除了简化发现之外,将小部件与应用操作集成还具有以下优势
- 参数访问: 助理会将从用户查询中提取的intent 参数提供给您的小部件,从而实现定制响应。
- 自定义 TTS 介绍: 您可以为助理提供一个文本转语音 (TTS) 字符串,以便在显示您的小部件时进行播报。
- 小部件固定: 助理会在您的小部件附近显示一个“添加此小部件”按钮,让用户可以轻松地将您的小部件固定到其启动器。固定功能需要 小部件扩展库。
实现小部件实现功能
要为您的 intent 实现小部件实现功能,请按照以下步骤操作
- 按照创建简单小部件中描述的步骤实现 Android 小部件。
- 在您应用的
shortcuts.xml资源文件中,将一个包含实现详情和 BII<parameter>标记的<app-widget>元素添加到您的 capability 中。更新您的小部件以处理参数。 - 添加所需的 小部件扩展库,该库允许助理将 BII 名称和参数传递给您的小部件。它还支持自定义 TTS 介绍和小部件固定功能。
以下部分介绍了 <app-widget> 架构的 shortcuts.xml。
小部件架构
<app-widget> 元素在 shortcuts.xml 的 <capability> 元素中定义为实现。它们需要以下属性,除非另有说明为可选属性
| `shortcuts.xml` 标记 | 包含于 | 属性 |
|---|---|---|
<app-widget> |
<capability> |
|
<parameter> |
<app-widget> |
|
<extra> |
<app-widget> |
|
小部件架构说明
<app-widget>
顶级小部件实现元素。
属性
android:identifier:此实现功能的标识符。此值在<capability>中定义的所有<app-widget>和<intent>实现元素中必须是唯一的。android:targetClass:处理 intent 的AppWidgetProvider的完整类名。
<parameter>
将 BII 参数映射到 intent <parameter> 值。您可以为每个 <app-widget> 元素定义零个或多个参数。在实现过程中,助理会通过以键值对形式更新小部件实例的 extra 来传递参数,格式如下
- 键:为参数定义的
android:key。 - 值:BII 从用户语音输入中提取的值。
您可以通过在关联的 AppWidgetManager 对象上调用 getAppWidgetOptions() 来访问这些 extra,该方法会返回一个 Bundle,其中包含触发 BII 的名称及其参数。有关详细信息,请参阅提取参数值。
有关 BII 参数匹配的更多信息,请参阅参数数据和匹配。
<extra>
可选标记,声明此小部件使用自定义 TTS 介绍。此标记需要以下属性值
android:name:"hasTts"android:value:"true"
示例代码
以下 shortcuts.xml 文件中的示例展示了 GET_EXERCISE_OBSERVATION BII capability 的小部件实现配置
<capability android:name="actions.intent.GET_EXERCISE_OBSERVATION">
<app-widget
android:identifier="GET_EXERCISE_OBSERVATION_1"
android:targetClass="com.exampleapp.providers.exampleAppWidgetProvider"
android:targetPackage="com.exampleapp">
<parameter
android:name="exerciseObservation.aboutExercise.name"
android:key="exercisename">
</parameter>
<extra android:name="hasTts" android:value="true"/>
</app-widget>
</capability>
您可以为每个 capability 指定多个 <app-widget> 元素,或结合使用 <app-widget> 和 <intent> 元素。这种方法使您可以根据用户提供的不同参数组合提供定制体验。例如,如果用户在查询中未指定下车地点,您可以将他们引导到应用中显示设置上车和下车地点选项的活动。有关定义回退 intent 的更多信息,请参阅回退 intent 部分。
提取参数值
在以下示例 AppWidgetProvider 类中,私有函数 updateAppWidget() 用于从小部件选项 Bundle 中提取 BII 名称和参数
Kotlin
package com.example.exampleapp //... Other module imports import com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.AppActionsWidgetExtension /** * Implementation of App Widget functionality. */ class MyAppWidget : AppWidgetProvider() { override fun onUpdate( context: Context, appWidgetManager: AppWidgetManager, appWidgetIds: IntArray ) { // There might be multiple widgets active, so update all of them for (appWidgetId in appWidgetIds) { updateAppWidget(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId) } } private fun updateAppWidget( context: Context, appWidgetManager: AppWidgetManager, appWidgetId: Int ) { val widgetText: CharSequence = context.getString(R.string.appwidget_text) // Construct the RemoteViews object val views = RemoteViews(context.packageName, R.layout.my_app_widget) views.setTextViewText(R.id.appwidget_text, widgetText) // Extract the name and parameters of the BII from the widget options val optionsBundle = appWidgetManager.getAppWidgetOptions(appWidgetId) val bii = optionsBundle.getString(AppActionsWidgetExtension.EXTRA_APP_ACTIONS_BII) // "actions.intent.CREATE_TAXI_RESERVATION" val params = optionsBundle.getBundle(AppActionsWidgetExtension.EXTRA_APP_ACTIONS_PARAMS) if (params != null && params.containsKey("dropoff")) { val dropoffLocation = params.getString("dropoff") // Build your RemoteViews with the extracted BII parameter // ... } appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views) } }
