1. 开始之前
手写笔是一种笔形工具,可帮助用户执行精确任务。在本 Codelab 中,您将学习如何使用 android.os 和 androidx 库实现自然的手写笔体验。您还将学习如何使用 MotionEvent 类支持压力、倾斜和方向,以及如何通过手掌防误触阻止意外触控。此外,您还将学习如何通过动作预测减少手写笔延迟,以及如何使用 OpenGL 和 SurfaceView 类实现低延迟图形。
前提条件
- 具备 Kotlin 和 Lambda 表达式的经验。
- 基本了解如何使用 Android Studio。
- 基本了解 Jetpack Compose。
- 基本了解用于低延迟图形的 OpenGL。
您将学到什么
- 如何将
MotionEvent类用于手写笔。 - 如何实现手写笔功能,包括支持压力、倾斜和方向。
- 如何在使用
Canvas类上绘图。 - 如何实现动作预测。
- 如何使用 OpenGL 和
SurfaceView类渲染低延迟图形。
您需要准备什么
- 最新版本的 Android Studio.
- 熟悉 Kotlin 语法,包括 Lambda 表达式。
- 具备 Compose 的基本经验。如果您不熟悉 Compose,请完成Jetpack Compose 基础知识 Codelab。
- 支持手写笔的设备。
- 一支主动式手写笔。
- Git。
2. 获取入门代码
如需获取包含入门应用主题设置和基本设置的代码,请按以下步骤操作:
- 克隆此 GitHub 代码库
git clone https://github.com/android/large-screen-codelabs
- 打开
advanced-stylus文件夹。start文件夹包含入门代码,end文件夹包含解决方案代码。
3. 实现基本的绘图应用
首先,您将构建一个基本的绘图应用所需布局,该应用允许用户绘图,并使用 Canvas Composable 函数在屏幕上显示手写笔属性。它如下所示:

上部是一个 Canvas Composable 函数,您可以在其中绘制手写笔可视化效果,并显示手写笔的不同属性,例如方向、倾斜和压力。下部是另一个接收手写笔输入并绘制简单线条的 Canvas Composable 函数。
如需实现绘图应用的基本布局,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在 Android Studio 中,打开克隆的代码库。
- 点击
app>java>com.example.stylus,然后双击MainActivity。打开MainActivity.kt文件。 - 在
MainActivity类中,注意StylusVisualization和DrawAreaComposable函数。本部分重点介绍DrawAreaComposable函数。
创建一个 StylusState 类
- 在同一
ui目录中,,点击 File > New > Kotlin/Class file。 - 在文本框中,将 Name 占位符替换为
StylusState.kt,然后按Enter键(或 macOS 上的return键)。 - 在
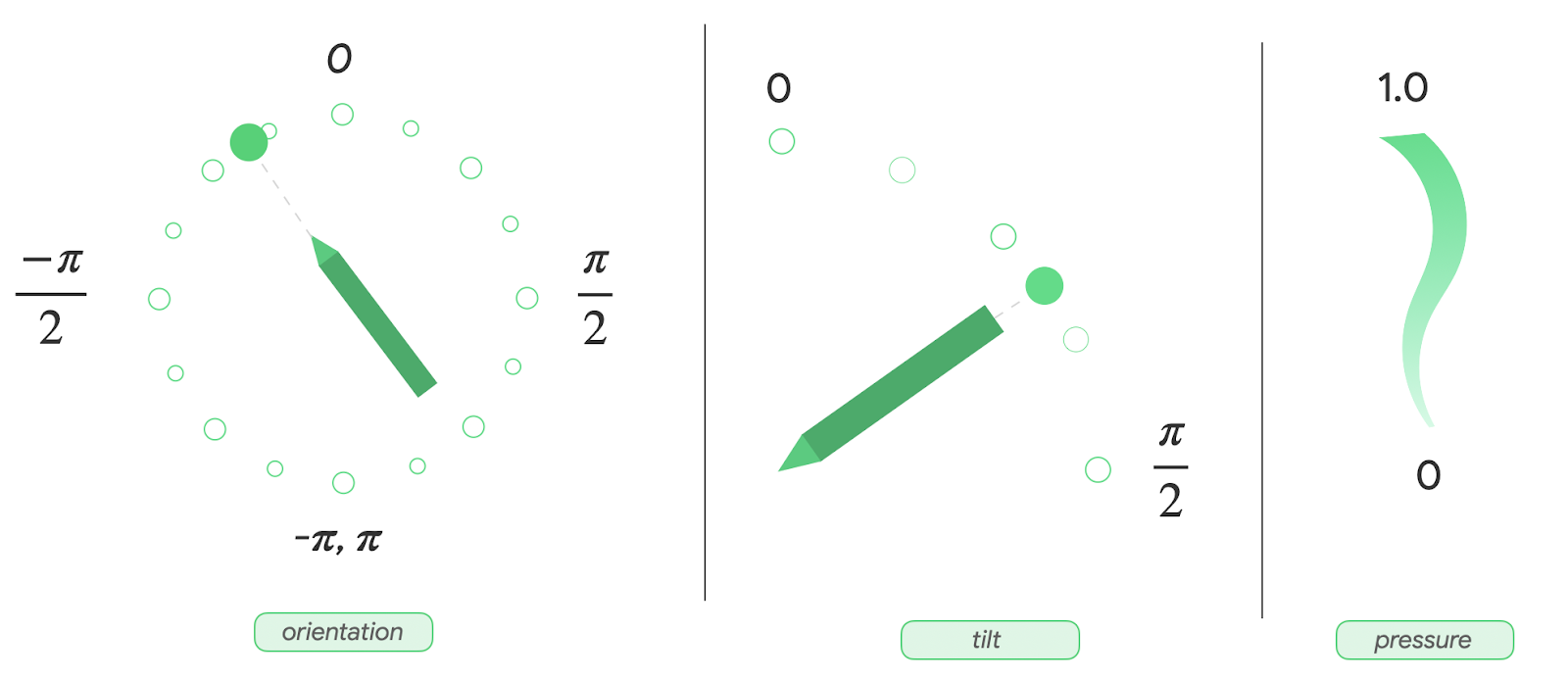
StylusState.kt文件中,创建StylusState数据类,然后添加下表中的变量:
变量 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|
| 取值范围从 0 到 1.0。 | |
|
| 取值范围从 -pi 到 pi 的弧度值。 | |
|
| 取值范围从 0 到 pi/2 的弧度值。 | |
|
| 使用 |
StylusState.kt
package com.example.stylus.ui
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Path
data class StylusState(
var pressure: Float = 0F,
var orientation: Float = 0F,
var tilt: Float = 0F,
var path: Path = Path(),
)
- 在
MainActivity.kt文件中,找到MainActivity类,然后使用mutableStateOf()函数添加手写笔状态:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf
import com.example.stylus.ui.StylusState
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
