1. 开始之前
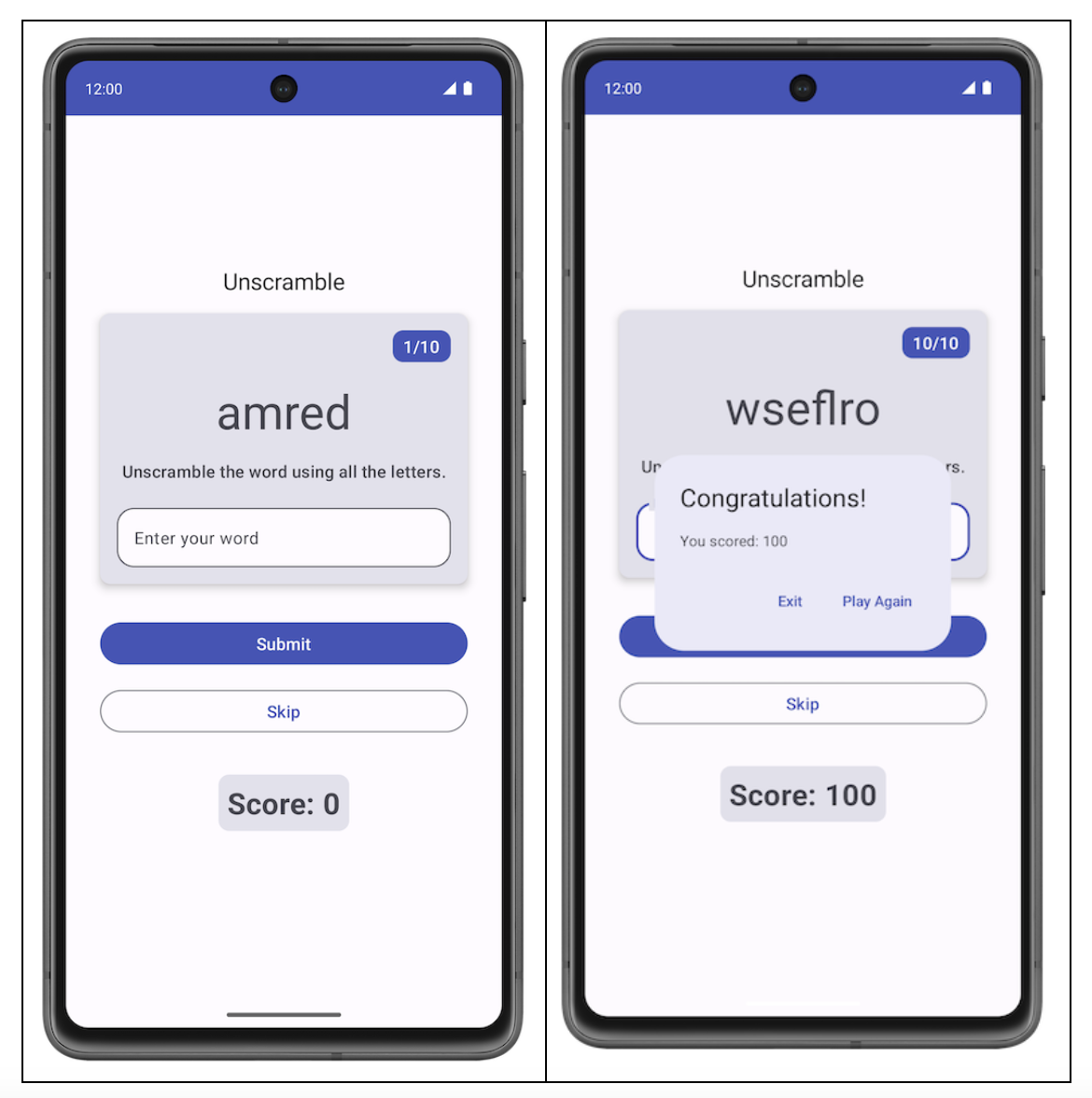
此 Codelab 教您编写单元测试以测试 ViewModel 组件。您将为 Unscramble 游戏应用添加单元测试。Unscramble 应用是一款有趣的文字游戏,用户需要猜出打乱的单词,并通过正确猜出单词来赚取积分。下图显示了该应用的预览
在 编写自动化测试 Codelab 中,您学习了什么是自动化测试以及为什么它们很重要。您还学习了如何实现单元测试。
您学习了
- 自动化测试是用于验证另一段代码准确性的代码。
- 测试是应用开发过程的重要组成部分。通过不断对您的应用运行测试,您可以在公开发布应用之前验证其功能行为和可用性。
- 使用单元测试,您可以测试函数、类和属性。
- 本地单元测试在您的工作站上执行,这意味着它们在开发环境中运行,无需 Android 设备或模拟器。换句话说,本地测试在您的计算机上运行。
在继续之前,请确保您已完成 编写自动化测试 和 ViewModel 和 Compose 中的状态 Codelab。
先决条件
- 熟悉 Kotlin,包括函数、lambda 表达式和无状态的可组合项
- 了解如何在 Jetpack Compose 中构建布局的基本知识
- 了解 Material Design 的基本知识
- 了解如何实现 ViewModel 的基本知识
您将学习的内容
- 如何在应用模块的
build.gradle.kts文件中添加单元测试的依赖项 - 如何创建用于实现单元测试的测试策略
- 如何使用 JUnit4 编写单元测试并了解测试实例生命周期
- 如何运行、分析和改进代码覆盖率
您将构建的内容
- 针对 Unscramble 游戏应用的单元测试
您将需要的内容
- 最新版本的 Android Studio
获取入门代码
要开始使用,请下载入门代码
或者,您可以克隆代码的 GitHub 存储库
$ git clone https://github.com/google-developer-training/basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble.git $ cd basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble $ git checkout viewmodel
您可以在 Unscramble GitHub 存储库中浏览代码。
