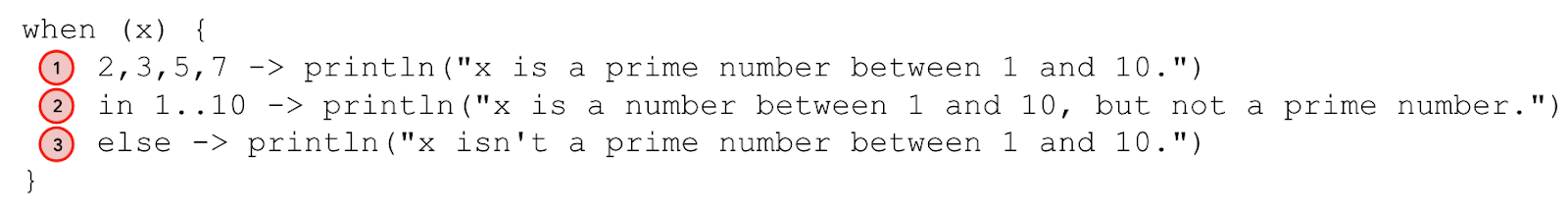1. 开始之前
条件语句是编程最重要的基础之一。条件语句是编程语言中用于处理决策的命令。通过条件语句,代码变得动态化,这意味着它可以在不同条件下表现不同。
本 Codelab 将教你如何在 Kotlin 中使用 if/else 和 when 语句和表达式来编写条件语句。
前提条件
- 了解 Kotlin 编程基础知识,包括变量以及
println()和main()函数
学习内容
- 如何编写布尔表达式。
- 如何编写
if/else语句。 - 如何编写
when语句。 - 如何编写
if/else表达式。 - 如何编写
when表达式。 - 如何在
when条件语句中使用逗号来定义多个分支的通用行为。 - 如何在
when条件语句中使用in范围来定义一系列分支的通用行为。 - 如何使用
is关键字编写when条件语句。
所需条件
- 可以使用 Kotlin Playground 的网页浏览器
2. 使用 if/else 语句表达条件
在生活中,根据所面临的情况采取不同的行动是很常见的。例如,如果天气冷,你会穿夹克,而如果天气暖和,你就不穿夹克。
决策也是编程中的一个基本概念。你会编写指令说明程序在给定情况下应该如何表现,以便它在情况发生时可以相应地行动或反应。在 Kotlin 中,当你想让程序根据条件执行不同的操作时,可以使用 if/else 语句。在下一节中,你将编写一个 if 语句。
使用布尔表达式编写 if 条件
想象一下你构建一个程序,告诉司机在红绿灯处应该做什么。重点关注第一个条件:红灯。在红灯处应该做什么?停车!
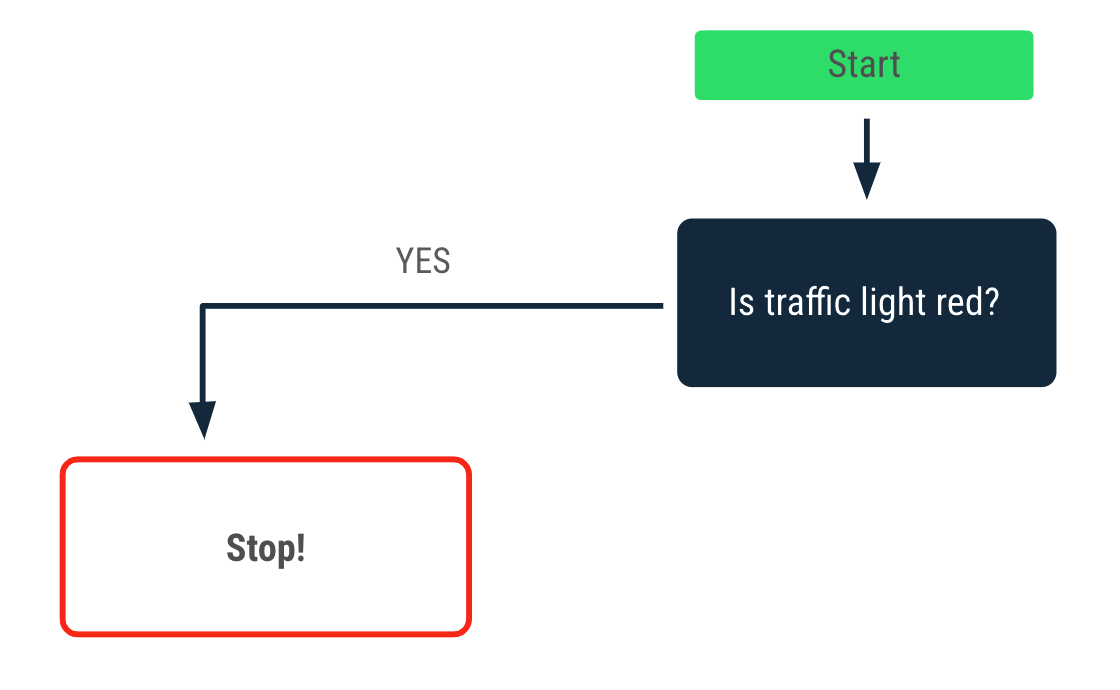
在 Kotlin 中,你可以使用 if 语句表达这个条件。看看 if 语句的结构
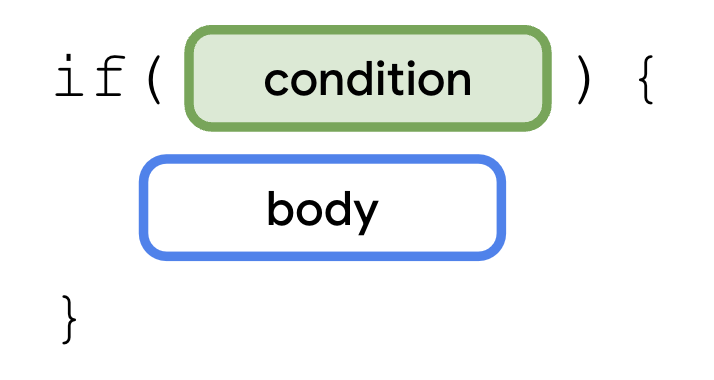
要使用 if 语句,你需要使用 if 关键字,后跟要评估的条件。你需要使用布尔表达式来表达条件。表达式结合值、变量和运算符,返回一个值。布尔表达式返回布尔值。
之前,你了解了赋值运算符,例如
val number = 1
= 赋值运算符将 1 值赋给 number 变量。
相比之下,布尔表达式使用比较运算符构建,比较等号两边的值或变量。看看一个比较运算符。
1 == 1
== 比较运算符比较两个值。你认为这个表达式会返回哪个布尔值?
