1. 简介
此 Codelab 教授 Advanced WorkManager 的概念。它基于 Background Work with WorkManager Codelab 中涵盖的基础材料。
其他可用于熟悉 WorkManager 的资源包括
- WorkManager 指南
- 博客系列:Introducing WorkManager
- ADS 2019 WorkManager 演讲:WorkManager: Beyond the Basics
- WorkManager - MAD Skills 系列
您将构建什么
在本 Codelab 中,您将使用 Blur-O-Matic 应用,该应用可模糊照片和图像,并将结果保存到文件中。如果您已完成 Background Work with WorkManager Codelab,此示例应用与前一个类似(唯一的区别在于,此示例应用允许您从照片库中选择自己的图像进行模糊处理)。这里您将为代码添加一些功能
- 自定义配置
- 使用 Progress API 在执行工作时更新界面
- 测试您的 Workers
您将需要什么
要完成此 Codelab,您需要最新稳定版 Android Studio。
您还应该熟悉 LiveData、ViewModel 和 View Binding。如果您是这些类的新手,请查看 Android Lifecycle-aware components Codelab(特别是 ViewModel 和 LiveData)或 Room with a View Codelab(架构组件简介)。
如果您在任何时候遇到困难
如果您在此 Codelab 的任何时候遇到困难,或者您想查看代码的最终状态,您可以
或者,如果您愿意,可以从 GitHub 克隆已完成的 WorkManager Codelab
$ git clone -b advanced https://github.com/googlecodelabs/android-workmanager
2. 开始设置
第 1 步 - 下载代码
点击以下链接下载与此 Codelab 相配套的代码版本
或者,如果您愿意,可以从 GitHub 克隆 Codelab
$ git clone -b advanced_start https://github.com/googlecodelabs/android-workmanager
第 2 步 - 运行应用
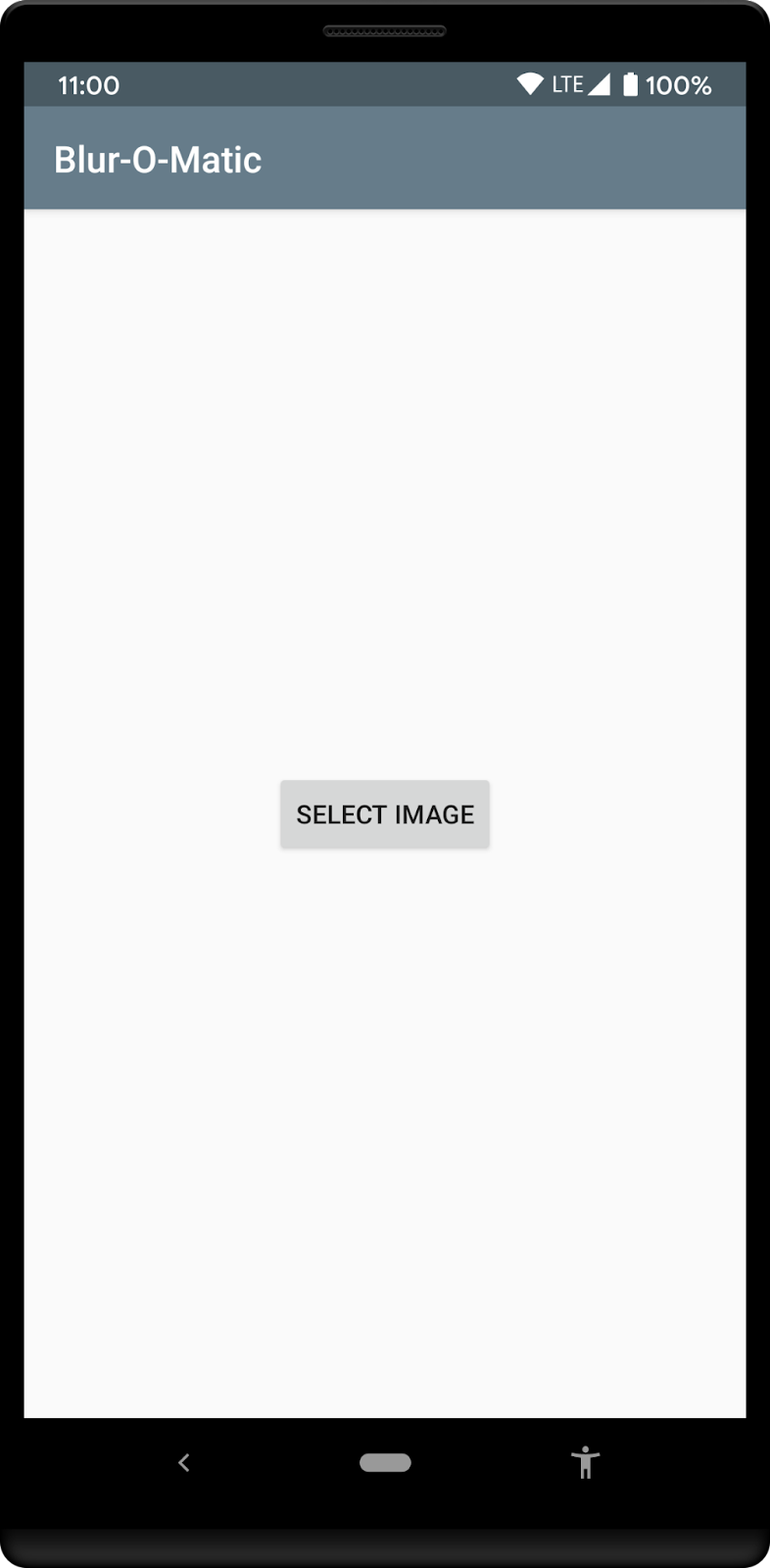
运行应用。您应该会看到以下屏幕。请确保在提示时授予应用访问您照片的权限。
|
|
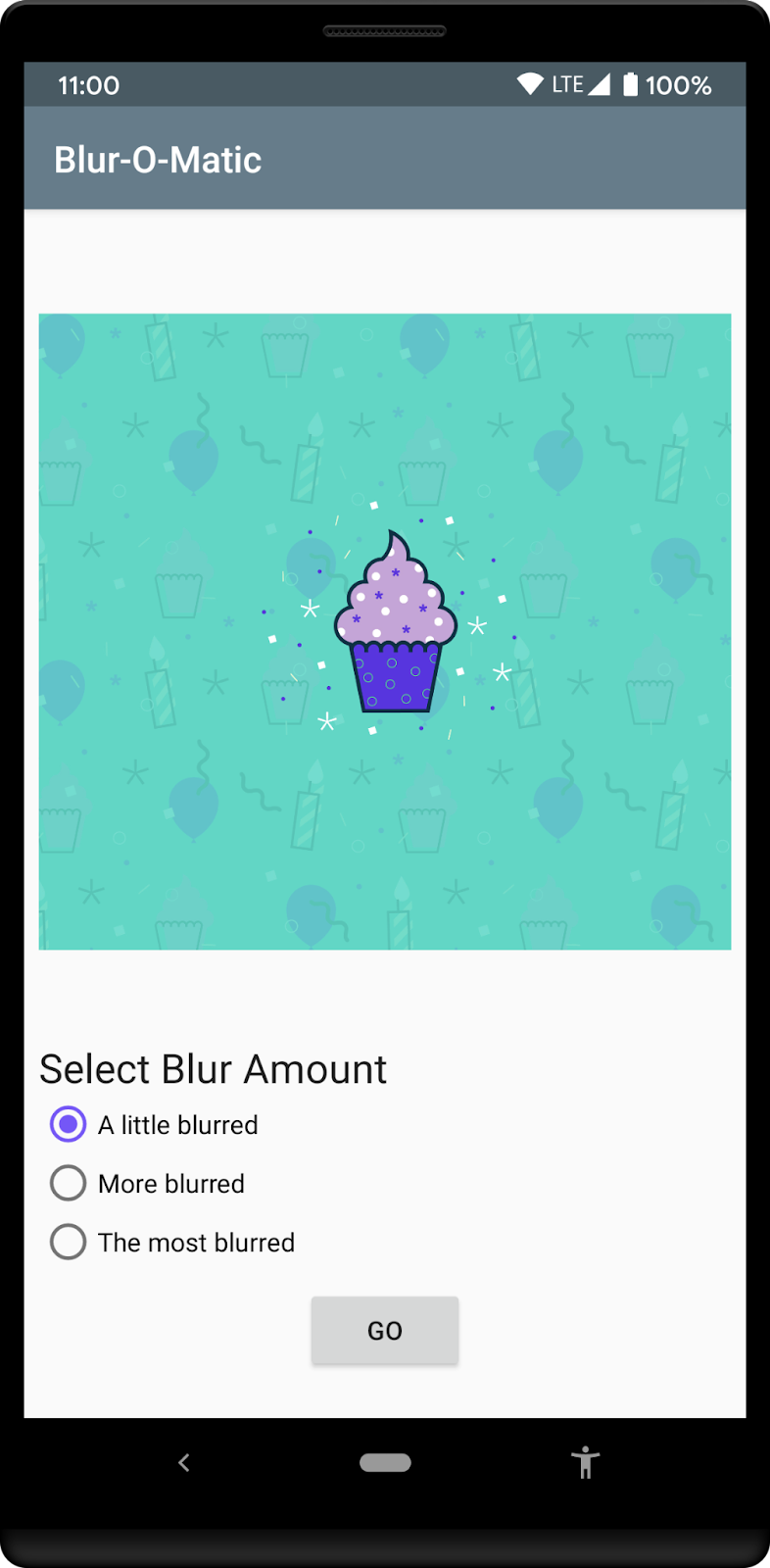
您可以选择一张图像,然后进入下一个屏幕,该屏幕有单选按钮,您可以在其中选择您希望图像有多模糊。按下 Go 按钮将模糊并保存图像。模糊过程中,应用会显示一个 Cancel 按钮,让您可以结束工作。
初始代码包含
WorkerUtils:此类包含实际模糊处理的代码,以及一些您稍后将用来显示 `Notifications` 和减慢应用的便利方法。BlurApplication:应用类,包含一个简单的onCreate()方法,用于为调试构建初始化 Timber 日志记录系统。BlurActivity:显示图像并包含用于选择模糊级别单选按钮的 activity。BlurViewModel:此视图模型存储显示BlurActivity所需的所有数据。它也是您使用 WorkManager 启动后台工作的类。Workers/CleanupWorker:此 Worker 始终删除临时文件(如果存在)。Workers/BlurWorker:此 Worker 模糊处理作为输入数据传入的带有 URI 的图像,并返回临时文件的 URI。Workers/SaveImageToFileWorker:此 Worker 将临时图像的 URI 作为输入,并返回最终文件的 URI。Constants:一个静态类,包含您在 Codelab 期间将使用的一些常量。SelectImageActivity:第一个 activity,允许您选择图像。res/activity_blur.xml和res/activity_select.xml:每个 activity 的布局文件。