2. 入门代码概述
在第二单元中,您学习了将单元测试代码放在 test 源集(位于 src 文件夹下),如下面的图像所示
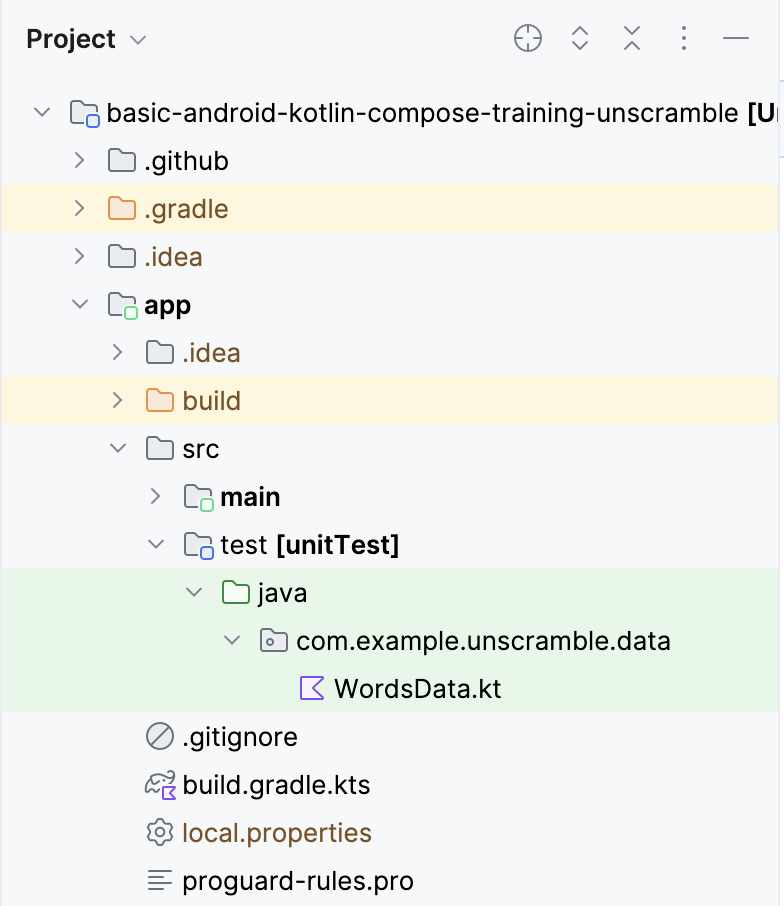
入门代码包含以下文件
WordsData.kt:此文件包含用于测试的单词列表和一个getUnscrambledWord()辅助函数,用于从打乱的单词中获取未打乱的单词。您不需要修改此文件。
3. 添加测试依赖项
在本 Codelab 中,您使用 JUnit 框架编写单元测试。要使用该框架,您需要在应用模块的 build.gradle.kts 文件中将其添加为依赖项。
您使用 implementation 配置来指定应用所需的依赖项。例如,要在您的应用中使用 ViewModel 库,您必须添加对 androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-compose 的依赖项,如以下代码片段所示
dependencies {
...
implementation("androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-compose:2.6.1")
}
您现在可以在应用的源代码中使用此库,Android Studio 将帮助将其添加到生成的应用包文件 (APK) 文件中。但是,您不希望您的单元测试代码成为 APK 文件的一部分。测试代码不会添加用户会使用的任何功能,并且代码还会影响 APK 的大小。您的测试代码所需的依赖项也是如此;您应该将它们分开。为此,您使用 testImplementation 配置,它表示该配置适用于本地测试源代码,而不是应用代码。
要将依赖项添加到您的项目中,请在 build.gradle.kts 文件的依赖项块中指定一个依赖项配置(例如 implementation 或 testImplementation)。每个依赖项配置都向 Gradle 提供关于如何使用依赖项的不同说明。
要添加依赖项
- 打开位于 Project 窗格中 app 目录下的应用模块的
build.gradle.kts文件。
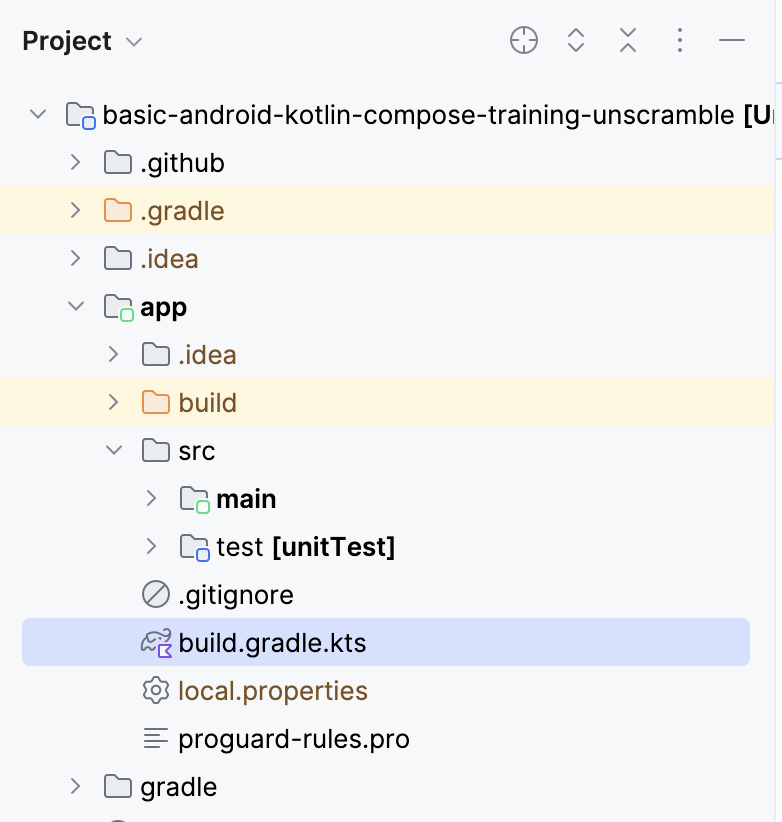
- 在文件中,向下滚动,直到找到
dependencies{}块。使用testImplementation配置为junit添加依赖项。
plugins {
...