找出这个表达式的布尔值
- 使用 Kotlin Playground 运行你的代码。
- 在函数体中,添加一个
println()函数,然后将1 == 1表达式作为参数传给它
fun main() {
println(1 == 1)
}
- 运行程序,然后查看输出
true
第一个 1 值等于第二个 1 值,因此布尔表达式返回 true 值,这是一个布尔值。
试一试
除了 == 比较运算符,还有其他一些可以用来创建布尔表达式的比较运算符
- 小于:
< - 大于:
> - 小于或等于:
<= - 大于或等于:
>= - 不等于:
!=
练习使用比较运算符编写简单表达式
- 在参数中,将
==比较运算符替换为<比较运算符
fun main() {
println(1 < 1)
}
- 运行程序,然后查看输出
输出返回 false 值,因为第一个 1 值不小于第二个 1 值。
false
- 使用其他比较运算符和数字重复前两步。
编写一个简单的 if 语句
现在你已经看到了一些如何编写布尔表达式的例子,你可以编写你的第一个 if 语句了。if 语句的语法如下
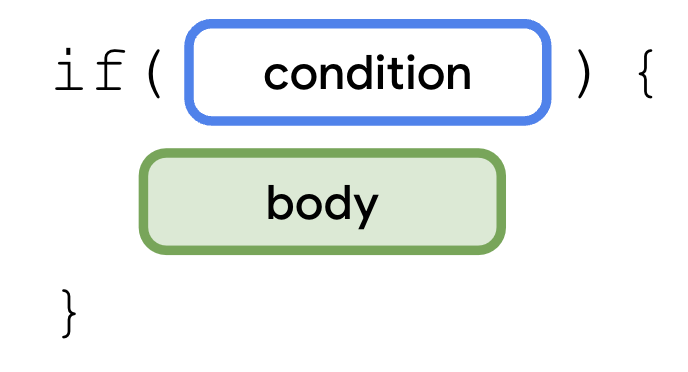
一个 if 语句以 if 关键字开头,后跟一个条件(一个放在括号内的布尔表达式)和一对花括号。主体是一系列语句或表达式,你将它们放在条件后的一对花括号内。这些语句或表达式仅在满足条件时执行。换句话说,只有当 if 分支中的布尔表达式返回 true 值时,花括号内的语句才会执行。
为红灯条件编写一个 if 语句
- 在
main()函数内,创建一个trafficLightColor变量并为其赋值"Red"
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Red"
}
- 为红灯条件添加一个
if语句,然后将trafficLightColor == "Red"表达式传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Red"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
}
}
- 在
if语句的主体中,添加一个println()函数,然后将"Stop"参数传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Red"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
}
}
- 运行程序,然后查看输出
Stop
表达式 trafficLightColor == "Red" 返回 true 值,因此执行 println("Stop") 语句,打印 Stop 消息。

添加一个 else 分支
现在你可以扩展程序,让它在红绿灯不是红色时告诉司机通行。
你需要添加一个 else 分支来创建 if/else 语句。一个分支是代码的不完整部分,你可以将其连接起来形成语句或表达式。else 分支需要跟在 if 分支之后。
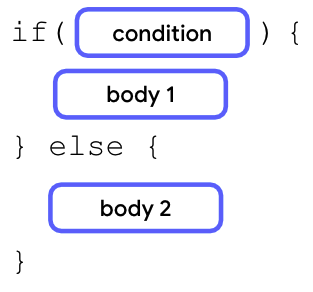
在 if 语句的闭花括号之后,添加 else 关键字,后跟一对花括号。在 else 语句的花括号内,你可以添加第二个主体,该主体仅在 if 分支中的条件为假时执行。