private var stylusState: StylusState by mutableStateOf(StylusState())
DrawPoint 类
DrawPoint 类存储屏幕上每个绘制点的数据;连接这些点即可创建线条。它模仿了 Path 对象的工作原理。
DrawPoint 类扩展了 PointF 类。它包含以下数据:
参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|
| 坐标 |
|
| 坐标 |
|
| 点的类型 |
DrawPoint 对象有两种类型,由 DrawPointType 枚举描述:
类型 | 说明 |
| 将线条的起点移动到某个位置。 |
| 从上一个点描绘一条线。 |
DrawPoint.kt
import android.graphics.PointF
class DrawPoint(x: Float, y: Float, val type: DrawPointType): PointF(x, y)
将数据点渲染成路径
对于此应用,StylusViewModel 类保存线条数据,准备用于渲染的数据,并对 Path 对象执行一些操作以实现手掌防误触。
- 如需保存线条数据,请在
StylusViewModel类中创建一个DrawPoint对象的可变列表:
StylusViewModel.kt
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import com.example.stylus.data.DrawPoint
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {private var currentPath = mutableListOf<DrawPoint>()
如需将数据点渲染成路径,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
StylusViewModel.kt文件的StylusViewModel类中,添加一个createPath函数。 - 使用
Path()构造函数创建一个类型为Path的path变量。 - 创建一个
for循环,遍历currentPath变量中的每个数据点。 - 如果数据点的类型为
START,则调用moveTo方法以在指定的x和y坐标处开始绘制一条线。 - 否则,调用
lineTo方法,传入数据点的x和y坐标,以连接到上一个点。 - 返回
path对象。
StylusViewModel.kt
import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Path
import com.example.stylus.data.DrawPoint
import com.example.stylus.data.DrawPointType
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var currentPath = mutableListOf<DrawPoint>()
private fun createPath(): Path {
val path = Path()
for (point in currentPath) {
if (point.type == DrawPointType.START) {
path.moveTo(point.x, point.y)
} else {
path.lineTo(point.x, point.y)
}
}
return path
}
private fun cancelLastStroke() {
}
处理 MotionEvent 对象
手写笔事件通过 MotionEvent 对象传递,后者提供了关于执行的操作和相关数据的信息,例如指针的位置和压力。下表包含 MotionEvent 对象的一些常量及其数据,您可以使用它们来识别用户在屏幕上执行的操作:
常量 | 数据 |
| 指针触摸屏幕。这是在 |
| 指针在屏幕上移动。这是正在绘制的线。 |
| 指针停止触摸屏幕。这是线的终点。 |
| 检测到意外触控。取消上一笔。 |
应用收到新的 MotionEvent 对象时,屏幕应重新渲染以反映新的用户输入。
- 如需在
StylusViewModel类中处理MotionEvent对象,请创建一个函数来收集线条坐标:
StylusViewModel.kt
import android.view.MotionEvent
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var currentPath = mutableListOf<DrawPoint>()
...