您将在以下类中进行代码更改:BlurApplication、BlurActivity、BlurViewModel 和 BlurWorker。
3. 将 WorkManager 添加到您的应用
WorkManager 需要以下 gradle 依赖项。这些依赖项已包含在文件中
app/build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation "androidx.work:work-runtime-ktx:$versions.work"
}
您应该从 WorkManager 发布页面获取最新版本的 work-runtime,并放入最新稳定版的版本号,或者使用下面的版本号
build.gradle
versions.work = "2.7.1"
请务必点击 Sync Now 以将您的项目与更改后的 Gradle 文件同步。
4. 添加 WorkManager 的自定义配置
在此步骤中,您将为应用添加自定义配置,以修改调试构建的 WorkManager 日志级别。
第 1 步 - 禁用默认初始化
如 Custom WorkManager configuration and initialization 文档中所述,您必须通过移除 WorkManager 库默认自动合并的节点来禁用 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中的默认初始化。
要移除此节点,您可以向 AndroidManifest.xml 添加一个新的 provider 节点,如下所示
AndroidManifest.xml
<application
...
<provider
android:name="androidx.work.impl.WorkManagerInitializer"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.workmanager-init"
tools:node="remove" />
</application>
您还需要向清单添加 tools 命名空间。包含这些更改的完整文件将是
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Copyright 2020 Google LLC.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 -->
<manifest package="com.example.background"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<application
android:name=".BlurApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".SelectImageActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".BlurActivity" />
<!-- ADD THE FOLLOWING NODE -->
<provider
android:name="androidx.work.impl.WorkManagerInitializer"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.workmanager-init"
tools:node="remove" />
</application>
</manifest>
步骤 2 - 添加 Configuration.Provider 到 Application 类