为你的程序添加一个 else 分支
- 在
if语句的闭花括号之后,添加else关键字,后跟另一对花括号
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Red"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else {
}
}
- 在
else关键字的花括号内,添加一个println()函数,然后将"Go"参数传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Red"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else {
println("Go")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出
Stop
程序行为与添加 else 分支之前相同,但没有打印 Go 消息。
- 将
trafficLightColor变量重新赋值为"Green",因为你想让司机在绿灯时通行
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Green"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else {
println("Go")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出
Go
如你所见,现在程序打印 Go 消息,而不是 Stop 消息。

你将 trafficLightColor 变量重新赋值为 "Green",因此在 if 分支中评估的表达式 trafficLightColor == "Red" 返回 false 值,因为 "Green" 值不等于 "Red" 值。
结果是,程序跳过 if 分支中的所有语句,转而执行 else 分支中的所有语句。这意味着执行 println("Go") 函数,但不执行 println("Stop") 函数。
添加一个 else if 分支
通常,红绿灯也有黄色,告诉司机减速慢行。你可以扩展程序的决策过程以反映这一点。
你学会了使用包含一个 if 和一个 else 分支的 if/else 语句来编写处理单个决策点的条件语句。如何处理具有多个决策点的更复杂的分支?当面临多个决策点时,你需要创建具有多层条件的条件语句,这可以通过在 if/else 语句中添加 else if 分支来实现。
在 if 分支的闭花括号之后,你需要添加 else if 关键字。在 else if 关键字的括号内,你需要添加一个布尔表达式作为 else if 分支的条件,后跟一对花括号内的主体。主体仅在条件 1 不满足但条件 2 满足时执行。
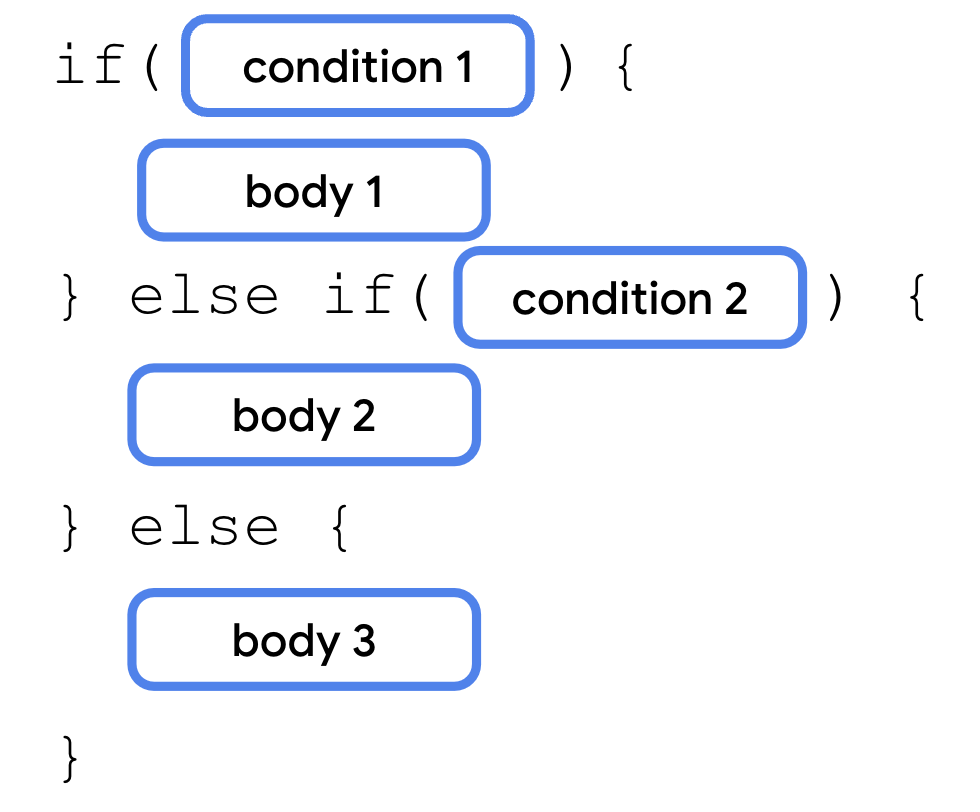
else if 分支总是位于 if 分支之后,else 分支之前。你可以在一个语句中使用多个 else if 分支
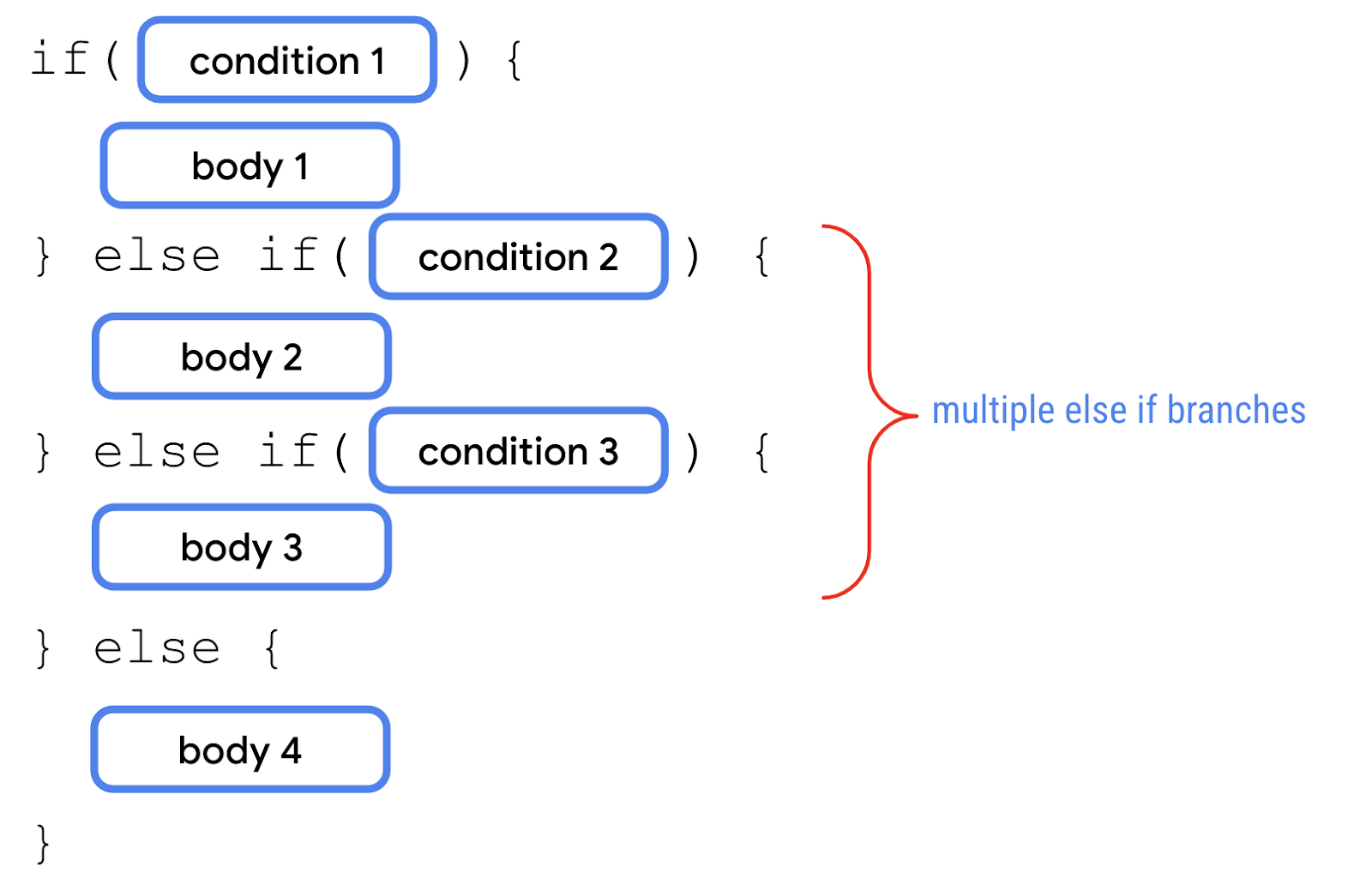
if 语句也可以只包含 if 分支和 else if 分支,而不包含任何 else 分支
为你的程序添加一个 else if 分支
- 在