fun processMotionEvent(motionEvent: MotionEvent): Boolean {
when (motionEvent.actionMasked) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
currentPath.add(
DrawPoint(motionEvent.x, motionEvent.y, DrawPointType.START)
)
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
currentPath.add(DrawPoint(motionEvent.x, motionEvent.y, DrawPointType.LINE))
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> {
currentPath.add(DrawPoint(motionEvent.x, motionEvent.y, DrawPointType.LINE))
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL -> {
// Unwanted touch detected.
cancelLastStroke()
}
else -> return false
}
return true
}
将数据发送到界面
如需更新 StylusViewModel 类,以便界面可以收集 StylusState 数据类中的更改,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
StylusViewModel类中,创建一个_stylusState变量,类型为StylusState类的MutableStateFlow;以及一个stylusState变量,类型为StylusState类的StateFlow。_stylusState变量在StylusViewModel类中手写笔状态改变时进行修改,而stylusState变量由MainActivity类中的界面使用。
StylusViewModel.kt
import com.example.stylus.ui.StylusState
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var _stylusState = MutableStateFlow(StylusState())
val stylusState: StateFlow<StylusState> = _stylusState
- 创建一个接受
StylusState对象参数的requestRendering函数:
StylusViewModel.kt
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.update
...
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var _stylusState = MutableStateFlow(StylusState())
val stylusState: StateFlow<StylusState> = _stylusState
...
private fun requestRendering(stylusState: StylusState) {
// Updates the stylusState, which triggers a flow.
_stylusState.update {
return@update stylusState
}
}
- 在
processMotionEvent函数的末尾,添加一个带有StylusState参数的requestRendering函数调用。 - 在
StylusState参数中,从motionEvent变量中检索倾斜、压力和方向值,然后使用createPath()函数创建路径。这会触发一个流事件,您稍后将在界面中连接该事件。
StylusViewModel.kt
...
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
...
fun processMotionEvent(motionEvent: MotionEvent): Boolean {
...
else -> return false
}
requestRendering(
StylusState(
tilt = motionEvent.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_TILT),
pressure = motionEvent.pressure,
orientation = motionEvent.orientation,
path = createPath()
)
)
将界面与 StylusViewModel 类关联起来
- 在
MainActivity类中,找到onCreate函数的super.onCreate函数,然后添加状态收集。如需详细了解状态收集,请参阅以生命周期感知的方式收集流。
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
import androidx.lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.onEach
import androidx.lifecycle.Lifecycle
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.collect
...
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
lifecycleScope.launch {
lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
viewModel.stylusState
.onEach {
stylusState = it
}
.collect()
}
}
现在,每当 StylusViewModel 类发布新的 StylusState 状态时,Activity 就会收到它,新的 StylusState 对象会更新本地 MainActivity 类的 stylusState 变量。
- 在
DrawAreaComposable函数的主体中,向CanvasComposable函数添加pointerInteropFilter修饰符,以提供MotionEvent对象。
- 将
MotionEvent对象发送到 StylusViewModel 的processMotionEvent函数进行处理:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.compose.ui.ExperimentalComposeUiApi
import androidx.compose.ui.input.pointer.pointerInteropFilter
...
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
...
@Composable
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class)
fun DrawArea(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Canvas(modifier = modifier
.clipToBounds()
.pointerInteropFilter {
viewModel.processMotionEvent(it)
}
) {
}
}
- 调用
drawPath函数,传入stylusState的path属性,然后提供颜色和描边样式。
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
...
@Composable
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class)
fun DrawArea(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Canvas(modifier = modifier
.clipToBounds()
.pointerInteropFilter {
viewModel.processMotionEvent(it)
}
) {
with(stylusState) {
drawPath(
path = this.path,
color = Color.Gray,
style = strokeStyle
)
}
}
}
- 运行应用,然后您会注意到可以在屏幕上绘图。
4. 实现压力、方向和倾斜支持
在上一节中,您了解了如何从 MotionEvent 对象中检索手写笔信息,例如压力、方向和倾斜。
StylusViewModel.kt
tilt = motionEvent.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_TILT),
pressure = motionEvent.pressure,
orientation = motionEvent.orientation,
但是,此快捷方式仅适用于第一个指针。当检测到多点触控时,会检测到多个指针,而此快捷方式仅返回第一个指针(或屏幕上的第一个指针)的值。如需请求特定指针的数据,您可以使用 pointerIndex 参数:
StylusViewModel.kt
tilt = motionEvent.getAxisValue(MotionEvent.AXIS_TILT, pointerIndex),
pressure = motionEvent.getPressure(pointerIndex),
orientation = motionEvent.getOrientation(pointerIndex)
如需详细了解指针和多点触控,请参阅处理多点触控手势。
添加压力、方向和倾斜的可视化效果
- 在
MainActivity.kt文件中,找到StylusVisualizationComposable函数,然后使用StylusState流对象的信息来渲染可视化效果:
MainActivity.kt
import StylusVisualization.drawOrientation
import StylusVisualization.drawPressure
import StylusVisualization.drawTilt
...
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
...