}
android {
...
}
dependencies {
...
testImplementation("junit:junit:4.13.2")
}
- 在 build.gradle.kts 文件顶部的通知栏中,单击 立即同步,让导入和构建完成,如以下屏幕截图所示

Compose 物料清单 (BOM)
Compose BOM 是管理 Compose 库版本的推荐方法。BOM 允许您通过仅指定 BOM 的版本来管理所有 Compose 库版本。
请注意应用模块的 build.gradle.kts 文件中的依赖项部分。
// No need to copy over
// This is part of starter code
dependencies {
// Import the Compose BOM
implementation (platform("androidx.compose:compose-bom:2023.06.01"))
...
implementation("androidx.compose.material3:material3")
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui")
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui-graphics")
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui-tooling-preview")
...
}
观察以下内容
- 未指定 Compose 库版本号。
- 使用
implementation platform("androidx.compose:compose-bom:2023.06.01")导入 BOM
这是因为 BOM 本身链接到不同 Compose 库的最新稳定版本,这些版本以一种相互良好协作的方式组合在一起。在您的应用中使用 BOM 时,您无需在 Compose 库依赖项本身中添加任何版本。当您更新 BOM 版本时,所有您使用的库都会自动更新到其新版本。
要将 BOM 与 compose 测试库(已检测测试)一起使用,您需要导入 androidTestImplementation platform("androidx.compose:compose-bom:xxxx.xx.xx")。您可以创建一个变量并在 implementation 和 androidTestImplementation 中重复使用它,如所示。
// Example, not need to copy over
dependencies {
// Import the Compose BOM
implementation(platform("androidx.compose:compose-bom:2023.06.01"))
implementation("androidx.compose.material:material")
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui")
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui-tooling-preview")
// ...
androidTestImplementation(platform("androidx.compose:compose-bom:2023.06.01"))
androidTestImplementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui-test-junit4")
}
太棒了!您已成功将测试依赖项添加到应用中,并了解了 BOM。您现在已准备好添加一些单元测试。
4. 测试策略
良好的测试策略围绕着覆盖代码的不同路径和边界而展开。在最基本的层面上,您可以将测试分为三种情况:成功路径、错误路径和边界情况。
- 成功路径:成功路径测试(也称为快乐路径测试)侧重于测试正向流程的功能。正向流程是指没有异常或错误条件的流程。与错误路径和边界情况场景相比,为成功路径创建详尽的场景列表很容易,因为它们侧重于应用的预期行为。
Unscramble 应用中成功路径的一个示例是,当用户输入正确的单词并单击 提交 按钮时,分数、单词计数和打乱的单词会正确更新。
- 错误路径:错误路径测试侧重于测试负向流程的功能,即检查应用如何响应错误条件或无效的用户输入。确定所有可能的错误流程非常具有挑战性,因为当预期行为没有实现时,可能会出现很多可能的结果。
一个普遍的建议是列出所有可能的错误路径,为它们编写测试,并在发现不同的场景时不断改进您的单元测试。
Unscramble 应用中错误路径的一个示例是,用户输入了错误的单词并单击了 提交 按钮,这会导致显示错误消息,并且分数和单词计数不会更新。
- 边界情况:边界情况侧重于测试应用中的边界条件。在 Unscramble 应用中,一个边界是检查应用加载时的 UI 状态和用户玩完最大数量的单词后的 UI 状态。
围绕这些类别创建测试场景可以作为测试计划的指南。
创建测试
一个好的单元测试通常具有以下四个特性
- 专注:它应该侧重于测试一个单元,例如一段代码。这段代码通常是一个类或一个方法。测试应该很窄,侧重于验证单个代码段的正确性,而不是同时验证多个代码段的正确性。
- 易于理解:当您阅读代码时,它应该简单易懂。开发人员应该能够一眼就立即理解测试背后的意图。
- 确定性:它应该始终通过或失败。当您多次运行测试时,如果未进行任何代码更改,测试应该产生相同的结果。测试不应该有波动性,即一次失败而另一次通过,尽管代码没有修改。
- 自包含:它不需要任何人工交互或设置,并且可以独立运行。
成功路径
要为成功路径编写单元测试,您需要断言,假设初始化了 GameViewModel 的实例,当 updateUserGuess() 方法使用正确的猜测单词调用,然后调用 checkUserGuess() 方法时,则
- 正确的猜测将传递给
updateUserGuess()方法。 - 将调用
checkUserGuess()方法。 - 值
score和isGuessedWordWrong状态更新正确。
完成以下步骤创建测试
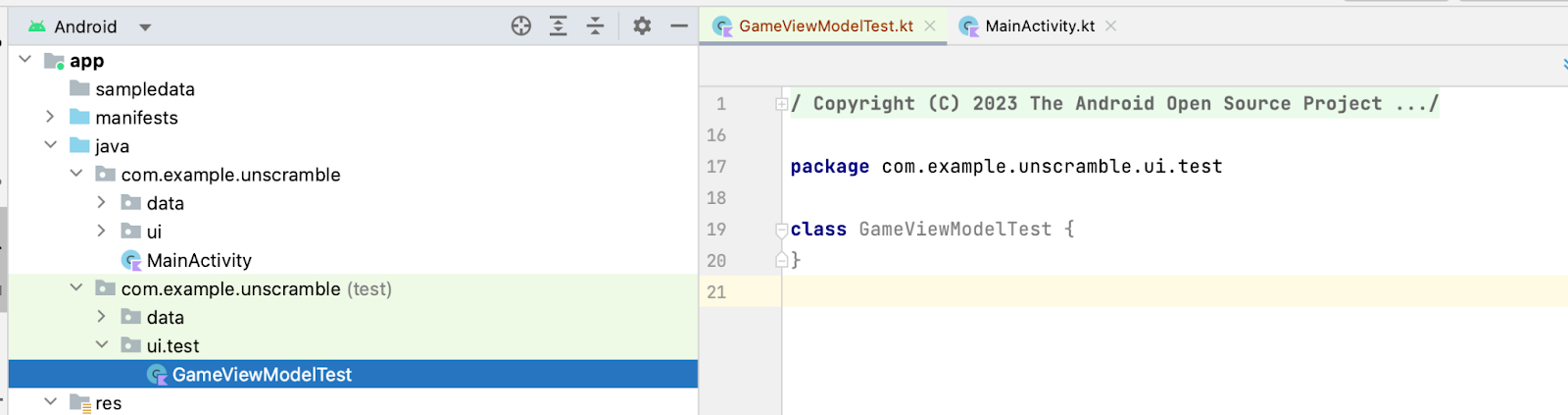
- 在测试源集中创建一个新包
com.example.android.unscramble.ui.test,并添加以下截图所示的文件

要为 GameViewModel 类编写单元测试,你需要一个类的实例,以便你可以调用类的函数并验证状态。
- 在
GameViewModelTest类的主体中,声明一个viewModel属性,并为其分配一个GameViewModel类实例。
class GameViewModelTest {
private val viewModel = GameViewModel()
}
- 要为成功路径编写单元测试,请创建一个
gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset()函数,并使用@Test注解对其进行注释。
class GameViewModelTest {
private val viewModel = GameViewModel()
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
}
}
- 导入以下内容
import org.junit.Test
要将正确的玩家单词传递给 viewModel.updateUserGuess() 函数,你需要从 GameUiState 中的打乱的单词获取正确的解乱单词。为此,首先获取当前的游戏界面状态。
- 在函数主体中,创建一个
currentGameUiState变量,并将其赋值为viewModel.uiState.value。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
}
- 要获取正确的玩家猜测,请使用