if语句的闭花括号之后,添加else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow")表达式,后跟花括号
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Green"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
} else {
println("Go")
}
}
- 在
else if分支的花括号内,添加一个println()语句,然后将"Slow"字符串参数传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Green"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else {
println("Go")
}
}
- 将
trafficLightColor变量重新赋值为"Yellow"字符串值
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Yellow"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else {
println("Go")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出
Slow
现在程序打印 Slow 消息,而不是 Stop 或 Go 消息。

下面是为什么它只打印 Slow 消息而不打印其他行
- 变量
trafficLightColor被赋值为"Yellow"。 "Yellow"值不等于"Red"值,因此if分支的布尔表达式(图片中标注为 1)返回false值。程序跳过if分支内的所有语句,不打印Stop消息。- 由于
if分支返回false值,程序继续评估else if分支内的布尔表达式。 "Yellow"值等于"Yellow"值,因此else if分支的布尔表达式(图片中标注为 2)返回true值。程序执行else if分支内的所有语句,并打印Slow消息。- 由于
else if分支的布尔表达式返回true值,程序跳过其余分支。因此,else分支中的所有语句都不会执行,程序也不会打印Go消息。
试一试
你注意到当前程序包含一个 bug 了吗?
在单元 1 中,你了解了一种叫做编译错误的 bug,Kotlin 由于代码中的语法错误无法编译代码,导致程序无法运行。在这里,你面临另一种叫做逻辑错误的 bug,程序可以运行,但输出结果并非预期。
假设你只希望司机在红绿灯为绿色时才通行。如果红绿灯坏了并关闭了怎么办?你希望司机通行还是收到警告说出了问题?
不幸的是,在当前程序中,如果红绿灯颜色是红色或黄色以外的任何其他颜色,程序仍然会建议司机通行。
解决这个问题
- 将
trafficLightColor变量重新赋值为"Black",以表示红绿灯已关闭的情况
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else {
println("Go")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出
Go
注意,即使 trafficLightColor 变量没有被赋值为 "Green",程序仍然打印 Go 消息。你能修改这个程序,使其反映正确的行为吗?