@Composable
fun StylusVisualization(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Canvas(
modifier = modifier
) {
with(stylusState) {
drawOrientation(this.orientation)
drawTilt(this.tilt)
drawPressure(this.pressure)
}
}
}
- 运行应用。您会在屏幕顶部看到三个指示器,分别指示方向、压力和倾斜。
- 使用手写笔在屏幕上随意涂写,然后观察每种可视化效果如何根据您的输入做出反应。
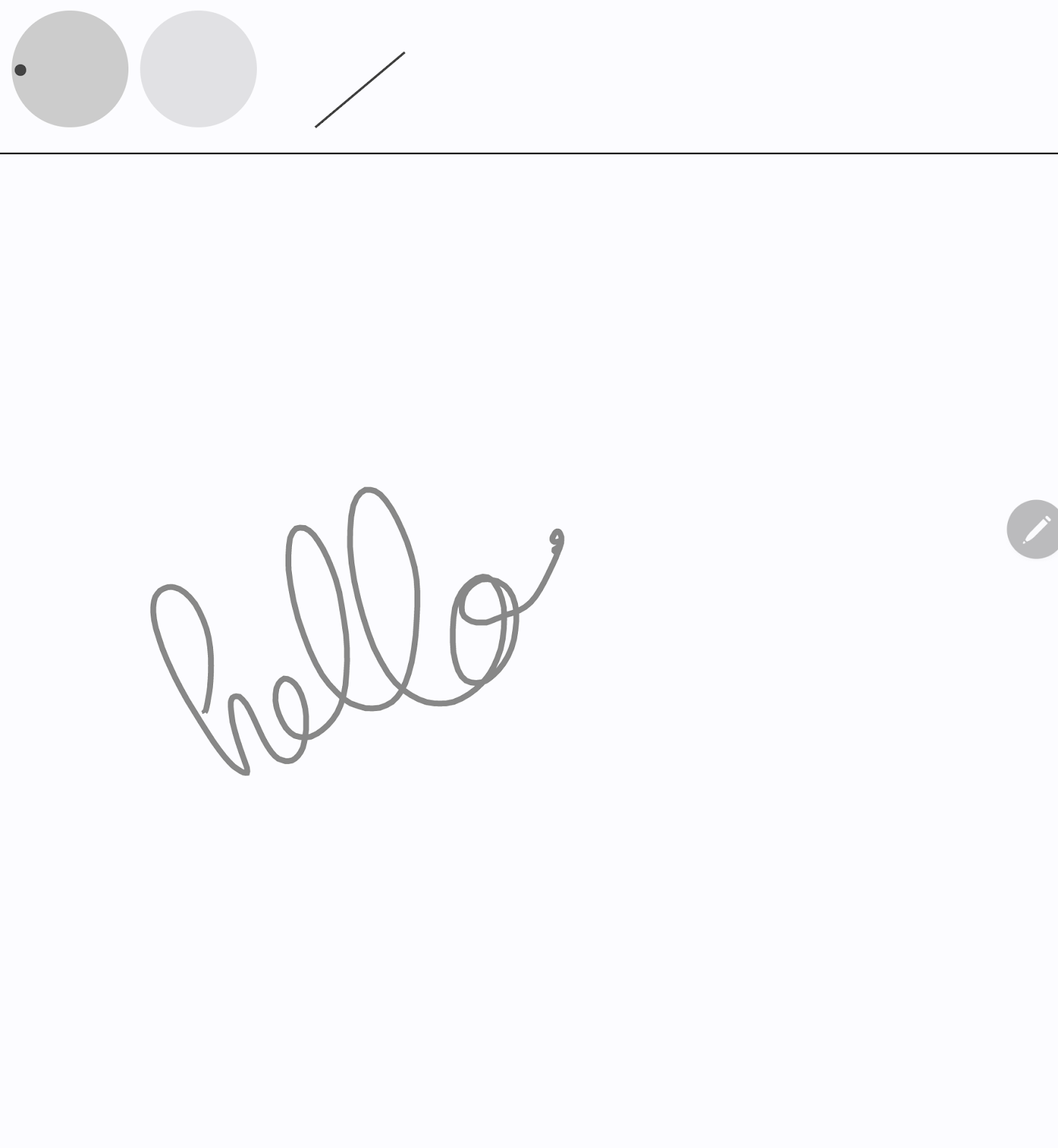
- 检查
StylusVisualization.kt文件,了解每种可视化效果的构建方式。
5. 实现手掌防误触
屏幕可能会记录意外触控。例如,当用户在手写时自然地将手放在屏幕上以获得支撑时,就会发生这种情况。
手掌防误触是一种机制,可检测此行为并通知开发者取消最后一组 MotionEvent 对象。一组 MotionEvent 对象以 ACTION_DOWN 常量开始。
这意味着您必须维护输入的历史记录,以便从屏幕上移除意外触控并重新渲染合法的用户输入。幸运的是,您已将历史记录存储在 StylusViewModel 类中的 currentPath 变量中。
Android 通过 MotionEvent 对象的 ACTION_CANCEL 常量向开发者告知意外触控。从 Android 13 开始,MotionEvent 对象提供了 FLAG_CANCELED 常量,应在 ACTION_POINTER_UP 常量上检查此常量。
实现 cancelLastStroke 函数
- 如需移除从最后一个
START数据点开始的数据点,请返回StylusViewModel类,然后创建一个cancelLastStroke函数,该函数查找最后一个START数据点的索引,并仅保留从第一个数据点到索引减一的数据:
StylusViewModel.kt
...