第 2 步 - 向 Application 类添加 Configuration.Provider
BlurApplication.kt
class BlurApplication : Application(), Configuration.Provider {
override fun getWorkManagerConfiguration(): Configuration =
Configuration.Builder()
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.DEBUG)
.build()
...
}
此更改后,WorkManager 将以日志级别设置为 DEBUG 运行。
更好的选择是仅为您应用的调试构建以这种方式设置 WorkManager,使用类似以下代码
BlurApplication.kt
class BlurApplication() : Application(), Configuration.Provider {
override fun getWorkManagerConfiguration(): Configuration {
return if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Configuration.Builder()
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.DEBUG)
.build()
} else {
Configuration.Builder()
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.ERROR)
.build()
}
}
...
}
完整的 BlurApplication.kt 变为
BlurApplication.kt
/* Copyright 2020 Google LLC.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package com.example.background
import android.app.Application
import androidx.work.Configuration
import timber.log.Timber
import timber.log.Timber.DebugTree
class BlurApplication() : Application(), Configuration.Provider {
override fun getWorkManagerConfiguration(): Configuration {
return if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Configuration.Builder()
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.DEBUG)
.build()
} else {
Configuration.Builder()
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(android.util.Log.ERROR)
.build()
}
}
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Timber.plant(DebugTree())
}
}
}
第 3 步 - 在调试模式下运行应用
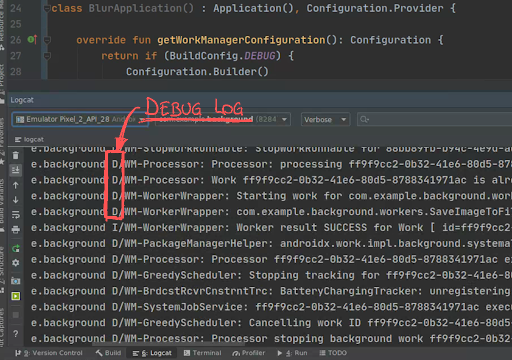
WorkManager 现在已配置,以便您的调试构建记录来自该库的所有消息。
运行应用,您可以在 Android Studio 的 logcat 选项卡中查看日志
第 4 步 - 您可以配置什么?