getUnscrambledWord()函数,它接收currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord作为参数并返回解乱单词。将此返回值存储在一个名为correctPlayerWord的新的只读变量中,并将getUnscrambledWord()函数返回的值分配给它。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
}
- 要验证猜测的单词是否正确,请添加对
viewModel.updateUserGuess()函数的调用,并将correctPlayerWord变量作为参数传递。然后添加对viewModel.checkUserGuess()函数的调用以验证猜测。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
}
你现在已准备好断言游戏状态是你期望的。
- 从
viewModel.uiState属性的值中获取GameUiState类的实例,并将其存储在currentGameUiState变量中。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
}
- 要检查猜测的单词是否正确以及分数是否更新,请使用
assertFalse()函数来验证currentGameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong属性是否为false,以及assertEquals()函数来验证currentGameUiState.score属性的值是否等于20。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
// Assert that checkUserGuess() method updates isGuessedWordWrong is updated correctly.
assertFalse(currentGameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong)
// Assert that score is updated correctly.
assertEquals(20, currentGameUiState.score)
}
- 导入以下内容
import org.junit.Assert.assertEquals
import org.junit.Assert.assertFalse
- 要使值
20可读且可重复使用,请创建一个伴随对象,并将20分配给名为SCORE_AFTER_FIRST_CORRECT_ANSWER的private常量。使用新创建的常量更新测试。
class GameViewModelTest {
...
@Test
fun gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset() {
...
// Assert that score is updated correctly.
assertEquals(SCORE_AFTER_FIRST_CORRECT_ANSWER, currentGameUiState.score)
}
companion object {
private const val SCORE_AFTER_FIRST_CORRECT_ANSWER = SCORE_INCREASE
}
}
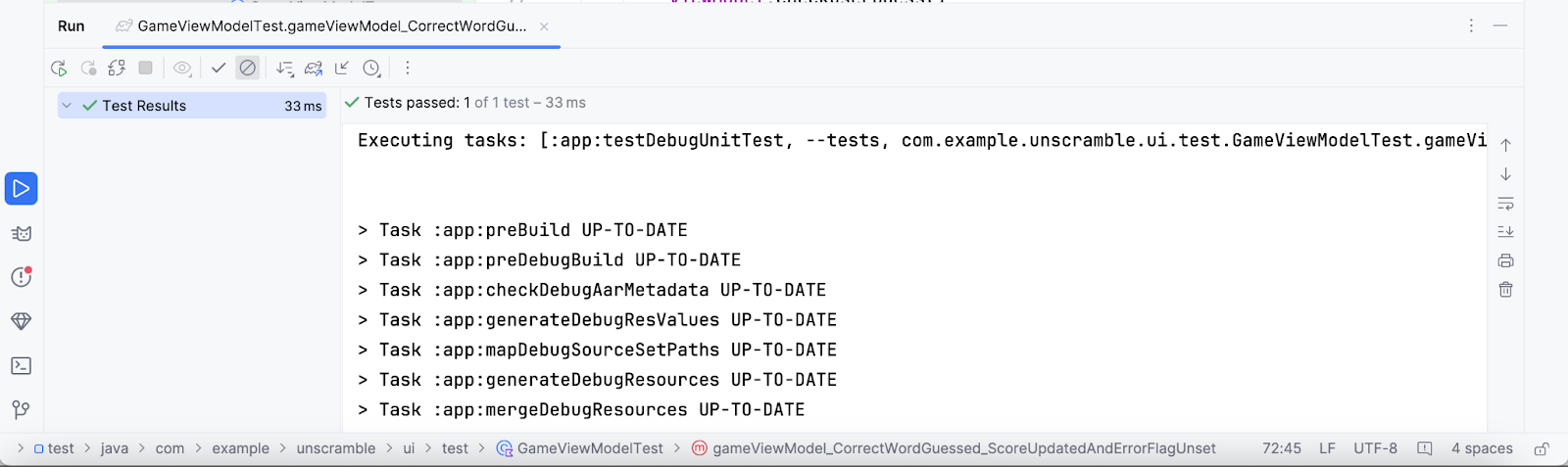
- 运行测试。
测试应该通过,因为所有断言都是有效的,如以下屏幕截图所示
错误路径
要为错误路径编写单元测试,你需要断言,当将不正确的单词作为参数传递给 viewModel.updateUserGuess() 函数并调用 viewModel.checkUserGuess() 函数时,将发生以下情况
currentGameUiState.score属性的值保持不变。currentGameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong属性的值被设置为true,因为猜测是错误的。
完成以下步骤创建测试
- 在
GameViewModelTest类的主体中,创建一个gameViewModel_IncorrectGuess_ErrorFlagSet()函数,并使用@Test注解对其进行注释。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_IncorrectGuess_ErrorFlagSet() {
}
- 定义一个
incorrectPlayerWord变量,并将其赋值为"and",它应该不存在于单词列表中。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_IncorrectGuess_ErrorFlagSet() {
// Given an incorrect word as input
val incorrectPlayerWord = "and"
}
- 添加对
viewModel.updateUserGuess()函数的调用,并将incorrectPlayerWord变量作为参数传递。 - 添加对
viewModel.checkUserGuess()函数的调用以验证猜测。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_IncorrectGuess_ErrorFlagSet() {
// Given an incorrect word as input
val incorrectPlayerWord = "and"
viewModel.updateUserGuess(incorrectPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
}
- 添加一个
currentGameUiState变量,并将viewModel.uiState.value状态的值分配给它。 - 使用断言函数来断言
currentGameUiState.score属性的值为0,以及currentGameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong属性的值被设置为true。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_IncorrectGuess_ErrorFlagSet() {
// Given an incorrect word as input
val incorrectPlayerWord = "and"
viewModel.updateUserGuess(incorrectPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
val currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
// Assert that score is unchanged
assertEquals(0, currentGameUiState.score)
// Assert that checkUserGuess() method updates isGuessedWordWrong correctly
assertTrue(currentGameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong)
}
- 导入以下内容
import org.junit.Assert.assertTrue
- 运行测试以确认它通过。
边界情况
要测试 UI 的初始状态,你需要为 GameViewModel 类编写单元测试。该测试必须断言,当 GameViewModel 初始化时,以下为真
currentWordCount属性被设置为1。score属性被设置为0。isGuessedWordWrong属性被设置为false。isGameOver属性被设置为false。
完成以下步骤添加测试
- 创建一个
gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded()函数,并使用@Test注解对其进行注释。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded() {
}
- 访问
viewModel.uiState.value属性以获取GameUiState类的初始实例。将其分配给一个名为gameUiState的新的只读变量。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded() {
val gameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
}
- 要获取正确的玩家单词,请使用
getUnscrambledWord()函数,它接收gameUiState.currentScrambledWord单词并返回解乱单词。将此返回值分配给一个名为unScrambledWord的新的只读变量。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded() {
val gameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val unScrambledWord = getUnscrambledWord(gameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
}
- 要验证状态是否正确,请添加
assertTrue()函数以断言currentWordCount属性被设置为1,以及score属性被设置为0。 - 添加
assertFalse()函数以验证isGuessedWordWrong属性是否为false,以及isGameOver属性是否被设置为false。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded() {
val gameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val unScrambledWord = getUnscrambledWord(gameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
// Assert that current word is scrambled.
assertNotEquals(unScrambledWord, gameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
// Assert that current word count is set to 1.
assertTrue(gameUiState.currentWordCount == 1)
// Assert that initially the score is 0.
assertTrue(gameUiState.score == 0)
// Assert that the wrong word guessed is false.
assertFalse(gameUiState.isGuessedWordWrong)
// Assert that game is not over.
assertFalse(gameUiState.isGameOver)
}
- 导入以下内容
import org.junit.Assert.assertNotEquals
- 运行测试以确认它通过。
另一个边界情况是测试用户猜测所有单词后的 UI 状态。你需要断言,当用户正确猜测所有单词时,以下为真
- 分数是最新的;
currentGameUiState.currentWordCount属性等于MAX_NO_OF_WORDS常量的值;currentGameUiState.isGameOver属性被设置为true。
完成以下步骤添加测试
- 创建一个
gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly()函数,并使用@Test注解对其进行注释。在该函数中,创建一个expectedScore变量,并将其赋值为0。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
}
- 要获取初始状态,请添加一个
currentGameUiState变量,并将viewModel.uiState.value属性的值分配给该变量。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
}
- 要获取正确的玩家单词,请使用
getUnscrambledWord()函数,它接收currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord单词并返回解乱单词。将此返回值存储在一个名为correctPlayerWord的新的只读变量中,并将getUnscrambledWord()函数返回的值分配给它。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
var correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
}
- 要测试用户是否猜测了所有答案,请使用
repeat块来重复执行viewModel.updateUserGuess()函数和viewModel.checkUserGuess()函数MAX_NO_OF_WORDS次。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
var correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
repeat(MAX_NO_OF_WORDS) {
}
}
- 在
repeat块中,将SCORE_INCREASE常量的值添加到expectedScore变量中,以断言在每次正确回答后分数都会增加。 - 添加对
viewModel.updateUserGuess()函数的调用,并将correctPlayerWord变量作为参数传递。 - 添加对
viewModel.checkUserGuess()函数的调用以触发对用户猜测的检查。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
var correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
repeat(MAX_NO_OF_WORDS) {
expectedScore += SCORE_INCREASE
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
}
}
- 更新当前玩家单词,使用
getUnscrambledWord()函数,它接收currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord作为参数并返回解乱单词。将此返回值存储在一个名为correctPlayerWord的新的只读变量中。要验证状态是否正确,请添加assertEquals()函数以检查currentGameUiState.score属性的值是否等于expectedScore变量的值。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
var correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
repeat(MAX_NO_OF_WORDS) {
expectedScore += SCORE_INCREASE
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
// Assert that after each correct answer, score is updated correctly.