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
...
private fun cancelLastStroke() {
// Find the last START event.
val lastIndex = currentPath.findLastIndex {
it.type == DrawPointType.START
}
// If found, keep the element from 0 until the very last event before the last MOVE event.
if (lastIndex > 0) {
currentPath = currentPath.subList(0, lastIndex - 1)
}
}
添加 ACTION_CANCEL 和 FLAG_CANCELED 常量
- 在
StylusViewModel.kt文件中,找到processMotionEvent函数。 - 在
ACTION_UP常量中,创建一个canceled变量,检查当前 SDK 版本是否为 Android 13 或更高版本,以及FLAG_CANCELED常量是否已激活。 - 在下一行,创建一个条件来检查
canceled变量是否为 true。如果是,则调用cancelLastStroke函数来移除最后一组MotionEvent对象。如果不是,则调用currentPath.add方法来添加最后一组MotionEvent对象。
StylusViewModel.kt
import android.os.Build
...
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
...
fun processMotionEvent(motionEvent: MotionEvent): Boolean {
...
MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP,
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> {
val canceled = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.TIRAMISU &&
(motionEvent.flags and MotionEvent.FLAG_CANCELED) == MotionEvent.FLAG_CANCELED
if(canceled) {
cancelLastStroke()
} else {
currentPath.add(DrawPoint(motionEvent.x, motionEvent.y, DrawPointType.LINE))
}
}
- 在
ACTION_CANCEL常量中,请注意cancelLastStroke函数:
StylusViewModel.kt
...
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
...
fun processMotionEvent(motionEvent: MotionEvent): Boolean {
...
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL -> {
// unwanted touch detected
cancelLastStroke()
}
手掌防误触已实现!您可以在 palm-rejection 文件夹中找到工作代码。
6. 实现低延迟
在本节中,您将减少用户输入和屏幕渲染之间的延迟,以提高性能。延迟有多种原因,其中之一是图形管道较长。您可以使用前缓冲区渲染来减少图形管道。前缓冲区渲染允许开发者直接访问屏幕缓冲区,这对于手写和素描非常有益。
androidx.graphics 库提供的 GLFrontBufferedRenderer 类负责前缓冲区和双缓冲区渲染。它使用 onDrawFrontBufferedLayer 回调函数优化 SurfaceView 对象以实现快速渲染,并使用 onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer 回调函数实现正常渲染。GLFrontBufferedRenderer 类和 GLFrontBufferedRenderer.Callback 接口适用于用户提供的数据类型。在此 Codelab 中,您将使用 Segment 类。
如需开始,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在 Android Studio 中,打开
low-latency文件夹,以便获取所有必需的文件: - 注意项目中的以下新文件:
- 在
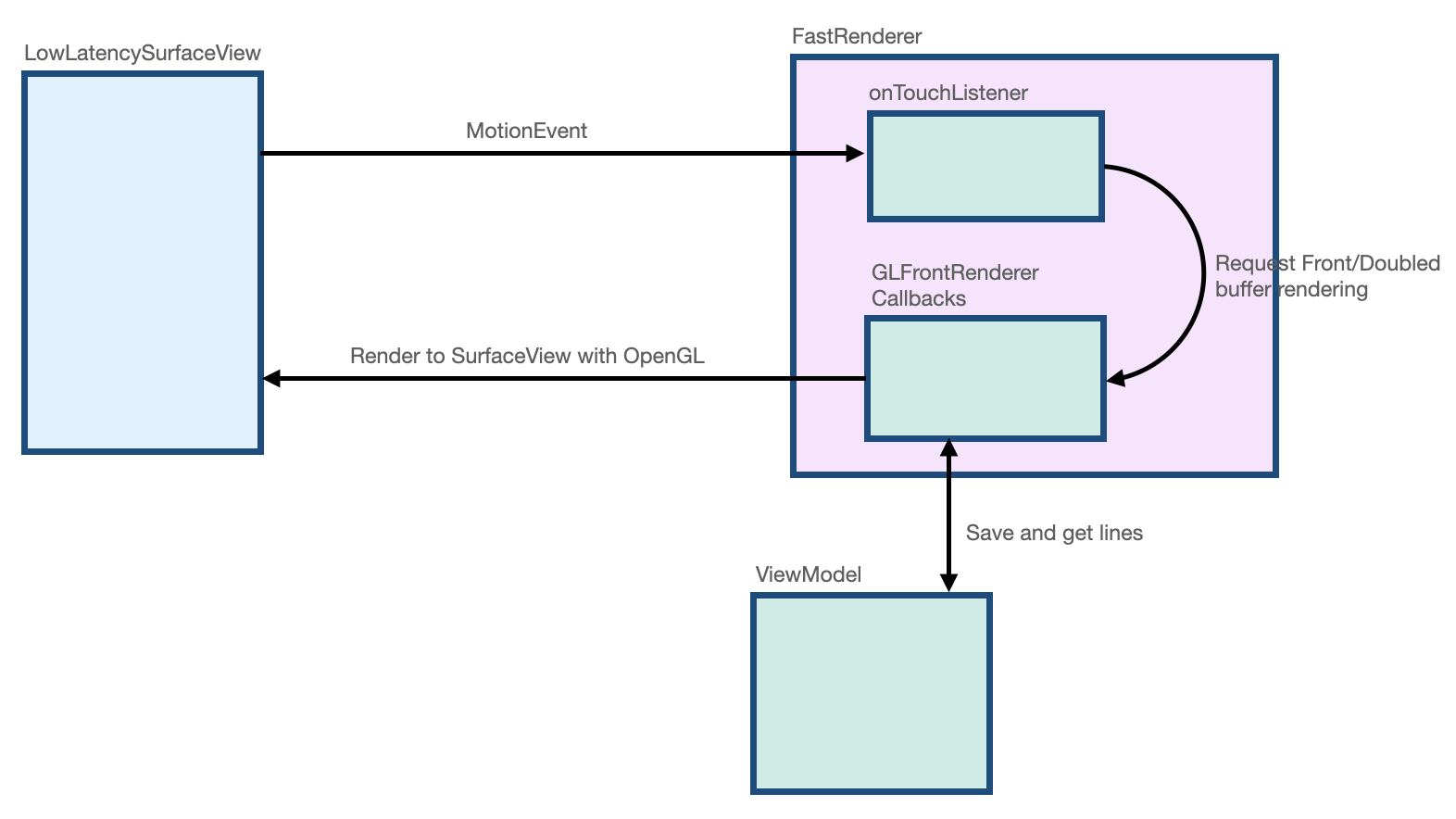
build.gradle文件中,已通过implementation "androidx.graphics:graphics-core:1.0.0-alpha03"声明导入androidx.graphics库。 LowLatencySurfaceView类扩展了SurfaceView类,用于在屏幕上渲染 OpenGL 代码。LineRenderer类包含用于在屏幕上渲染线条的 OpenGL 代码。FastRenderer类支持快速渲染并实现了GLFrontBufferedRenderer.Callback接口。它还拦截MotionEvent对象。StylusViewModel类使用LineManager接口保存数据点。Segment类定义了一个线段,如下所示:x1,y1: 第一个点的坐标x2,y2: 第二个点的坐标
下图显示了数据如何在每个类之间移动:
创建低延迟曲面和布局
- 在
MainActivity.kt文件中,找到MainActivity类的onCreate函数。 - 在
onCreate函数的主体中,创建一个FastRenderer对象,然后传入一个viewModel对象:
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
...
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
fastRendering = FastRenderer(viewModel)
lifecycleScope.launch {
...
- 在同一文件中,创建一个
DrawAreaLowLatencyComposable函数。 - 在函数主体中,使用
AndroidViewAPI 封装LowLatencySurfaceView视图,然后提供fastRendering对象:
MainActivity.kt
import androidx.compose.ui.viewinterop.AndroidView
import com.example.stylus.gl.LowLatencySurfaceView
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
...
@Composable
fun DrawAreaLowLatency(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
AndroidView(factory = { context ->
LowLatencySurfaceView(context, fastRenderer = fastRendering)
}, modifier = modifier)
}
- 在
onCreate函数中,在DividerComposable函数之后,将DrawAreaLowLatencyComposable函数添加到布局中:
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
...
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
Surface(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.background
) {
Column {
StylusVisualization(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(100.dp)
)
Divider(
thickness = 1.dp,
color = Color.Black,
)
DrawAreaLowLatency()
}
}
- 在
gl目录中,打开LowLatencySurfaceView.kt文件,然后注意LowLatencySurfaceView类中的以下内容:
LowLatencySurfaceView类扩展了SurfaceView类。它使用fastRenderer对象的onTouchListener方法。- 当调用
onAttachedToWindow函数时,通过fastRenderer类实现的GLFrontBufferedRenderer.Callback接口需要附加到SurfaceView对象,以便回调可以渲染到SurfaceView视图。 - 当调用
onDetachedFromWindow函数时,通过fastRenderer类实现的GLFrontBufferedRenderer.Callback接口需要释放。
LowLatencySurfaceView.kt
class LowLatencySurfaceView(context: Context, private val fastRenderer: FastRenderer) :
SurfaceView(context) {
init {
setOnTouchListener(fastRenderer.onTouchListener)
}
override fun onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow()
fastRenderer.attachSurfaceView(this)
}
override fun onDetachedFromWindow() {
fastRenderer.release()
super.onDetachedFromWindow()
}
}
使用 onTouchListener 接口处理 MotionEvent 对象
如需在检测到 ACTION_DOWN 常量时处理 MotionEvent 对象,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
gl目录中,打开FastRenderer.kt文件。 - 在
ACTION_DOWN常量的主体中,创建一个currentX变量,用于存储MotionEvent对象的x坐标;以及一个currentY变量,用于存储其y坐标。 - 创建一个
Segment变量,用于存储接受两个currentX参数实例和两个currentY参数实例的Segment对象,因为它是线的起点。 - 调用
renderFrontBufferedLayer方法,传入segment参数,以触发onDrawFrontBufferedLayer函数上的回调。
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer ( ... ) {
...
val onTouchListener = View.OnTouchListener { view, event ->
...