参数的完整列表位于 WorkManager 的 Configuration.Builder 参考指南中。请注意另外两个参数
WorkerFactoryJobId范围
修改 WorkerFactory 允许向 Worker 的构造函数添加其他参数。您可以在此 Customizing WorkManager 文章中找到有关如何实现自定义 WorkerFactory 的更多信息。如果您在应用中同时使用 WorkManager 和 JobScheduler API,最好自定义 JobId 范围,以避免两个 API 使用相同的 JobId 范围。
分享 WorkManager 的进度
WorkManager v2.3 添加了使用 setProgressAsync()(或从 CoroutineWorker 使用时使用 setProgress())从 Worker 向应用分享进度信息的功能。可以通过 WorkInfo 观察此信息,旨在用于在界面中向用户提供反馈。当 worker 达到最终状态(`SUCCEEDED`、`FAILED` 或 `CANCELLED`)时,进度数据将被取消。要了解有关如何发布和监听进度的更多信息,请阅读 Observing intermediate Worker progress。
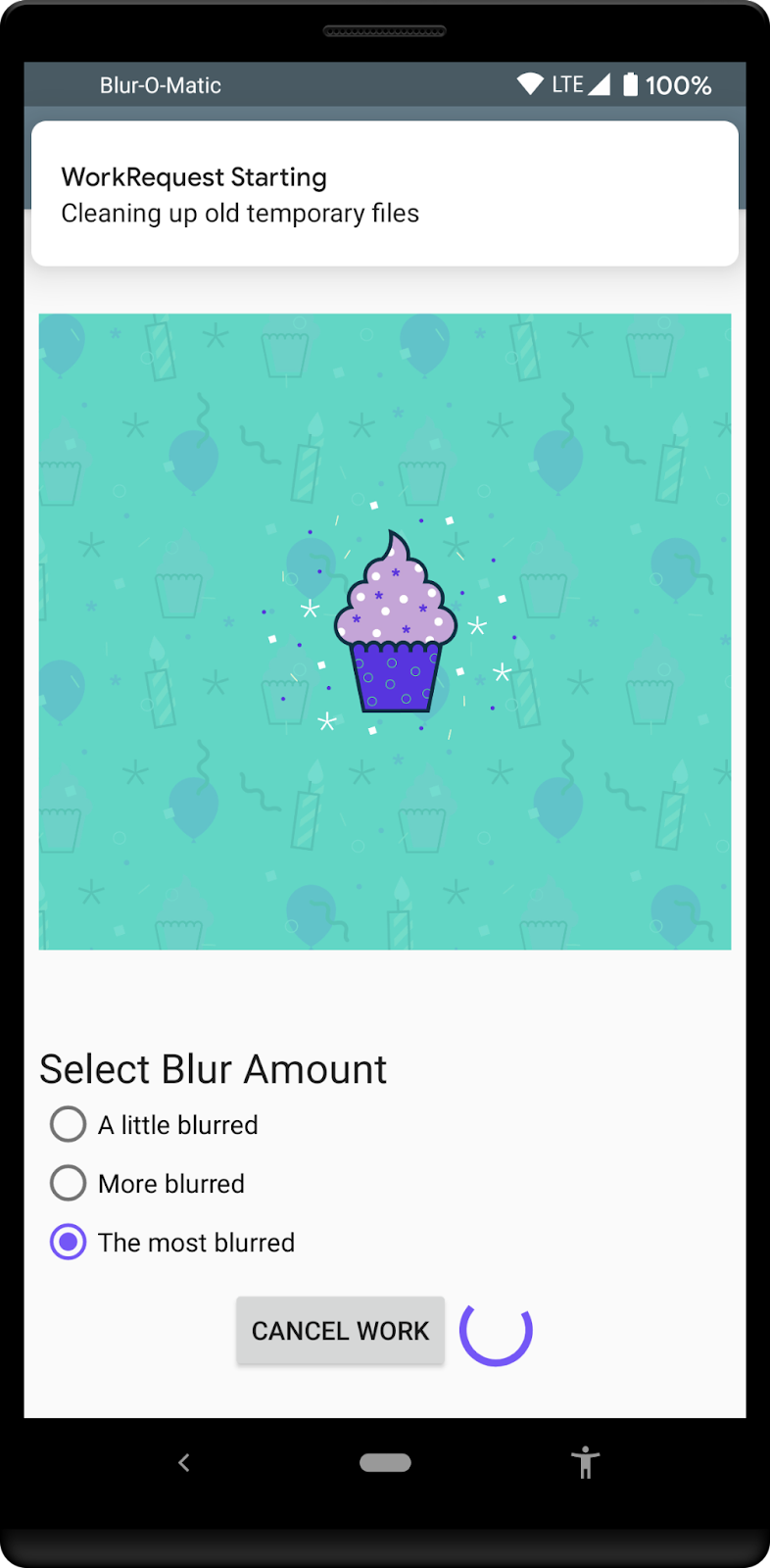
现在您将要做的是在界面中添加一个进度条,以便如果应用位于前台,用户可以看到模糊处理的进度。最终结果将类似于
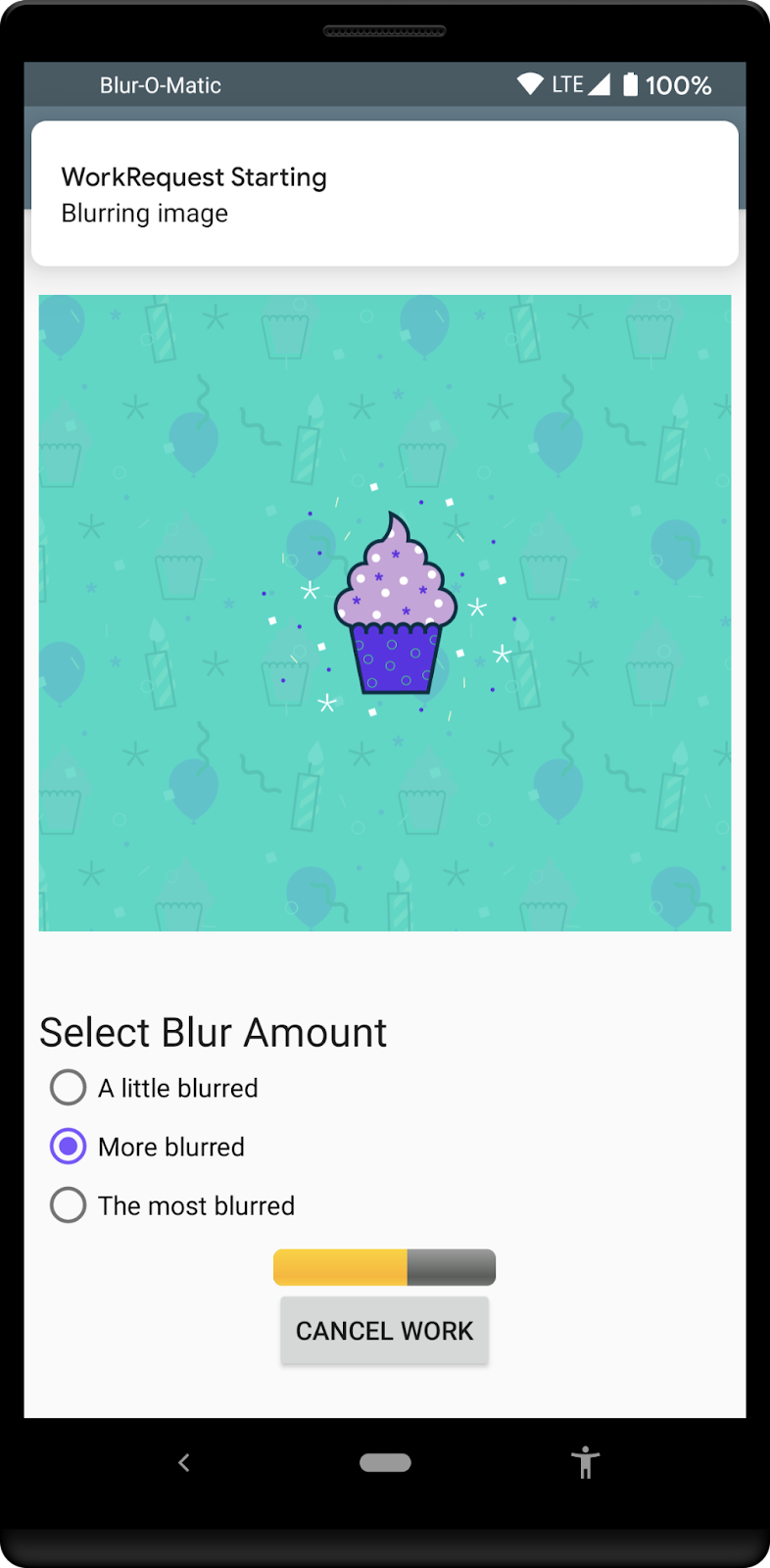
第 1 步 - 修改 ProgressBar
要修改布局中的 `ProgressBar`,您需要删除 android:indeterminate="true" 参数,添加样式 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal",并使用 android:progress="0" 设置初始值。您还需要将 LinearLayout 的 orientation 设置为 "vertical"
app/src/main/res/layout/activity_blur.xml
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progress_bar"
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:progress="0"
android:visibility="gone"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/cancel_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/cancel_work"
android:visibility="gone"
/>
</LinearLayout>
另一个需要的更改是确保 `ProgressBar` 在初始位置重新开始。您可以通过更新 BlurActivity.kt 文件中的 showWorkFinished() 函数来完成此操作
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/BlurActivity.kt
/**
* Shows and hides views for when the Activity is done processing an image
*/
private fun showWorkFinished() {
with(binding) {
progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