assertEquals(expectedScore, currentGameUiState.score)
}
}
- 添加一个
assertEquals()函数以断言currentGameUiState.currentWordCount属性的值等于MAX_NO_OF_WORDS常量的值,以及currentGameUiState.isGameOver属性的值被设置为true。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_AllWordsGuessed_UiStateUpdatedCorrectly() {
var expectedScore = 0
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
var correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
repeat(MAX_NO_OF_WORDS) {
expectedScore += SCORE_INCREASE
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
// Assert that after each correct answer, score is updated correctly.
assertEquals(expectedScore, currentGameUiState.score)
}
// Assert that after all questions are answered, the current word count is up-to-date.
assertEquals(MAX_NO_OF_WORDS, currentGameUiState.currentWordCount)
// Assert that after 10 questions are answered, the game is over.
assertTrue(currentGameUiState.isGameOver)
}
- 导入以下内容
import com.example.unscramble.data.MAX_NO_OF_WORDS
- 运行测试以确认它通过。
测试实例生命周期概述
当你仔细查看 viewModel 在测试中初始化的方式时,你可能会注意到,即使所有测试都使用它,viewModel 也只初始化一次。此代码片段显示了 viewModel 属性的定义。
class GameViewModelTest {
private val viewModel = GameViewModel()
@Test
fun gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded() {
val gameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
...
}
...
}
你可能想知道以下问题
- 这是否意味着同一个
viewModel实例被重复用于所有测试? - 这会导致任何问题吗?例如,如果
gameViewModel_Initialization_FirstWordLoaded测试函数在gameViewModel_CorrectWordGuessed_ScoreUpdatedAndErrorFlagUnset测试函数之后执行?初始化测试会失败吗?
这两个问题的答案都是否定的。测试函数以隔离方式执行,以避免可变测试实例状态带来的意外副作用。默认情况下,在执行每个测试函数之前,JUnit 会创建一个测试类的全新实例。