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
// Ask that the input system not batch MotionEvent objects,
// but instead deliver them as soon as they're available.
view.requestUnbufferedDispatch(event)
currentX = event.x
currentY = event.y
// Create a single point.
val segment = Segment(currentX, currentY, currentX, currentY)
frontBufferRenderer?.renderFrontBufferedLayer(segment)
}
如需在检测到 ACTION_MOVE 常量时处理 MotionEvent 对象,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
ACTION_MOVE常量的主体中,创建一个previousX变量,用于存储currentX变量;以及一个previousY变量,用于存储currentY变量。 - 创建一个
currentX变量,用于保存MotionEvent对象的当前x坐标;以及一个currentY变量,用于保存其当前y坐标。 - 创建一个
Segment变量,用于存储接受previousX、previousY、currentX和currentY参数的Segment对象。 - 调用
renderFrontBufferedLayer方法,传入segment参数,以触发onDrawFrontBufferedLayer函数上的回调并执行 OpenGL 代码。
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer ( ... ) {
...
val onTouchListener = View.OnTouchListener { view, event ->
...
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
previousX = currentX
previousY = currentY
currentX = event.x
currentY = event.y
val segment = Segment(previousX, previousY, currentX, currentY)
// Send the short line to front buffered layer: fast rendering
frontBufferRenderer?.renderFrontBufferedLayer(segment)
}
- 如需在检测到
ACTION_UP常量时处理MotionEvent对象,请调用commit方法以触发onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer函数的调用并执行 OpenGL 代码:
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer ( ... ) {
...
val onTouchListener = View.OnTouchListener { view, event ->
...
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> {
frontBufferRenderer?.commit()
}
实现 GLFrontBufferedRenderer 回调函数
在 FastRenderer.kt 文件中,onDrawFrontBufferedLayer 和 onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer 回调函数执行 OpenGL 代码。在每个回调函数的开头,以下 OpenGL 函数将 Android 数据映射到 OpenGL 工作空间:
GLES20.glViewport函数定义了渲染场景的矩形区域大小。Matrix.orthoM函数计算ModelViewProjection矩阵。Matrix.multiplyMM函数执行矩阵乘法,将 Android 数据转换为 OpenGL 参考,并为projection矩阵提供设置。
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
override fun onDraw[Front/Double]BufferedLayer(
eglManager: EGLManager,
bufferInfo: BufferInfo,
transform: FloatArray,
params: Collection<Segment>
) {
val bufferWidth = bufferInfo.width
val bufferHeight = bufferInfo.height
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, bufferWidth, bufferHeight)
// Map Android coordinates to OpenGL coordinates.
Matrix.orthoM(
mvpMatrix,
0,
0f,
bufferWidth.toFloat(),
0f,
bufferHeight.toFloat(),
-1f,
1f
)
Matrix.multiplyMM(projection, 0, mvpMatrix, 0, transform, 0)
这一部分代码已为您准备好,您可以专注于执行实际渲染的代码。onDrawFrontBufferedLayer 回调函数渲染屏幕的一小块区域。它提供了 Segment 类型的 param 值,以便您可以快速渲染单个线段。LineRenderer 类是用于画笔的 OpenGL 渲染器,它应用线条的颜色和大小。
如需实现 onDrawFrontBufferedLayer 回调函数,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
FastRenderer.kt文件中,找到onDrawFrontBufferedLayer回调函数。 - 在
onDrawFrontBufferedLayer回调函数的主体中,调用obtainRenderer函数以获取LineRenderer实例。 - 调用
LineRenderer函数的drawLine方法,传入以下参数:
- 之前计算的
projection矩阵。 - 一个
Segment对象列表,此处为单个线段。 - 线条的
color。
FastRenderer.kt
import android.graphics.Color
import androidx.core.graphics.toColor
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
override fun onDrawFrontBufferedLayer(
eglManager: EGLManager,
bufferInfo: BufferInfo,
transform: FloatArray,
params: Collection<Segment>
) {
...