Java
package com.example.exampleapp; //... Other module imports import com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.AppActionsWidgetExtension; /** * Implementation of App Widget functionality. */ public class MyAppWidget extends AppWidgetProvider { @Override public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) { // There might be multiple widgets active, so update all of them for (int appWidgetId : appWidgetIds) { updateAppWidget(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId); } } private static void updateAppWidget(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int appWidgetId) { CharSequence widgetText = context.getString(R.string.appwidget_text); // Construct the RemoteViews object RemoteViews views = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.my_app_widget); views.setTextViewText(R.id.appwidget_text, widgetText); // Extract the name and parameters of the BII from the widget options Bundle optionsBundle = appWidgetManager.getAppWidgetOptions(appWidgetId); String bii = optionsBundle.getString(AppActionsWidgetExtension.EXTRA_APP_ACTIONS_BII); // "actions.intent.CREATE_TAXI_RESERVATION" Bundle params = optionsBundle.getBundle(AppActionsWidgetExtension.EXTRA_APP_ACTIONS_PARAMS); if (params != null && params.containsKey(("dropoff"))){ String dropoffLocation = params.getString("dropoff"); // Build your RemoteViews with the extracted BII parameter // ... } appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views); } }
小部件扩展库
应用操作小部件扩展库可增强您的小部件,以提供语音优先的助理体验。此库允许您的小部件从触发 BII 接收重要的实现信息,包括 BII 名称和从用户查询中提取的任何 intent 参数。
这个 Maven 库允许您为每个小部件提供自定义的文本转语音 (TTS) 介绍,使助理能够向用户播报正在视觉呈现的内容摘要。它还支持启动器固定,使用户可以轻松地将助理中显示的小部件保存到其启动器屏幕。
通过将库添加到应用模块的 build.gradle 文件的 dependencies 部分来开始使用
dependencies {
//...
implementation "com.google.assistant.appactions:widgets:0.0.1"
}
自定义介绍
导入小部件扩展库后,您可以为小部件提供自定义 TTS 介绍。要将您的定义添加到小部件的 AppWidgetProvider 中,请在 IDE 中打开该类并导入小部件扩展库
Kotlin
import com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.AppActionsWidgetExtension
Java
import com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.AppActionsWidgetExtension;
Kotlin
package com.example.exampleapp //... Other module imports import com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.AppActionsWidgetExtension /** * Implementation of App Widget functionality. */ object MyAppWidget : AppWidgetProvider() { fun updateAppWidget( context: Context?, appWidgetManager: AppWidgetManager, appWidgetId: Int ) { val appActionsWidgetExtension = AppActionsWidgetExtension.newBuilder(appWidgetManager) .setResponseSpeech("Hello world") // TTS to be played back to the user .setResponseText("Hello world!") // Response text to be displayed in Assistant .build() // Update widget with TTS appActionsWidgetExtension.updateWidget(appWidgetId) // Update widget UI appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views) } }
Java