cancelButton.visibility = View.GONE
goButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
progressBar.progress = 0 // <-- ADD THIS LINE
}
}
第 2 步 - 在 ViewModel 中观察进度信息
BlurViewModel 文件中已有一个 observer,用于检查您的链何时完成。添加一个新的 observer,用于观察由 BlurWorker 发布 的进度。
首先,在 Constants.kt 文件末尾添加几个常量来跟踪此信息
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/Constants.kt
// Progress Data Key
const val PROGRESS = "PROGRESS"
const val TAG_PROGRESS = "TAG_PROGRESS"
下一步是将此标签添加到 BlurViewModel.kt 文件中的 BlurWorker 的 WorkRequest,以便您可以检索其 WorkInfo。从该 WorkInfo,您可以检索 worker 的进度信息
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/BlurViewModel.kt
// Add WorkRequests to blur the image the number of times requested
for (i in 0 until blurLevel) {
val blurBuilder = OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder<BlurWorker>()
// Input the Uri if this is the first blur operation
// After the first blur operation the input will be the output of previous
// blur operations.
if (i == 0) {
blurBuilder.setInputData(createInputDataForUri())
}
blurBuilder.addTag(TAG_PROGRESS) // <-- ADD THIS
continuation = continuation.then(blurBuilder.build())
}
向 BlurViewModel.kt 文件添加一个新的 LiveData 来跟踪此 WorkRequest,并在 init 块中初始化 LiveData
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/BlurViewModel.kt
class BlurViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
internal var imageUri: Uri? = null
internal var outputUri: Uri? = null
internal val outputWorkInfoItems: LiveData<List<WorkInfo>>
internal val progressWorkInfoItems: LiveData<List<WorkInfo>> // <-- ADD THIS
private val workManager: WorkManager = WorkManager.getInstance(application)