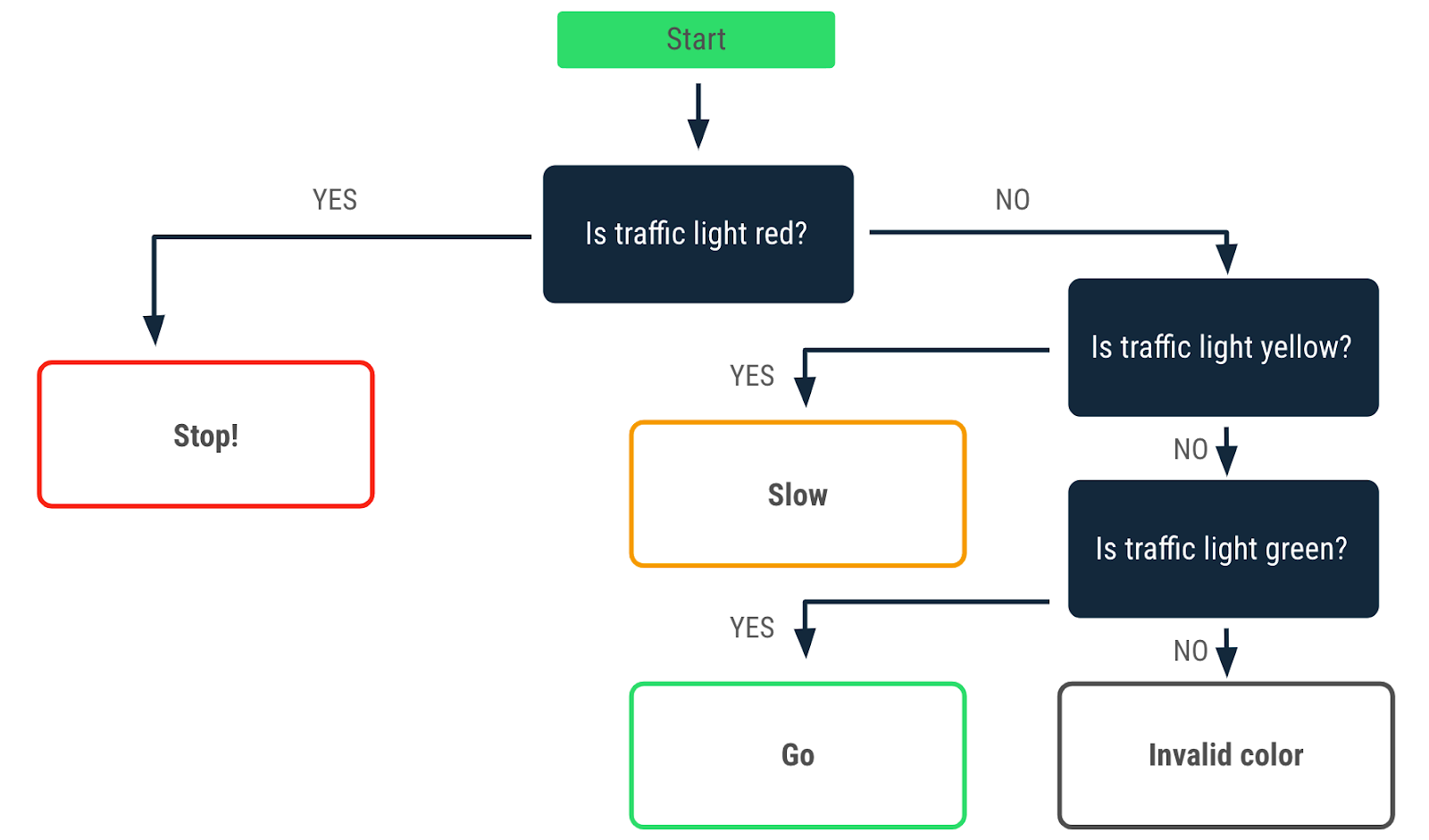
你需要修改程序,使其打印
- 只有当
trafficLightColor变量被赋值为"Green"时,才打印Go消息。 - 当
trafficLightColor变量未被赋值为"Red"、"Yellow"或"Green"时,打印Invalid traffic-light color消息。
修复 else 分支
else 分支总是位于 if/else 语句的末尾,因为它是一个包罗万象的分支。当前面所有分支的条件都不满足时,它会自动执行。因此,当你只想让某个操作在满足特定条件时执行时,else 分支并不合适。在红绿灯的情况下,你可以使用 else if 分支来指定绿灯的条件。
使用 else if 分支评估绿灯条件
- 在当前的
else if分支之后,添加另一个else if (trafficLightColor == "Green")分支
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Green") {
println("Go")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出。
输出为空,因为当前面的条件都不满足时,你没有 else 分支来执行。
- 在最后一个
else if分支之后,添加一个else分支,并在其内部添加println("Invalid traffic-light color")语句
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Green") {
println("Go")
} else {
println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出
Invalid traffic-light color
- 将
trafficLightColor变量赋值为"Red"、"Yellow"或"Green"以外的其他值,然后重新运行程序。
程序的输出是什么?