package com.example.exampleapp; //... Other module imports import com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.AppActionsWidgetExtension; /** * Implementation of App Widget functionality. */ public class MyAppWidget extends AppWidgetProvider { static void updateAppWidget(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int appWidgetId) { AppActionsWidgetExtension appActionsWidgetExtension = AppActionsWidgetExtension.newBuilder(appWidgetManager) .setResponseSpeech("Hello world") // TTS to be played back to the user .setResponseText("Hello world!") // Response text to be displayed in Assistant .build(); // Update widget with TTS appActionsWidgetExtension.updateWidget(appWidgetId); // Update widget UI appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views); } }
TTS 样式建议
使用以下样式建议来优化您的自定义小部件介绍,以适应 TTS 和显示的提示。
| 建议 | 推荐 | 不推荐 |
|---|---|---|
缩略语在 TTS 提示中使用缩略语。没有缩略语的消息听起来生硬和机械,而非自然和对话式。说出“cannot”和“do not”等词语可能会听起来带有惩罚性和严厉性。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)抱歉,我找不到预订信息。 ResponseText抱歉,我找不到预订信息。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)抱歉,我无法找到预订信息。 ResponseText抱歉,我无法找到预订信息。 |
逗号在三个或更多项目的列表中使用连串逗号,以增加清晰度。如果没有连串逗号,列表中的单个项目可能会被错误地听成或读成一组。例如,在“daffodils, daisies and sunflowers”中,“daisies and sunflowers”听起来像是一个整体。而在“daffodils, daisies, and sunflowers”中,所有三个都清楚地分开。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)我们最受欢迎的包括黄玫瑰、水仙花、雏菊和向日葵。 ResponseText我们最受欢迎的包括黄玫瑰、水仙花、雏菊和向日葵。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)我们最受欢迎的包括黄玫瑰、水仙花、雏菊和向日葵。 ResponseText我们最受欢迎的包括黄玫瑰、水仙花、雏菊和向日葵。 |
数字使用数字而非文本,使视觉内容更易于浏览。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您的血压是 100/80。 ResponseText您的血压是 100/80。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您的血压是 100/80。 ResponseText您的血压是一百八十。 |
符号使用专用符号而非文本,使视觉内容更易于浏览。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您上次购买花费了 $24.65。 ResponseText您上次购买花费了 $24.65。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您上次购买花费了二十四美元六十五美分。 ResponseText您上次购买花费了二十四美元六十五美分。 |
避免客套话客套话会让回复显得疏远和正式。抛弃它们,让对话保持友好和非正式。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您的订单已送达。 ResponseText您的订单已送达。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)当然,我可以告诉您。您的订单已送达。 ResponseText当然,我可以告诉您。您的订单已送达。 |
避免感叹号它们可能被视为喊叫。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您今天跑了 1.5 英里。 ResponseText您今天跑了 1.5 英里。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您今天跑了 1.5 英里! ResponseText您今天跑了 1.5 英里! |
时间使用数字:“5:15”,而不是“五点十五”或“五点一刻”。对于 12 小时制,请使用 AM 或 PM。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您的快递应在上午 8:15 前送达。 ResponseText您的快递应在上午 8:15 前送达。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您的快递应在今天早上 8 点过 15 分前送达。 ResponseText您的快递应在今天早上 8 点过 15 分前送达。 |
不要长篇大论提供信息,但保持回复简洁。不要在没有明确用户利益的情况下深入细节。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)上个月您使用了 159 小时的能量。 ResponseText上个月您使用了 159 小时的能量。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)节约能源对地球和环境非常重要。上个月您使用了 159 小时的能量。本月您使用了 58 小时的能量。 ResponseText节约能源对地球和环境非常重要。上个月您使用了 159 小时的能量。本月您使用了 58 小时的能量。 |
使用简短、简单的词语简单明了的语言具有最广泛的吸引力,使之能被所有背景的人理解。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)您上次的血糖读数是 126。 ResponseText您上次的血糖读数是 126 毫克/分升。 |
ResponseSpeech (TTS)倒数第二次血糖水平为 126。 ResponseText倒数第二次血糖水平为 126。 |
启动器固定
小部件扩展库允许在助理中与您的小部件一起显示“添加此小部件”按钮。要启用固定功能,请将以下接收器定义添加到 AndroidManifest.xml
<application>
<receiver android:name="com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.pinappwidget.PinAppWidgetBroadcastReceiver"
android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.COMPLETE_PIN_APP_WIDGET" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<service
android:name=