init {
// This transformation makes sure that whenever the current work Id changes the WorkStatus
// the UI is listening to changes
outputWorkInfoItems = workManager.getWorkInfosByTagLiveData(TAG_OUTPUT)
progressWorkInfoItems = workManager.getWorkInfosByTagLiveData(TAG_PROGRESS) // <-- ADD THIS
}
...
}
步骤 3 - 在 Activity 中观察 LiveData
第 3 步 - 在 Activity 中观察 LiveData
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/BlurActivity.kt
// Show work status
viewModel.outputWorkInfoItems.observe(this, outputObserver())
// ADD THE FOLLOWING LINES
// Show work progress
viewModel.progressWorkInfoItems.observe(this, progressObserver())
现在,您可以在 observer 中检查接收到的 WorkInfo,以查看是否有任何进度信息,并相应地更新 ProgressBar
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/BlurActivity.kt
private fun progressObserver(): Observer<List<WorkInfo>> {
return Observer { listOfWorkInfo ->
if (listOfWorkInfo.isNullOrEmpty()) {
return@Observer
}
listOfWorkInfo.forEach { workInfo ->
if (WorkInfo.State.RUNNING == workInfo.state) {
val progress = workInfo.progress.getInt(PROGRESS, 0)
binding.progressBar.progress = progress
}
}
}
}
第 4 步 - 从 BlurWorker 发布进度
显示进度信息所需的所有部分现已到位。是时候向 BlurWorker 添加实际的进度信息发布了。
此示例仅在我们的 doWork() 函数中模拟了一些耗时过程,以便它可以在定义的时间内发布进度信息。
此处的更改是用 10 个较小的延迟替换单个延迟,并在每次迭代时设置新的进度
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/workers/BlurWorker.kt
override fun doWork(): Result {
val appContext = applicationContext
val resourceUri = inputData.getString(KEY_IMAGE_URI)
makeStatusNotification("Blurring image", appContext)
// sleep()
(0..100 step 10).forEach {
setProgressAsync(workDataOf(PROGRESS to it))
sleep()
}
...