使用显式的 else if 分支作为绿色的输入验证,并使用 else 分支来捕获其他无效输入,这是一个良好的编程习惯。这确保了只有当红绿灯为绿色时,司机才被指示通行。对于其他情况,会明确传递红绿灯行为异常的消息。
3. 对多个分支使用 when 语句
你的 trafficLightColor 程序在处理多个条件(也称为分支)时显得更复杂。你可能想知道是否可以简化具有更多分支的程序。
在 Kotlin 中,当你处理多个分支时,可以使用 when 语句代替 if/else 语句,因为它可以提高可读性,即可读性是指人类读者(通常是开发者)阅读代码的容易程度。在编写代码时考虑可读性非常重要,因为很可能其他开发者需要在代码的整个生命周期中审查和修改你的代码。良好的可读性确保开发者能够正确理解你的代码,并且不会无意中引入 bug。
当需要考虑的分支多于两个时,优先使用 when 语句。
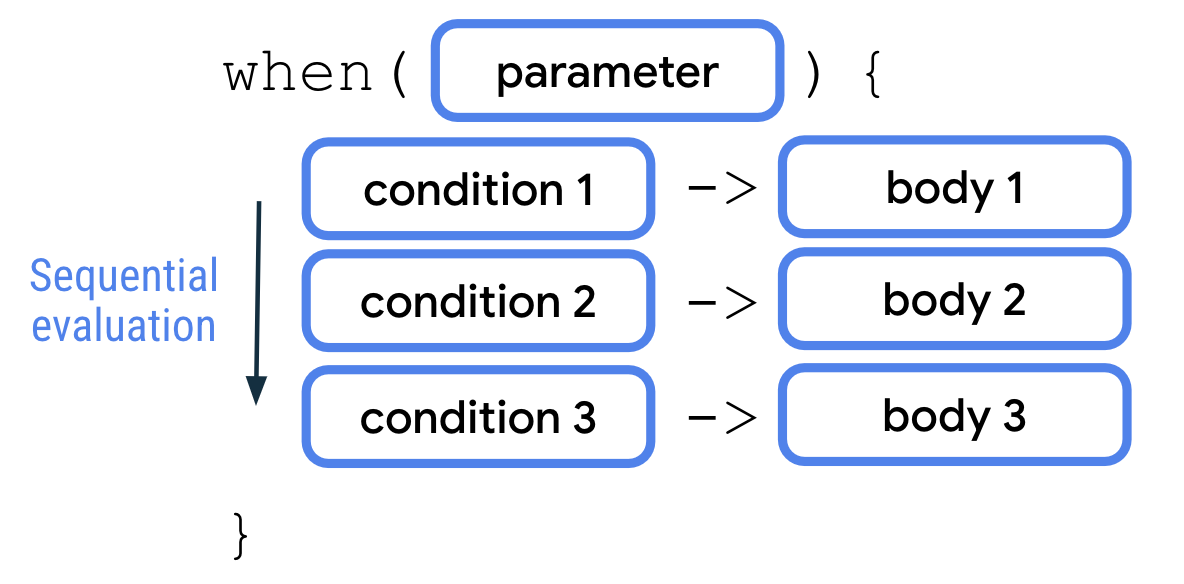
一个 when 语句通过参数接受一个单一值。然后将该值按顺序与每个条件进行评估。满足的第一个条件对应的代码主体就会被执行。每个条件和主体之间用箭头 (->) 分隔。类似于 if/else 语句,when 语句中的每对条件和主体被称为一个分支。同样类似于 if/else 语句,你可以在 when 语句中添加一个 else 分支作为最终条件,它充当一个包罗万象的分支。
用 when 语句重写 if/else 语句
在红绿灯程序中,已经有多个分支
- 红色交通灯颜色
- 黄色交通灯颜色
- 绿色交通灯颜色
- 其他交通灯颜色
将程序转换为使用 when 语句
- 在
main()函数中,移除if/else语句
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
}
- 添加一个
when语句,然后将trafficLightColor变量作为参数传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
when (trafficLightColor) {
}
}
- 在
when语句的主体中,添加"Red"条件,后跟箭头和println("Stop")主体
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
}
}
- 在下一行,添加
"Yellow"条件,后跟箭头和println("Slow")主体
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow" -> println("Slow")
}
}
- 在下一行,添加
"Green"条件,后跟箭头,然后是println("Go")主体
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
}
}
- 在下一行,添加
else关键字,后跟箭头,然后是println("Invalid traffic-light color")主体
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
else -> println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
- 将
trafficLightColor变量重新赋值为"Yellow"
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Yellow"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
else -> println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
运行此程序时,你认为输出会是什么?
- 运行程序,然后查看输出
Slow

输出是 Slow 消息,因为
- 变量
trafficLightColor被赋值为"Yellow"。 - 程序按顺序逐个评估每个条件。
"Yellow"值不等于"Red"值,因此程序跳过第一个主体。"Yellow"值等于"Yellow"值,因此程序执行第二个主体,并打印Slow消息。- 一个主体被执行了,因此程序忽略了第三和第四个分支,并退出
when语句。
在 when 语句中编写更复杂的条件
到目前为止,你学习了如何为单个相等条件编写 when 条件,例如当 trafficLightColor 变量被赋值为 "Yellow" 时。接下来,你将学习如何使用逗号 (,)、in 关键字和 is 关键字来形成更复杂的 when 条件。
构建一个程序,判断 1 到 10 之间的数字是否为素数
- 在单独的窗口中打开 Kotlin playground。
稍后你将回到红绿灯程序。
- 定义一个
x变量,然后为其赋值3
fun main() {
val x = 3
}
- 添加一个
when语句,包含2、3、5和7条件的多个分支,并在每个分支后跟一个println("x 是 1 到 10 之间的素数。")主体
fun main() {
val x = 3
when (x) {
2 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
3 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
5 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 添加一个
else分支,并在其内部添加println("x 不是 1 到 10 之间的素数。")主体
fun main() {
val x = 3
when (x) {
2 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
3 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
5 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 运行程序,然后验证输出是否符合预期
x is a prime number between 1 and 10.
使用逗号 (,) 表示多个条件
素数程序中包含很多重复的 println() 语句。编写 when 语句时,可以使用逗号 (,) 来表示对应同一个主体的多个条件。
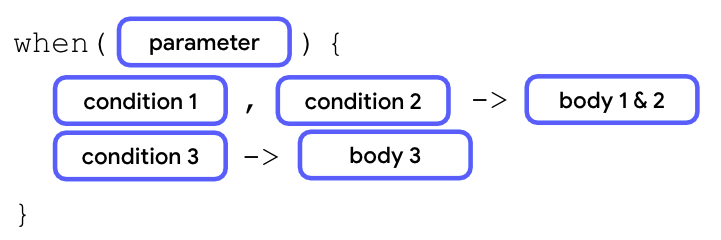
在上一张图中,如果满足第一个或第二个条件,则执行相应的主体。
使用这个概念重写素数程序
- 在
2条件的分支中,添加3、5和7,用逗号 (,) 分隔
fun main() {
val x = 3
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
3 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
5 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 移除
3、5和7条件的单独分支
fun main() {
val x = 3
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 运行程序,然后验证输出是否符合预期
x is a prime number between 1 and 10.