由于你的 GameViewModelTest 类中目前有四个测试函数,因此 GameViewModelTest 会实例化四次。每个实例都有其自身的 viewModel 属性副本。因此,测试执行的顺序无关紧要。
5. 代码覆盖率简介
代码覆盖率在确定你是否充分测试了构成应用程序的类、函数和代码行方面起着至关重要的作用。
Android Studio 提供了一个用于本地单元测试的测试覆盖率工具,用于跟踪您的单元测试覆盖的应用程序代码的百分比和区域。
使用 Android Studio 运行带有覆盖率的测试
要运行带有覆盖率的测试
- 右键单击项目窗格中的
GameViewModelTest.kt文件,然后选择 运行“GameViewModelTest”并覆盖。
运行“GameViewModelTest”并覆盖。
- 测试执行完成后,在右侧的覆盖率面板中,单击扁平化包选项。
- 注意下图所示的
com.example.android.unscramble.ui包。
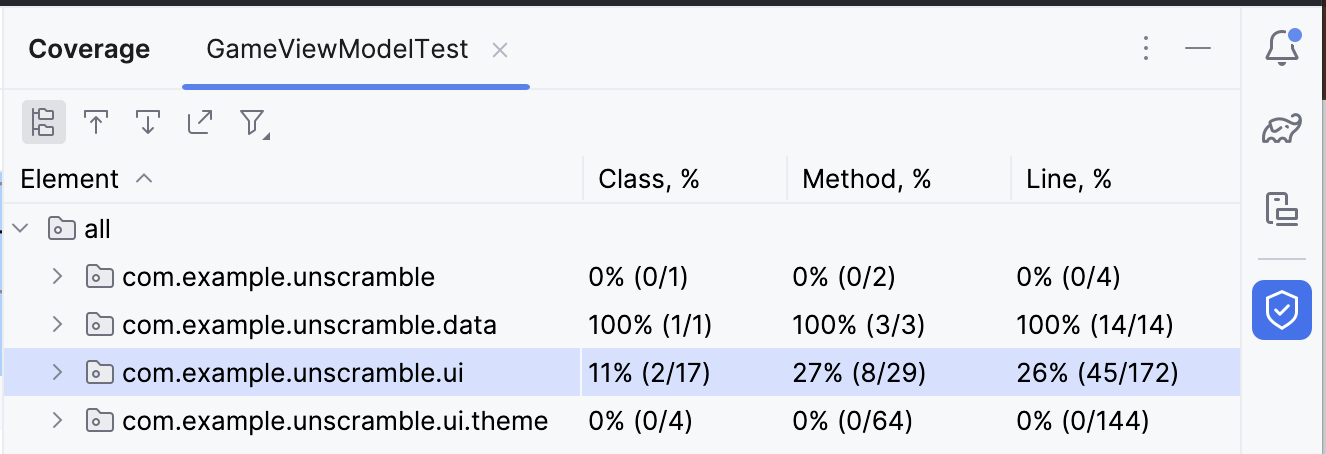
- 双击包
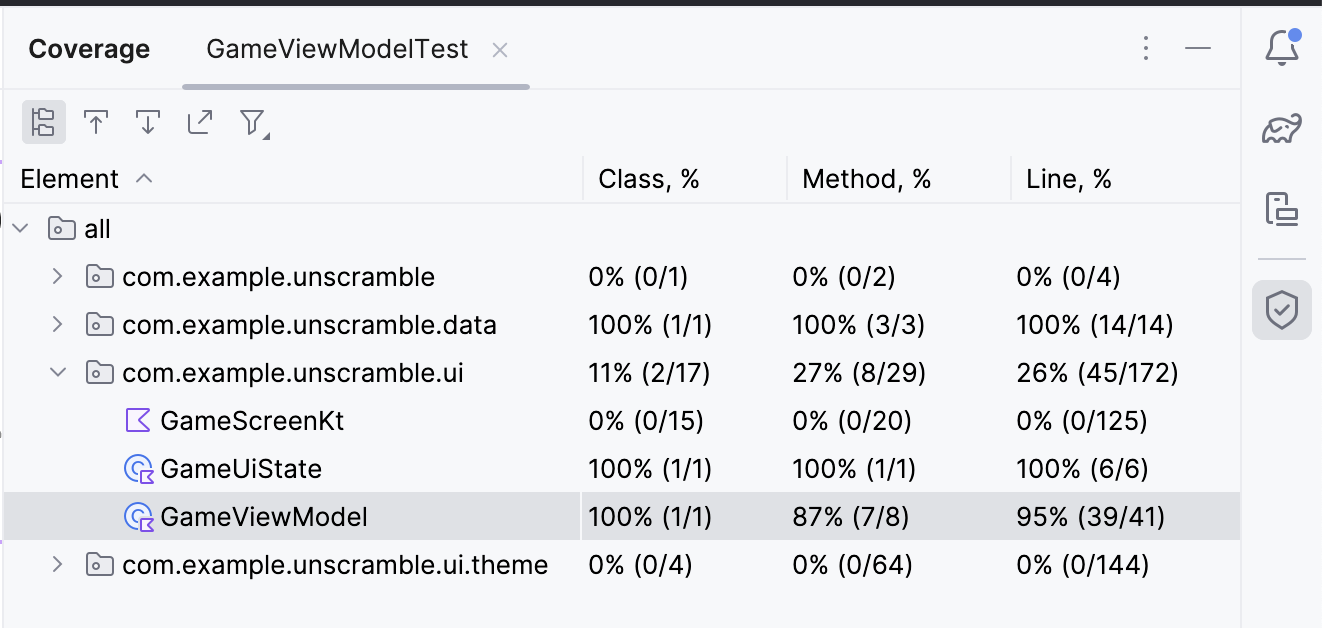
com.example.android.unscramble.ui名称,将显示GameViewModel的覆盖率,如下图所示
分析测试报告
下图所示的报告分为两个方面
- 单元测试覆盖的方法百分比:在示例图中,您编写的测试到目前为止覆盖了 8 个方法中的 7 个。 占总方法的 87%。
- 单元测试覆盖的行百分比:在示例图中,您编写的测试覆盖了 41 行代码中的 39 行。 占代码行的 95%。
报告表明,您编写的单元测试到目前为止错过了代码的某些部分。 要确定错过了哪些部分,请完成以下步骤
- 双击GameViewModel。

Android Studio 将显示 GameViewModel.kt 文件,窗口左侧将显示额外的颜色编码。 亮绿色表示这些代码行已被覆盖。
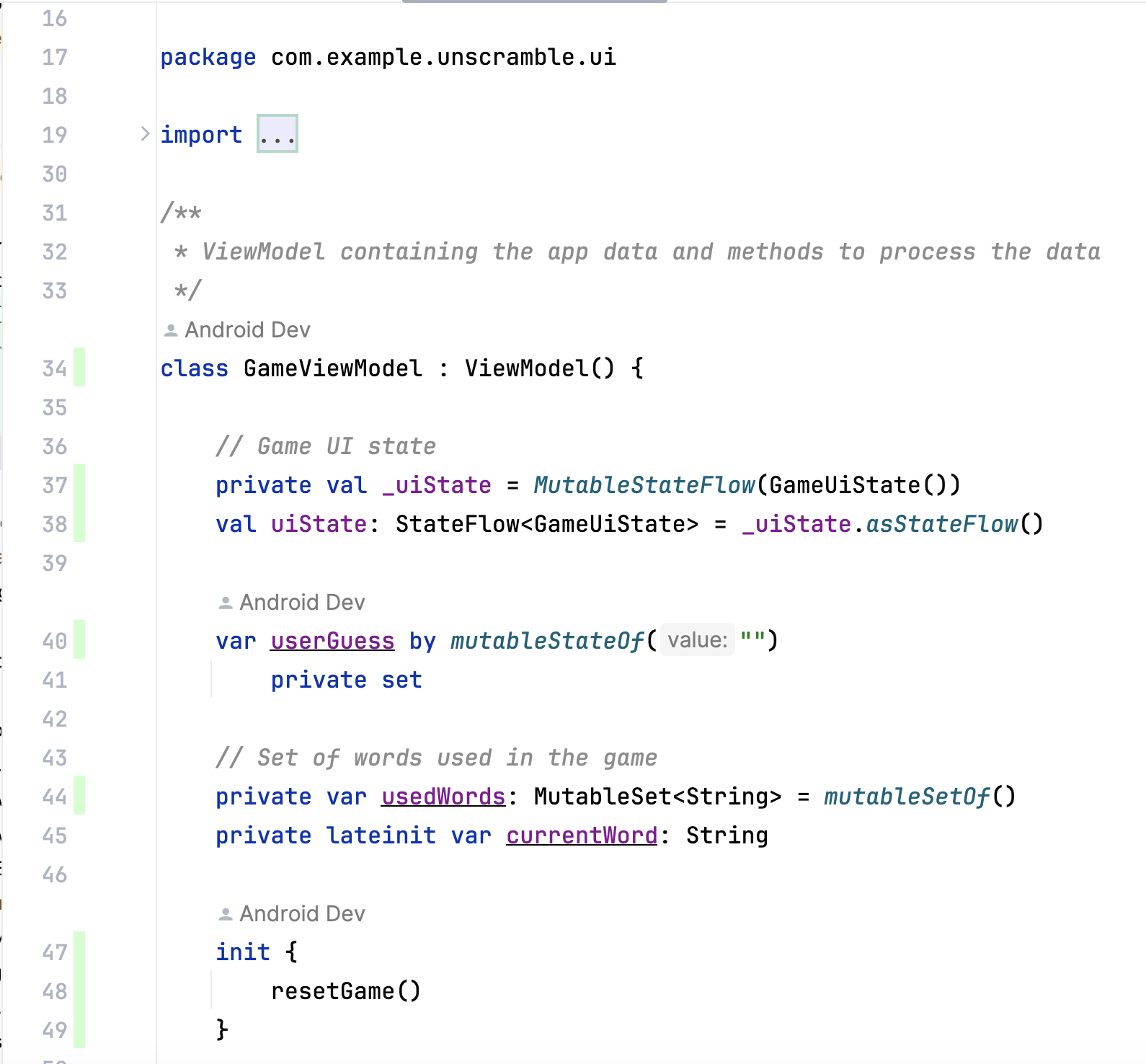
当您向下滚动 GameViewModel 时,您可能会注意到几行用浅粉色标记。 此颜色表示这些代码行未被单元测试覆盖。

提高覆盖率
要提高覆盖率,您需要编写一个测试来覆盖缺失的路径。 您需要添加一个测试来断言当用户跳过一个词时,以下为真
currentGameUiState.score属性保持不变。currentGameUiState.currentWordCount属性增加 1,如以下代码段所示。
要准备提高覆盖率,请将以下测试方法添加到 GameViewModelTest 类中。
@Test
fun gameViewModel_WordSkipped_ScoreUnchangedAndWordCountIncreased() {
var currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val correctPlayerWord = getUnscrambledWord(currentGameUiState.currentScrambledWord)
viewModel.updateUserGuess(correctPlayerWord)
viewModel.checkUserGuess()
currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
val lastWordCount = currentGameUiState.currentWordCount
viewModel.skipWord()