}
由于原始延迟为 3 秒,将其减小十倍到 0.3 秒可能是一个好主意
app/src/main/java/com/example/background/Constants.kt
// const val DELAY_TIME_MILLIS: Long = 3000
const val DELAY_TIME_MILLIS: Long = 300
第 5 步 - 运行
此时运行应用时,它应该显示由 BlurWorker 发送的消息填充的 ProgressBar。
5. 测试 WorkManager
测试是每个应用的重要组成部分,引入像 WorkManager 这样的库时,提供工具以轻松测试您的代码非常重要。
对于 WorkManager,我们也提供了一些帮助程序来轻松测试您的 Workers。要了解有关如何为 worker 创建测试的更多信息,您可以参考 WorkManager 测试文档。
在此 Codelab 的此部分中,我们将介绍针对我们的 Worker 类的一些测试,展示一些常见的用例。
首先,我们希望提供一种简单的方法来设置我们的测试,为此我们可以创建一个设置 WorkManager 的 TestRule
- 添加依赖项
- 创建
WorkManagerTestRule和TestUtils - 为
CleanupWorker创建测试 - 为
BlurWorker创建测试
假设您已经在项目中创建了 AndroidTest 文件夹,我们需要添加一些依赖项以在测试中使用
app/build.gradle
androidTestImplementation "androidx.arch.core:core-testing:2.1.0"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.3"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.test:rules:1.4.0"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.test:runner:1.4.0"
androidTestImplementation "androidx.work:work-testing:$versions.work"
现在我们可以开始将这些部分与一个可以在测试中使用的 TestRule 组合起来
app/src/androidTest/java/com/example/background/workers/WorkManagerTestRule.kt
/* Copyright 2020 Google LLC.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package com.example.background.workers
import android.content.Context
import android.util.Log
import androidx.test.platform.app.InstrumentationRegistry
import androidx.work.Configuration
import androidx.work.WorkManager
import androidx.work.testing.SynchronousExecutor
import androidx.work.testing.WorkManagerTestInitHelper
import org.junit.rules.TestWatcher
import org.junit.runner.Description
class WorkManagerTestRule : TestWatcher() {
lateinit var targetContext: Context
lateinit var testContext: Context
lateinit var configuration: Configuration
lateinit var workManager: WorkManager
override fun starting(description: Description?) {
targetContext = InstrumentationRegistry.getInstrumentation().targetContext
testContext = InstrumentationRegistry.getInstrumentation().context
configuration = Configuration.Builder()
// Set log level to Log.DEBUG to make it easier to debug
.setMinimumLoggingLevel(Log.DEBUG)
// Use a SynchronousExecutor here to make it easier to write tests
.setExecutor(SynchronousExecutor())
.build()
// Initialize WorkManager for instrumentation tests.
WorkManagerTestInitHelper.initializeTestWorkManager(targetContext, configuration)
workManager = WorkManager.getInstance(targetContext)
}
}
由于我们需要设备上(运行测试的地方)的此测试图像,我们可以创建几个帮助函数以在测试中使用
app/src/androidTest/java/com/example/background/workers/TestUtils.kt
/* Copyright 2020 Google LLC.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package com.example.background.workers
import android.content.Context
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory
import android.net.Uri
import com.example.background.OUTPUT_PATH
import java.io.BufferedInputStream
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream
import java.io.File
import java.io.FileNotFoundException
import java.io.FileOutputStream
import java.util.UUID
/**
* Copy a file from the asset folder in the testContext to the OUTPUT_PATH in the target context.
* @param testCtx android test context
* @param targetCtx target context
* @param filename source asset file
* @return Uri for temp file
*/
@Throws(Exception::class)
fun copyFileFromTestToTargetCtx(testCtx: Context, targetCtx: Context, filename: String): Uri {
// Create test image
val destinationFilename = String.format("blur-test-%s.png", UUID.randomUUID().toString())
val outputDir = File(targetCtx.filesDir, OUTPUT_PATH)
if (!outputDir.exists()) {
outputDir.mkdirs()
}
val outputFile = File(outputDir, destinationFilename)
val bis = BufferedInputStream(testCtx.assets.open(filename))
val bos = BufferedOutputStream(FileOutputStream(outputFile))
val buf = ByteArray(1024)
bis.read(buf)
do {
bos.write(buf)
} while (bis.read(buf) != -1)
bis.close()
bos.close()
return Uri.fromFile(outputFile)
}
/**
* Check if a file exists in the given context.