使用 in 关键字表示一系列条件
除了用逗号 (,) 符号表示多个条件外,你还可以在 when 分支中使用 in 关键字和值范围。
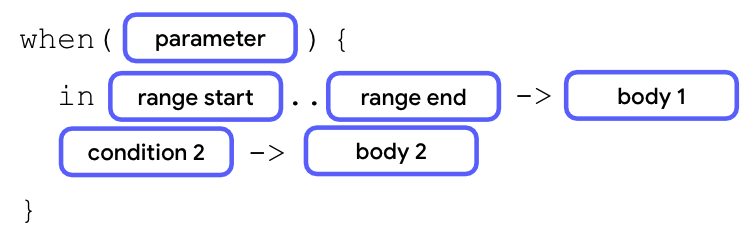
要使用值范围,添加表示范围起始的数字,后跟两个不带空格的句点,然后以另一个表示范围结束的数字结束。
当参数值等于范围起始和范围结束之间的任何值时,执行第一个主体。
在你的素数程序中,如果数字在 1 到 10 之间但不是素数,你能打印一条消息吗?
添加另一个带有 in 关键字的分支
- 在
when语句的第一个分支之后,添加第二个分支,带有in关键字,后跟1..10范围和println("x 是 1 到 10 之间的数字,但不是素数。")主体
fun main() {
val x = 3
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
in 1..10 -> println("x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 将
x变量更改为4
fun main() {
val x = 4
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
in 1..10 -> println("x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 运行程序,然后验证输出
x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.
程序打印第二个分支的消息,但不打印第一个或第三个分支的消息。
程序工作原理如下
- 变量
x被赋值为4。 - 程序继续评估第一个分支的条件。
4值不是2、3、5或7值,因此程序跳过第一个分支主体的执行,继续第二个分支。 4值在1和10之间,因此打印x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.主体的消息。- 一个主体被执行了,因此程序继续退出
when语句,并忽略else分支。
使用 is 关键字检查数据类型
你可以使用 is 关键字作为条件来检查评估值的数据类型。
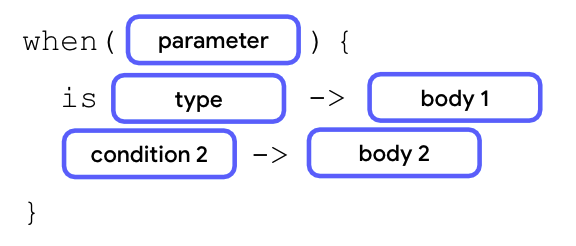
在上一张图中,如果参数值是指定的数据类型,则执行第一个主体。
在你的素数程序中,如果输入是一个不在 1 到 10 范围内的整数,你能打印一条消息吗?
添加另一个带有 is 关键字的分支
- 修改
x的类型为Any。这表明x可以是Int类型以外的值。
fun main() {
val x: Any = 4
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
in 1..10 -> println("x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 在
when语句的第二个分支之后,添加is关键字和一个Int数据类型,并添加println("x 是一个整数,但不在 1 到 10 之间。")主体
fun main() {
val x: Any = 4
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
in 1..10 -> println("x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.")
is Int -> println("x is an integer number, but not between 1 and 10.")
else -> println("x isn't a prime number between 1 and 10.")
}
}
- 在
else分支中,将主体更改为println("x 不是整数。")主体
fun main() {
val x: Any = 4
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
in 1..10 -> println("x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.")
is Int -> println("x is an integer number, but not between 1 and 10.")
else -> println("x isn't an integer number.")
}
}
- 将
x变量更改为20
fun main() {
val x: Any = 20
when (x) {
2, 3, 5, 7 -> println("x is a prime number between 1 and 10.")
in 1..10 -> println("x is a number between 1 and 10, but not a prime number.")
is Int -> println("x is an integer number, but not between 1 and 10.")
else -> println("x isn't an integer number.")
}
}
- 运行程序,然后验证输出
x is an integer number, but not between 1 and 10.
程序打印第三个分支的消息,但不打印第一个、第二个或第四个分支的消息。
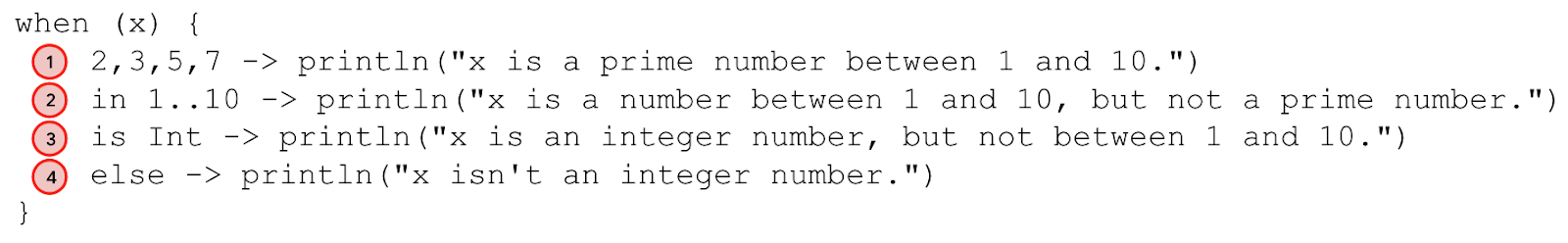
程序工作原理如下
- 变量
x被赋值为20。 - 程序继续评估第一个分支的条件。
20值不是2、3、5或7值,因此程序跳过第一个分支主体的执行,继续第二个分支。 20值不在1到10的范围内,因此程序跳过第二个分支主体的执行,继续第三个分支。20值是Int类型,因此打印x is an integer number, but not between 1 and 10主体。- 一个主体被执行了,因此程序继续退出
when语句,并忽略else分支。
试一试
现在在你的红绿灯程序中练习你学到的内容。
想象一下,有些国家有琥珀色的交通灯,其警告方式与其他国家的黄灯相同。你能修改程序,使其涵盖这个附加条件并保持原有的条件吗?