Matrix.multiplyMM(projection, 0, mvpMatrix, 0, transform, 0)
obtainRenderer().drawLine(projection, listOf(param), Color.GRAY.toColor())
}
- 运行应用,然后您会注意到可以在屏幕上以最小延迟进行绘图。但是,应用不会持久保留线条,因为您仍需要实现
onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer回调函数。
在调用 commit 函数后会调用 onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer 回调函数,以实现线条的持久化。回调提供了 params 值,其中包含 Segment 对象的集合。前缓冲区上的所有线段都会在双缓冲区中重新绘制以实现持久化。
如需实现 onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer 回调函数,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
StylusViewModel.kt文件中,找到StylusViewModel类,然后创建一个openGlLines变量,用于存储Segment对象的可变列表:
StylusViewModel.kt
import com.example.stylus.data.Segment
class StylusViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var _stylusState = MutableStateFlow(StylusState())
val stylusState: StateFlow<StylusState> = _stylusState
val openGlLines = mutableListOf<List<Segment>>()
private fun requestRendering(stylusState: StylusState) {
- 在
FastRenderer.kt文件中,找到FastRenderer类的onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer回调函数。 - 在
onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer回调函数的主体中,使用GLES20.glClearColor和GLES20.glClear方法清除屏幕,以便可以从头开始渲染场景,并将线条添加到viewModel对象以实现持久化:
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
override fun onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer(
eglManager: EGLManager,
bufferInfo: BufferInfo,
transform: FloatArray,
params: Collection<Segment>
) {
...
// Clear the screen with black.
GLES20.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
viewModel.openGlLines.add(params.toList())
- 创建一个
for循环,遍历并渲染viewModel对象中的每条线:
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
override fun onDrawDoubleBufferedLayer(
eglManager: EGLManager,
bufferInfo: BufferInfo,
transform: FloatArray,
params: Collection<Segment>
) {
...
// Clear the screen with black.
GLES20.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
viewModel.openGlLines.add(params.toList())
// Render the entire scene (all lines).
for (line in viewModel.openGlLines) {
obtainRenderer().drawLine(projection, line, Color.GRAY.toColor())
}
}
- 运行应用,然后您会注意到可以在屏幕上绘图,并且在触发
ACTION_UP常量后线条会保留下来。
7. 实现动作预测
您可以使用 androidx.input 库进一步提高延迟,该库分析手写笔的轨迹,预测下一个点的位置并将其插入进行渲染。
如需设置动作预测,请按以下步骤操作:
- 在
app/build.gradle文件中,在依赖项部分导入该库:
app/build.gradle
...
dependencies {
...
implementation"androidx.input:input-motionprediction:1.0.0-beta01"
- 点击 File > Sync project with Gradle files。
- 在
FastRendering.kt文件中的FastRendering类中,将motionEventPredictor对象声明为一个属性:
FastRenderer.kt
import androidx.input.motionprediction.MotionEventPredictor
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
private var frontBufferRenderer: GLFrontBufferedRenderer<Segment>? = null
private var motionEventPredictor: MotionEventPredictor? = null
- 在
attachSurfaceView函数中,初始化motionEventPredictor变量:
FastRenderer.kt
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
fun attachSurfaceView(surfaceView: SurfaceView) {
frontBufferRenderer = GLFrontBufferedRenderer(surfaceView, this)
motionEventPredictor = MotionEventPredictor.newInstance(surfaceView)
}
- 在
onTouchListener变量中,调用motionEventPredictor?.record方法,以便motionEventPredictor对象获取运动数据:
FastRendering.kt
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
val onTouchListener = View.OnTouchListener { view, event ->
motionEventPredictor?.record(event)
...
when (event?.action) {
下一步是使用 predict 函数预测一个 MotionEvent 对象。我们建议在收到 ACTION_MOVE 常量后以及记录 MotionEvent 对象后进行预测。换句话说,您应该在描绘进行中时进行预测。
- 使用
predict方法预测一个人工MotionEvent对象。 - 创建一个使用当前和预测的 *x* 和 *y* 坐标的
Segment对象。 - 使用
frontBufferRenderer?.renderFrontBufferedLayer(predictedSegment)方法请求对预测线段进行快速渲染。
FastRendering.kt
class FastRenderer( ... ) {
...
val onTouchListener = View.OnTouchListener { view, event ->
motionEventPredictor?.record(event)
...
when (event?.action) {
...
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
...
frontBufferRenderer?.renderFrontBufferedLayer(segment)
val motionEventPredicted = motionEventPredictor?.predict()
if(motionEventPredicted != null) {
val predictedSegment = Segment(currentX, currentY,
motionEventPredicted.x, motionEventPredicted.y)
frontBufferRenderer?.renderFrontBufferedLayer(predictedSegment)
}
}
...
}
预测事件会插入进行渲染,从而提高了延迟。
- 运行应用,然后您会注意到延迟有所改善。
改善延迟将为手写笔用户提供更自然的手写笔体验。
8. 恭喜
恭喜!您现在像专业人士一样知道如何处理手写笔了!
您学习了如何处理 MotionEvent 对象以提取压力、方向和倾斜信息。您还学习了如何通过同时实现 androidx.graphics 库和 androidx.input 库来改进延迟。这些增强功能的协同实现,提供了更自然的手写笔体验。