* @param testCtx android test context
* @param uri for the file
* @return true if file exist, false if the file does not exist of the Uri is not valid
*/
fun uriFileExists(targetCtx: Context, uri: String?): Boolean {
if (uri.isNullOrEmpty()) {
return false
}
val resolver = targetCtx.contentResolver
// Create a bitmap
try {
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(
resolver.openInputStream(Uri.parse(uri)))
} catch (e: FileNotFoundException) {
return false
}
return true
}
完成此工作后,我们可以开始编写测试了。
首先我们测试 CleanupWorker,以检查它是否确实删除了我们的文件。为此,在测试中将测试图像复制到设备上,然后检查 CleanupWorker 执行后它是否仍在。
app/src/androidTest/java/com/example/background/workers/CleanupWorkerTest.kt
/* Copyright 2020 Google LLC.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package com.example.background.workers
import androidx.arch.core.executor.testing.InstantTaskExecutorRule
import androidx.work.OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder
import androidx.work.WorkInfo
import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.`is`
import org.junit.Assert.assertThat
import org.junit.Rule
import org.junit.Test
class CleanupWorkerTest {
@get:Rule
var instantTaskExecutorRule = InstantTaskExecutorRule()
@get:Rule
var wmRule = WorkManagerTestRule()
@Test
fun testCleanupWork() {
val testUri = copyFileFromTestToTargetCtx(
wmRule.testContext, wmRule.targetContext, "test_image.png")
assertThat(uriFileExists(wmRule.targetContext, testUri.toString()), `is`(true))
// Create request
val request = OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder<CleanupWorker>().build()
// Enqueue and wait for result. This also runs the Worker synchronously
// because we are using a SynchronousExecutor.
wmRule.workManager.enqueue(request).result.get()
// Get WorkInfo
val workInfo = wmRule.workManager.getWorkInfoById(request.id).get()
// Assert
assertThat(uriFileExists(wmRule.targetContext, testUri.toString()), `is`(false))
assertThat(workInfo.state, `is`(WorkInfo.State.SUCCEEDED))
}
}
您现在可以从 Android Studio 的 Run 菜单运行此测试,或使用测试类左侧的绿色矩形运行。
您还可以从命令行使用项目根文件夹中的命令 ./gradlew cAT 运行测试。
您应该看到您的测试正确执行。
接下来我们可以测试我们的 `BlurWorker`。此 worker 需要带有待处理图像 URI 的输入数据,因此我们可以构建几个测试:一个检查如果输入 URI 不存在 worker 是否失败,另一个实际处理输入图像。
app/src/androidTest/java/com/example/background/workers/BlurWorkerTest.kt
/* Copyright 2020 Google LLC.
SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0 */
package com.example.background.workers
import androidx.arch.core.executor.testing.InstantTaskExecutorRule
import androidx.work.OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder
import androidx.work.WorkInfo
import androidx.work.workDataOf
import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.`is`
import org.junit.Assert.assertThat
import org.junit.Rule
import com.example.background.KEY_IMAGE_URI
import org.junit.Test
class BlurWorkerTest {
@get:Rule
var instantTaskExecutorRule = InstantTaskExecutorRule()
@get:Rule
var wmRule = WorkManagerTestRule()
@Test
fun testFailsIfNoInput() {
// Define input data
// Create request
val request = OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder<BlurWorker>().build()
// Enqueue and wait for result. This also runs the Worker synchronously
// because we are using a SynchronousExecutor.
wmRule.workManager.enqueue(request).result.get()
// Get WorkInfo
val workInfo = wmRule.workManager.getWorkInfoById(request.id).get()
// Assert
assertThat(workInfo.state, `is`(WorkInfo.State.FAILED))
}
@Test
@Throws(Exception::class)
fun testAppliesBlur() {
// Define input data
val inputDataUri = copyFileFromTestToTargetCtx(
wmRule.testContext,
wmRule.targetContext,
"test_image.png")
val inputData = workDataOf(KEY_IMAGE_URI to inputDataUri.toString())
// Create request
val request = OneTimeWorkRequestBuilder<BlurWorker>()
.setInputData(inputData)
.build()
// Enqueue and wait for result. This also runs the Worker synchronously
// because we are using a SynchronousExecutor.
wmRule.workManager.enqueue(request).result.get()
// Get WorkInfo
val workInfo = wmRule.workManager.getWorkInfoById(request.id).get()
val outputUri = workInfo.outputData.getString(KEY_IMAGE_URI)
// Assert
assertThat(uriFileExists(wmRule.targetContext, outputUri), `is`(true))
assertThat(workInfo.state, `is`(WorkInfo.State.SUCCEEDED))
}
}
如果您运行这些测试,它们都应该成功。
6. 恭喜
恭喜!您已完成 Blur-O-Matic 应用,在此过程中,您学习了如何
- 创建自定义配置
- 从您的 Worker 发布进度
- 在界面中显示工作进度
- 为您的 Workers 编写测试
“干得”漂亮!要查看代码的最终状态和所有更改,请查看
或者,如果您愿意,可以从 GitHub 克隆 WorkManager 的 Codelab
$ git clone -b advanced https://github.com/googlecodelabs/android-workmanager
WorkManager 支持的功能远多于此 Codelab 所能涵盖的。要了解更多信息,请访问 WorkManager 文档。