添加一个具有相同主体的附加条件
为红绿灯程序添加一个附加条件
- 如果你仍然打开着,回到带有红绿灯程序的 Kotlin Playground 实例。
- 如果你关闭了它,打开一个新的 Kotlin Playground 实例并输入此代码
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Yellow"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
else -> println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
- 在
when语句的第二个分支中,在"Yellow"条件后添加一个逗号,然后添加一个"Amber"条件
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Yellow"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow", "Amber" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
else -> println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
- 将
trafficLightColor变量更改为"Amber"
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Amber"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow", "Amber" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
else -> println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
- 运行此程序,然后验证输出
Slow
4. 将 if/else 和 when 用作表达式
你学习了如何将 if/else 和 when 用作语句。当你将条件语句用作语句时,你让每个分支根据条件执行主体中的不同操作。
你还可以将条件语句用作表达式,为每个条件分支返回不同的值。当每个分支的主体看起来相似时,与条件语句相比,可以使用条件表达式来提高代码的可读性。
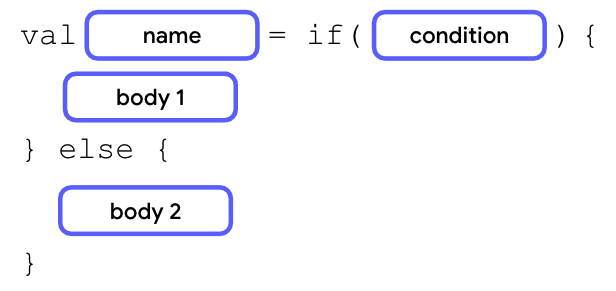
将条件语句用作表达式的语法与语句相似,但每个分支主体中的最后一行需要返回一个值或表达式,并且条件语句被赋值给一个变量。
如果主体只包含返回值或表达式,可以删除花括号以使代码更简洁。

在下一节中,你将通过红绿灯程序了解 if/else 表达式。
将 if 语句转换为表达式
在这个 if/else 语句中有很多 println() 语句重复
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Green") {
println("Go")
} else {
println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
将这个 if/else 语句转换为 if/else 表达式,并去除重复
- 在 Kotlin playground 中,输入之前的红绿灯程序。
- 定义一个
message变量,然后为其赋值一个if/else语句
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
val message = if (trafficLightColor == "Red") {
println("Stop")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") {
println("Slow")
} else if (trafficLightColor == "Green") {
println("Go")
} else {
println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
- 移除所有
println()语句及其花括号,但保留其中的值
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
val message =
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") "Stop"
else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") "Slow"
else if (trafficLightColor == "Green") "Go"
else "Invalid traffic-light color"
}
- 在程序末尾添加一个
println()语句,然后将message变量作为参数传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Black"
val message =
if (trafficLightColor == "Red") "Stop"
else if (trafficLightColor == "Yellow") "Slow"
else if (trafficLightColor == "Green") "Go"
else "Invalid traffic-light color"
println(message)
}
- 运行此程序,然后查看输出
Invalid traffic-light color
试一试
将红绿灯程序转换为使用 when 表达式,而不是 when 语句
- 在 Kotlin Playground 中,输入此代码
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Amber"
when (trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> println("Stop")
"Yellow", "Amber" -> println("Slow")
"Green" -> println("Go")
else -> println("Invalid traffic-light color")
}
}
你能将 when 语句转换为表达式,这样就不会重复 println() 语句了吗?
- 创建一个
message变量,并将其赋值给when表达式
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Amber"
val message = when(trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> "Stop"
"Yellow", "Amber" -> "Slow"
"Green" -> "Go"
else -> "Invalid traffic-light color"
}
}
- 在程序末尾添加一个
println()语句,然后将message变量作为参数传给它
fun main() {
val trafficLightColor = "Amber"
val message = when(trafficLightColor) {
"Red" -> "Stop"
"Yellow", "Amber" -> "Slow"
"Green" -> "Go"
else -> "Invalid traffic-light color"
}
println(message)
}
5. 结论
恭喜!你学习了条件语句以及如何在 Kotlin 中编写它们。
总结
- 在 Kotlin 中,可以使用
if/else或when条件语句实现分支。 if/else条件语句中if分支的主体仅在if分支条件内的布尔表达式返回true值时执行。if/else条件语句中后续的else if分支仅在前一个if或else if分支返回false值时执行。if/else条件语句中最后的else分支仅在所有前一个if或else if分支返回false值时执行。- 当分支多于两个时,建议使用
when条件语句替换if/else条件语句。 - 你可以在
when条件语句中使用逗号 (,)、in范围和is关键字编写更复杂的条件。 if/else和when条件语句可以作为语句或表达式。