"com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.pinappwidget.PinAppWidgetService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="com.google.assistant.appactions.widgets.PIN_APP_WIDGET" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
库存可用性
支持内联库存或网络库存的 BII 可以将这些库存扩展到您的小部件实现中。
内联库存
以下 shortcuts.xml 示例文件中的代码演示了配置为支持内联库存和小部件实现的 START_EXERCISE BII capability
<capability
android:name="actions.intent.START_EXERCISE">
<app-widget
android:identifier="START_EXERCISE_1"
android:targetClass="com.example.exampleapp.StartExerciseAppWidgetProvider">
<parameter
android:name="exercise.name"
android:key="exerciseName"
app:shortcutMatchRequired="true">
</parameter>
</app-widget>
</capability>
<shortcut android:shortcutId="RunningShortcut">
<intent
android:action="android.intent.action.VIEW"
android:targetClass="com.example.exampleapp.StartExcerciseActivity" />
<capability-binding
android:capability="actions.intent.START_EXERCISE"
android:parameter="exercise.name"
android:value="running;runs" />
</shortcut>
在上述示例中,当用户通过向助理询问 “使用 ExampleApp 开始跑步” 来触发此 capability 时,<app-widget> 实现的选项 bundle 包含以下键值对
- 键 =
“exerciseName” - 值 =
“RunningShortcut”
网络库存
以下 shortcuts.xml 示例文件中的代码显示了一个为网络库存和小部件实现启用的 capability
<shortcuts>
<capability
android:name="actions.intent.START_EXERCISE">
<app-widget
android:identifier="START_EXERCISE_1"
android:targetClass="com.example.exampleapp.CreateTaxiAppWidgetProvider">
<parameter
android:name="exercise.name"
android:key="exerciseName"
android:mimeType="text/*">
<data android:pathPattern="https://exampleapp.com/exercise/.*" />
</parameter>
</app-widget>
</capability>
</shortcuts>
测试应用操作
使用应用操作测试工具(Android Studio 的 Google 助理插件的一项功能)在物理设备或虚拟设备上测试小部件。要使用测试工具,请按照以下步骤操作
- 连接您的测试设备,并运行您的应用。
- 在 Android Studio 中,转到 Tools > App Actions > App Actions Test Tool。
- 点击创建预览。
- 使用 Android Studio,在您的测试设备上运行您的应用。
- 在您的测试设备上使用助理应用来测试您的应用操作。例如,您可以说 “嘿 Google,我这周在 ExampleApp 上跑了多少英里?”
- 观察您的应用行为,或使用 Android Studio 调试器,以验证所需的操作结果。
质量指南
本节重点介绍了将应用操作与小部件集成时的主要要求和最佳实践。
小部件中的内容
- (必需) 不要在您的小部件中显示广告。
- 小部件内容应完全专注于实现 intent。不要试图用一个小部件实现多个 intent 或添加不相关的内容。
处理身份验证
- (必需) 在需要用户身份验证才能完成用户流程的情况下,返回一个说明用户需要在应用中继续的小部件。Google 助理中的内联用户身份验证不支持应用操作。
- 如果用户允许您的应用使用小部件显示数据,您可以在运行时为未经授权的用户返回一个错误小部件。
回退 intent
(必需) 在您的
shortcuts.xml中,除了您为给定 capability 实现的小部件之外,始终提供一个回退<intent>。回退 intent 是一个没有所需<parameter>值的<intent>元素。这使得助理能够在用户查询不包含该 capability 中定义的其他实现元素所需的参数时执行操作。此规则的例外情况是,如果该 capability 没有必需参数,则只需要小部件实现。
使用回退 intent 将您的应用打开到相关屏幕,而不是主屏幕。
以下 shortcuts.xml 示例文件中的代码演示了一个包含回退 <intent> 并支持主要 <app-widget> 实现的 <capability>
<shortcuts>
<capability
android:name="actions.intent.CREATE_TAXI_RESERVATION">
<!-- Widget with required parameter, specified using the "android:required" attribute. -->
<app-widget
android:identifier="CREATE_TAXI_RESERVATION_1"
android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.CreateTaxiAppWidgetProvider">
<parameter
android:name="taxiReservation.dropoffLocation.name"
android:key="dropoff"
android:required="true">
</parameter>
</app-widget>
<!-- Fallback intent with no parameters required to successfully execute. -->
<intent
android:identifier="CREATE_TAXI_RESERVATION_3"
android:action="myapplication.intent.CREATE_TAXI_RESERVATION_1"
android:targetClass="com.example.myapplication.TaxiReservationActivity">
</intent>
</capability>
</shortcuts>
Google Play 数据披露
本节列出了最新版本小部件扩展库收集的最终用户数据。
此 SDK 发送开发者提供的文本转语音 (TTS) 响应,Google 助理使用助理的语音技术将其播报给用户。此信息不会由 Google 存储。
应用操作还可能收集客户端应用元数据,用于以下目的
- 监控不同 SDK 版本的采用率。
- 量化 SDK 功能在应用中的使用情况。