currentGameUiState = viewModel.uiState.value
// Assert that score remains unchanged after word is skipped.
assertEquals(SCORE_AFTER_FIRST_CORRECT_ANSWER, currentGameUiState.score)
// Assert that word count is increased by 1 after word is skipped.
assertEquals(lastWordCount + 1, currentGameUiState.currentWordCount)
}
完成以下步骤以重新运行覆盖率
- 右键单击
GameViewModelTest.kt文件,然后从菜单中选择运行“GameViewModelTest”并覆盖。 - 构建成功后,再次导航到GameViewModel 元素,并确认覆盖率百分比为 100%。 最终覆盖率报告如下图所示。
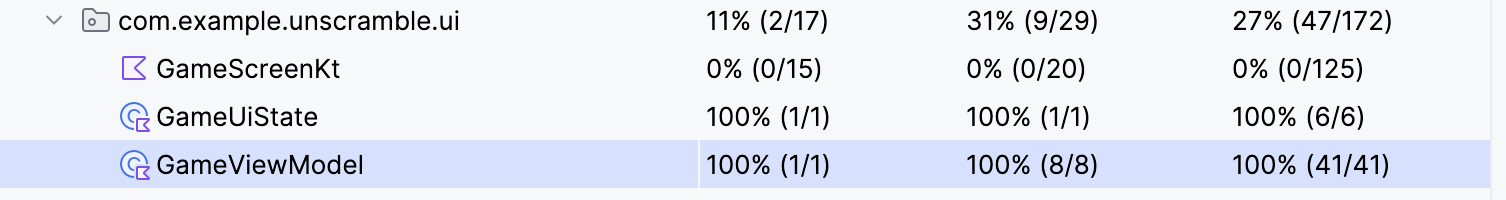
- 导航到
GameViewModel.kt文件,并向下滚动以检查之前错过的路径是否现在已覆盖。
您学习了如何运行、分析和提高应用程序代码的代码覆盖率。
高代码覆盖率百分比是否意味着高应用程序代码质量? 否。 代码覆盖率表示被您的单元测试覆盖或执行的代码的百分比。 它不表示代码已验证。 如果您从单元测试代码中删除所有断言并运行代码覆盖率,它仍然显示 100% 的覆盖率。
高覆盖率并不表示测试设计正确,也不表示测试验证了应用程序的行为。 您需要确保编写的测试包含断言,以验证正在测试的类的行为。 您也不必努力编写单元测试来获得整个应用程序 100% 的测试覆盖率。 您应该使用 UI 测试而不是单元测试来测试应用程序代码的某些部分,例如活动。
但是,低覆盖率意味着您的代码的大部分完全未经测试。 使用代码覆盖率作为工具来查找未被您的测试执行的代码部分,而不是作为衡量代码质量的工具。
6. 获取解决方案代码
要下载完成的 codelab 的代码,您可以使用以下 git 命令
$ git clone https://github.com/google-developer-training/basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble.git $ cd basic-android-kotlin-compose-training-unscramble $ git checkout main
或者,您可以将存储库下载为 zip 文件,解压缩它,然后在 Android Studio 中打开它。
如果您想查看解决方案代码,在 GitHub 上查看。
7. 结论
恭喜! 您学习了如何定义测试策略并实现单元测试来测试 Unscramble 应用程序中的 ViewModel 和 StateFlow。 当您继续构建 Android 应用程序时,请确保在应用程序功能旁边编写测试以确认您的应用程序在整个开发过程中都能正常工作。
摘要
- 使用
testImplementation配置来指示依赖项适用于本地测试源代码,而不是应用程序代码。 - 目标是将测试分类为三种情况:成功路径、错误路径和边界情况。
- 一个好的单元测试至少具有四个特征:它们专注、易于理解、确定性和独立。
- 测试方法是独立执行的,以避免来自可变测试实例状态的意外副作用。
- 默认情况下,在每个测试方法执行之前,JUnit 会创建一个测试类的新的实例。
- 代码覆盖率在确定您是否充分测试了构成应用程序的类、方法和代码行方面起着至关重要的作用。
